Inder Kumar Gujral — A Gentle Statesman, His Doctrine, and Legacy
Inder Kumar Gujral's life was a narrative of conviction, calm statesmanship and the quiet pursuit of stronger ties with India's neighbours. This biography tells his story — from early years and political sacrifices to the ideas and actions that defined his public life.

Quick Facts
Full name: Inder Kumar Gujral
Born: 4 December 1919, Jhelum (now in Pakistan).
Died: 30 November 2012 (Gurgaon / New Delhi area).
Major public office: 12th Prime Minister of India (21 April 1997 – 19 March 1998).
Personal Life — Roots that Shaped a Statesman
Early life and family
Born into a family with deep nationalist convictions, Gujral's childhood in Jhelum exposed him early to political ideas and the urgency of India’s freedom movement. His parents, notably his mother Pushpa Gujral, and his family's public-spirited outlook played a large role in shaping his values and choices.
Marriage and family
He married Sheila Gujral, a noted poet and social worker. The couple shared a long life that combined public service with a rich cultural and literary interest. Their son, Naresh Gujral, also entered public life as a politician.
Education and Early Interests
Gujral studied in Lahore at institutions such as Hailey College of Commerce and Forman Christian College. He pursued studies in the sciences for a time and later moved into public service and politics. His early exposure to literature, languages and poetry — including a strong affinity for Urdu poetry — informed both his worldview and his diplomatic temperament.
Political Journey — From Freedom Struggle to Prime Minister
Participation in the independence movement
Like many of his generation, Gujral took part in the independence movement and spent time in prison for his activities. After independence he gradually moved into active public service and national politics.
Key offices held
- Union Minister of External Affairs (served in different governments, notably 1989–1990 and 1996–1998).
- Prime Minister of India (21 April 1997 – 19 March 1998), leading the United Front coalition government during a complex political period.
“Calm, scholarly and soft-spoken” — Gujral was widely remembered for his measured style and diplomacy.
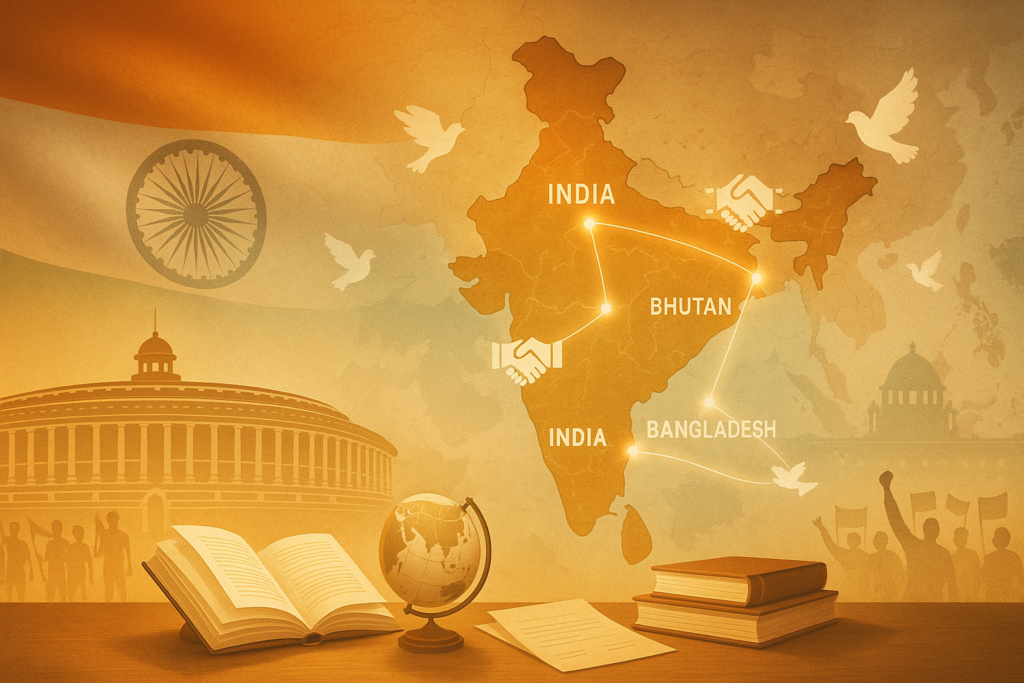
The Gujral Doctrine — A Regional Outlook
The Gujral Doctrine is the name given to a set of principles Inder Kumar Gujral advocated for India’s relations with its immediate neighbours. At its core it recommended that India offer gestures of goodwill, minimise immediate quid pro quo expectations, and build trust through unilateral, confidence-building measures — especially toward smaller neighbours such as Nepal, Bhutan and Sri Lanka. The doctrine aimed to create a more cooperative regional atmosphere and reduce friction through pragmatic diplomacy.
Writing & Reflection
Autobiography
Gujral recorded his reflections in Matters of Discretion: An Autobiography, where he discussed his life, political experiences and the thinking behind his foreign-policy choices. The book is a candid account of his public life and the difficult choices that accompany governance.
Legacy — How History Remembers Him
Inder Kumar Gujral is remembered as a gentle, principled and scholarly leader. He made a distinctive contribution to India’s diplomatic vocabulary by arguing for a neighbour-first sensibility in foreign policy. His calm demeanour, respect for culture and emphasis on building trust remain central to his public image.
Why his story matters today
In an era of hard-edged rhetoric, Gujral's approach is a reminder that soft power, credibility and consistent engagement can be powerful tools in international relations. For students of diplomacy and public service, his career provides lessons in patience, listening and principled flexibility.
Conclusion — Lessons from a Life of Service
Inder Kumar Gujral’s life offers a steady lesson: leadership often thrives in restraint. He combined deep cultural sensibility with practical politics, and he leaves behind an example of how diplomacy and quiet statesmanship can shape a nation's relations with the world. Whether one studies his doctrine, reads his autobiography, or examines his public decisions, the enduring message is one of measured leadership guided by trust and respect for neighbours.
Read sources & referencesInder Kumar Gujral – Education, Political Journey & Key Positions
Inder Kumar Gujral’s education and political journey played a major role in shaping him into a thoughtful, intellectual and visionary leader. Below is a detailed and structured account of his educational background, early political involvement, achievements and key positions held during his long public life.
Inder Kumar Gujral – Education
Inder Kumar Gujral’s education deeply influenced his personality, intellectual outlook and political thought. He was admired as an educated, cultured and analytical leader.
🎓 Education Details
Early Education
He completed his early education in Jhelum and later in Lahore (now in Pakistan). These academic beginnings laid the foundation for his intellectual development.
College Education
He studied at two prestigious institutions of British India:
- Hailey College of Commerce, Lahore
- Forman Christian College, Lahore
Both institutions were well known for academic excellence and shaped his disciplined academic approach.
Subjects Studied
During college, he studied Commerce and for some time pursued Physics. Along with academics, he actively participated in the freedom movement, due to which he had to drop out for a period.
📚 Interests Beyond Academics
Gujral’s interests reached beyond education. He was deeply engaged in:
- Politics
- Literature
- Social service
Even during student life, he actively participated in the freedom struggle. He had a strong interest in multiple languages, especially Urdu, Hindi, Punjabi and English.
🧠 Intellectual Image
His education broadened his intellectual capacity. He emerged as a scholar and analytical thinker. His understanding of global politics later contributed greatly to his effectiveness as a Foreign Minister and eventually as the Prime Minister of India.
Inder Kumar Gujral – Political Journey
The political journey of Inder Kumar Gujral is an important chapter in Indian politics. From his early involvement in the freedom struggle to serving as the 12th Prime Minister of India, his career was marked by thoughtfulness, diplomacy and commitment to peace.
Beginning of Political Life
His political career formally began in 1938 with anti-British activities. He participated actively in the freedom struggle and became widely known for his involvement in national causes.
After independence, he joined the Indian National Congress and remained active in socio-political initiatives.
🏛️ Important Political Observations
🔹 Member of Rajya Sabha
Gujral served multiple terms representing Punjab in the Rajya Sabha. His calm and intellectual nature made him widely respected.
🔹 Union Minister
He worked in several key ministries:
- Minister of Information & Broadcasting (1975–77)
Served during a critical political period and was known for his firm principles. - Foreign Minister of India
- First term: 1989–1990 (V.P. Singh Government)
- Second term: 1996–1998 (before and after becoming Prime Minister)
During this time, he introduced the historic “Gujral Doctrine”, which emphasized trust-building and cooperation with neighbouring countries.
🇮🇳 Prime Minister of India
Tenure: 21 April 1997 – 19 March 1998 He became the 12th Prime Minister of India as the candidate of the United Front government.
🔸 Major Achievements as Prime Minister
- Foreign policy reforms: Strengthened partnerships with neighbouring nations.
- Gujral Doctrine: Emphasized unconditional cooperation with South Asian neighbours.
- Clean, controversy-free image: Widely respected for simplicity and integrity.
🔸 Fall of the Government
The government collapsed after the Congress Party withdrew its support, resulting in the end of his 13-month tenure.
📚 Later Life
After stepping down as Prime Minister, Gujral gradually distanced himself from active politics. In 2004, he published his well-known autobiography “Matters of Conscience” (often also referenced as “Matters of Discretion”).
🏅 Political Characteristics
- Thoughtful and visionary leader
- Expert in foreign policy
- Soft-spoken, diplomatic and principled
- Known for consensus-building and calm governance
Inder Kumar Gujral – Key Positions
Throughout his long political career, Inder Kumar Gujral held several significant positions that shaped India's domestic and foreign policy.
🏛️ 1. Prime Minister of India
Tenure: 21 April 1997 – 19 March 1998 He became the 12th Prime Minister as the consensus candidate of the United Front coalition. His tenure is remembered for introducing the foreign-policy landmark, the Gujral Doctrine.
🌐 2. Minister of External Affairs (Foreign Minister)
He served twice as India’s Foreign Minister:
- 1989–1990 (V.P. Singh Government)
- 1996–1998 (before and after becoming PM)
His diplomatic approach strengthened India’s relations with South Asian nations.
📺 3. Minister of Information & Broadcasting
Tenure: 1975–1977 (Indira Gandhi Government) He played an important role during a politically sensitive period marked by censorship and political unrest.
🏗️ 4. Minister of Urban Development
Tenure: 1989–1990 (V.P. Singh Government) He supervised urban planning, housing policies and development programmes.
🗳️ 5. Member of Parliament
Inder Kumar Gujral served as a member of both houses:
- Rajya Sabha: Multiple terms representing Punjab
- Lok Sabha: Represented constituencies including Patna and others
📘 6. Writer & Thinker
He authored the autobiography “Matters of Conscience / Matters of Discretion”, which offers deep insight into Indian politics, foreign policy and his personal journey.
His leadership style, democratic values and consultative approach created a unique and respected image in Indian politics.

If you want details on any specific position, tenure or policy, feel free to ask!
Inder Kumar Gujral – Foreign Minister, Prime Minister of India & Gujral Doctrine
Inder Kumar Gujral as Foreign Minister of India
Inder Kumar Gujral is particularly remembered for his influential role as the Foreign Minister of India. He held this post twice and played a defining role in shaping India’s modern foreign policy and regional diplomacy.
🌐 Tenure as Foreign Minister
- 1989–1990 – Under Prime Minister V. P. Singh (First term)
- 1996–1998 – In the United Front Government (Second term). Later, when he became Prime Minister, he continued to handle the Foreign Affairs ministry.
🎯 Major Achievements & Contributions
1. 🇮🇳 Gujral Doctrine (Gujral Principle)
The Gujral Doctrine is the most famous and defining aspect of his foreign policy vision. Its core objective was to improve India’s relations with its neighbouring countries without insisting on strict reciprocity.
Five major principles of the Gujral Doctrine:
- India will provide unconditional assistance to smaller neighbouring countries (Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka).
- India will not interfere in the internal affairs of neighbouring countries.
- All disputes will be resolved through peaceful and diplomatic means.
- India will respect the sovereignty and territorial integrity of its neighbours.
- India will strengthen friendly relations based on trust and mutual respect.
2. 🌏 Improving Relations with Neighbouring Countries
Gujral worked to reduce tension and promote cooperation with Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka. He engaged directly with leaders of these countries to strengthen diplomatic, cultural and economic ties.
3. 🕊️ Non-Aggressive Foreign Policy
He consistently supported a soft, dialogue-based approach. He believed that “Dialogue and cooperation must be the core of India’s foreign policy in South Asia.”
4. 🗣️ India on the International Stage
He enhanced India’s image as a peace-loving, democratic and responsible country. He also represented India in major international forums with dignity and strategic clarity.
🔍 His Foreign Policy Philosophy
According to Gujral:
The duty of a big power is to assist its smaller neighbours without coercion.
He always emphasised sovereignty, peaceful coexistence and mutual respect.
🏁 Conclusion – Foreign Minister Gujral
Inder Kumar Gujral’s contribution as Foreign Minister reflected maturity, wisdom and farsightedness. His Gujral Doctrine continues to be studied globally and remains one of the most important foreign policy frameworks in India’s history.
Inder Kumar Gujral – Prime Minister of India
Inder Kumar Gujral was the 12th Prime Minister of India. Though his tenure was short, he is remembered for his diplomatic approach, balanced leadership and commitment to coalition governance.
🇮🇳 Tenure as Prime Minister
- From: 21 April 1997
- To: 19 March 1998
- Duration: Approximately 11 months
He was the third Prime Minister to assume office from the Rajya Sabha (after Indira Gandhi and H. D. Deve Gowda).
🔷 How He Became Prime Minister
- In 1996, no party secured a clear majority in Lok Sabha.
- The United Front coalition formed the government.
- After H. D. Deve Gowda resigned, Congress supported Gujral’s name for PM.
- He led the coalition government during a politically complex environment.
🧠 Main Policies & Contributions
1. 🌐 Implementation of the Gujral Doctrine
As Prime Minister, he continued to advocate unconditional cooperation with neighbouring countries and peaceful diplomacy.
2. 🗣️ Balance in Coalition Politics
He maintained harmony within the United Front coalition and was respected as a calm, balanced and principled leader.
3. 📉 Fall of the Government
The government fell after the Congress withdrew support over the Jain Commission report (related to the Rajiv Gandhi assassination case). Gujral refused to drop the DMK from the coalition, following his principles, and the government collapsed.
📌 Image as Prime Minister
- Scholarly, ethical and soft-spoken
- Known for non-aggressive politics
- Committed to constitutional values and democratic ethics
After the Prime Ministership
After 1998, he slowly stepped back from active politics. In 2004, he published his autobiography “Matters of Conscience / Matters of Discretion”.
🏁 Conclusion – Prime Minister Gujral
Inder Kumar Gujral’s tenure may have been brief, but his foreign policy vision, dignified leadership and ability to maintain balance in coalition politics have made him a respected figure in Indian history.
Gujral Doctrine – Regional Theory
The Gujral Doctrine is a historic and influential foreign policy framework introduced by Inder Kumar Gujral. It emphasized generosity, trust-building and peaceful cooperation with India’s neighbours.
📜 What is the Regional Theory?
The theory states that India should offer support and cooperation to its smaller neighbours without expecting reciprocal benefits.
Five Major Principles of the Gujral Doctrine
- India respects the sovereignty and territorial integrity of its neighbours.
- No interference in the internal affairs of neighbouring countries.
- All disputes should be resolved peacefully.
- Relations should be based on mutual benefit and goodwill.
- India will provide assistance to smaller neighbouring nations without expecting anything in return.
Countries Mainly Covered
This doctrine mainly focused on five neighbours:
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- Bangladesh
- Maldives (corrected)
- Sri Lanka
Pakistan was excluded due to its complex and sensitive relationship with India.
🎯 Objectives of the Policy
- Promote peace and stability in South Asia
- Strengthen India’s role as a responsible regional power
- Win the trust of neighbouring countries
- Encourage regional cooperation through SAARC and other mechanisms
📝 Examples of Implementation
- Economic and technical assistance to Bangladesh
- Strong energy, education and health cooperation with Nepal and Bhutan
- Humanitarian support to Sri Lanka without political conditions
🧠 Importance & Criticism
Positive Impact
- Strengthened India’s image as a responsible regional leader
- Built trust among neighbouring countries
- Promoted peaceful dialogue
Criticism
- Some argued it was “too generous” and did not protect India’s strategic interests enough.
- Lack of reciprocity sometimes led neighbours to take benefits without offering cooperation.
🏁 Conclusion – Gujral Doctrine
The Gujral Doctrine remains a visionary, ethical and influential policy. It continues to be studied as a model for peaceful regional diplomacy and responsible leadership in South Asia.
Writing Work & Legacy of Inder Kumar Gujral
Inder Kumar Gujral was not only a distinguished politician but also a writer, thinker and intellectual personality. His writings reflect deep political insight, rich experience and thoughtful analysis of India’s foreign policy and political journey.

Writing Work of Inder Kumar Gujral
📚 Major Writing Contributions
✍️ 1. Matters of Conscience: An Autobiography (2006)
This autobiography is one of the most comprehensive records of his personal journey, political experiences and foreign-policy vision.
📖 Major Topics Covered in the Book
- His childhood and youth
- Participation in the Indian freedom struggle
- Experiences during the post-independence political system
- Roles as Foreign Minister and Prime Minister
- The background and objectives of the Gujral Doctrine
- Detailed observations on India–neighbour relations
- Coalition politics and the challenges he faced as Prime Minister
🧠 Features of the Book
- A deep blend of personal and political insights
- Emphasis on democracy, ethics and discipline in politics
- More than storytelling—includes thoughtful analysis
📜 Other Writings & Contributions
Inder Kumar Gujral wrote several articles and papers for national and international journals. His writings primarily focused on:
- Foreign policy and diplomacy
- South Asian regional politics
- India–Pakistan relations
- Coalition politics in India
He wrote in multiple languages including Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu and English.
🎭 Interest in Poetry & Literature
His wife Sheila Gujral was a renowned poet. Inder Kumar Gujral himself had deep interest in Urdu and Punjabi poetry, literature and culture. This literary background shaped his calm, sensitive and cultured public image.
🏁 Conclusion – Writing Work
Inder Kumar Gujral’s writings reflect his experience, maturity and dedication to the nation. His autobiography “Matters of Conscience” remains an important historical document for understanding India’s politics, diplomacy and coalition era.
Legacy of Inder Kumar Gujral
Inder Kumar Gujral’s legacy continues to inspire Indian politics, foreign-policy thinkers and advocates of peaceful diplomacy. His calm leadership and progressive foreign policy reshaped India’s relations with its neighbours.
🌍 Key Principles of His Legacy
1. Contribution to Foreign Policy – The Gujral Doctrine
His most famous legacy is the Gujral Doctrine, a foreign-policy principle that strengthened India’s regional diplomacy. Its focus on unconditional cooperation with neighbouring countries made India a trusted and responsible regional power.
2. Balance in Political Alliances
Gujral was a master of coalition politics. He proved that even in complex alliances, dialogue and cooperation can maintain stability. His leadership style demonstrated that coalitions can function smoothly with mutual respect.
3. Symbol of Simplicity & Integrity
Gujral led a life of simplicity, honesty and commitment to national interest. He avoided conflicts, political aggression and personal gain. His ethical leadership remains a role model for Indian leaders.
4. Political Thinking & Intellectual Contribution
His autobiography “Matters of Conscience” shared deep insights into diplomacy, governance and political behaviour. These writings make him not just a politician but a critical thinker and statesman.
5. Recognition & Influence
Inder Kumar Gujral was respected across political parties for his calm temperament, wisdom and visionary thinking. His influence extended beyond India to South Asia and international diplomatic circles.
🏁 Conclusion – Legacy
Inder Kumar Gujral’s legacy is not limited to his political positions; it lies in his ethical leadership, thoughtful diplomacy and visionary approach. His Gujral Doctrine and contributions to coalition politics continue to guide foreign-policy experts, political leaders and students even today.
Conclusion
Inder Kumar Gujral’s life, writings, foreign policy vision, and leadership style form an integral part of India’s political and diplomatic legacy. As a writer, thinker, and statesman, he contributed significantly to shaping India’s approach to regional cooperation and ethical governance. His “Gujral Doctrine” remains a landmark in South Asian diplomacy, built on mutual trust, respect, and peaceful engagement.
His autobiography “Matters of Conscience” is not just a personal narrative but a valuable document for understanding India’s democratic processes, foreign policy decisions, and the complexities of coalition politics. His simplicity, calmness, integrity, and faith in dialogue continue to inspire future generations of leaders and policymakers.
Thus, the legacy of Inder Kumar Gujral extends far beyond his political positions. It lives on through his ideas, his policies, and his unwavering dedication to the national interest. He remains an enduring example of how humility, balance, and thoughtful leadership can become a nation’s greatest strength.
References

- Gujral, Inder Kumar. Matters of Conscience: An Autobiography. New Delhi: Rupa Publications, 2006.
- Government of India – Prime Minister’s Office. “Former Prime Ministers: Shri Inder Kumar Gujral.” Official archival records and biographical notes.
- Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India. “Gujral Doctrine and India’s Neighbourhood Policy.” Policy papers and public statements.
- Parliament of India – Rajya Sabha & Lok Sabha Secretariat. “Biographical Sketch of Shri I. K. Gujral.” Parliamentary records and tenure details.
- Encyclopaedia Britannica. “Inder Kumar Gujral – Prime Minister of India.” Historical and biographical summary.
- Articles and public lectures delivered by Inder Kumar Gujral on foreign policy, South Asian regional cooperation, and Indo-Pakistan relations.