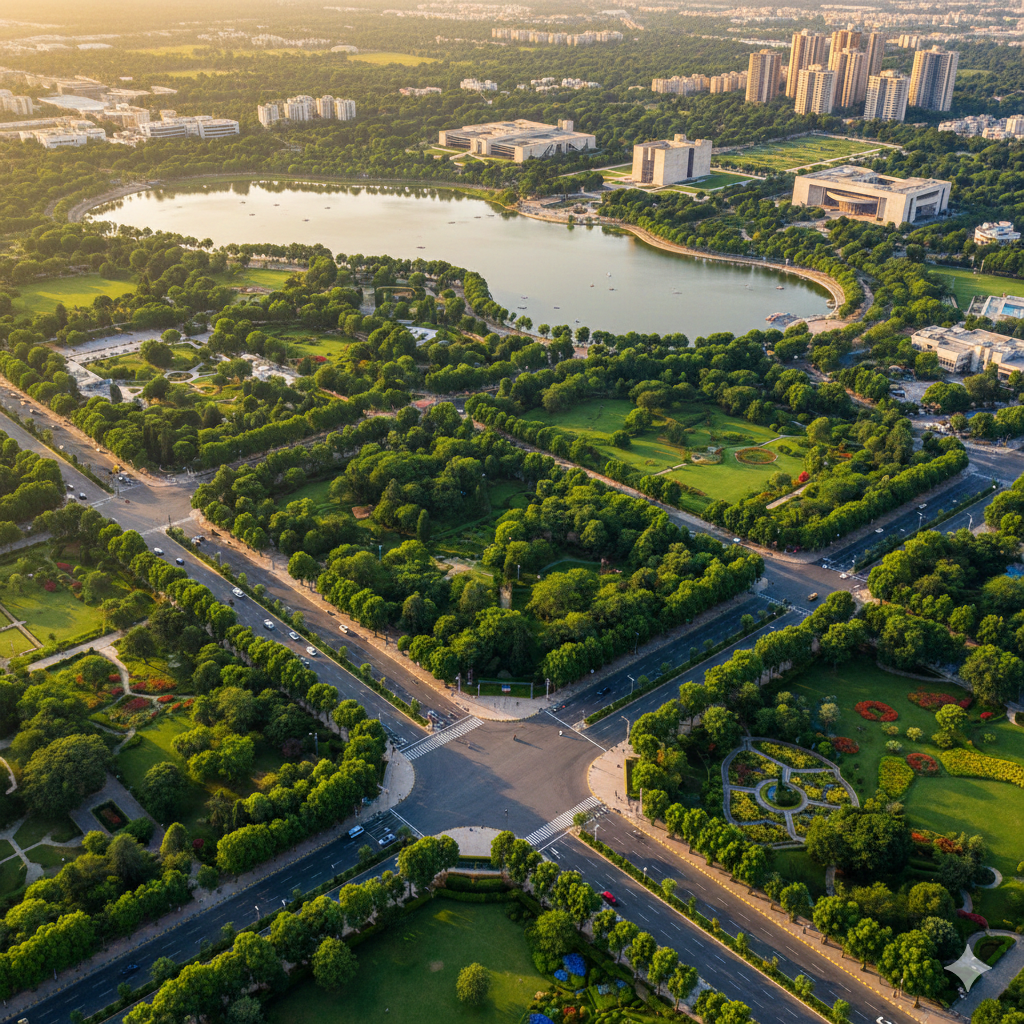
Chandigarh – A Modern, Green, and Well-Planned City
Chandigarh is a union territory of India and the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The city is known for its exceptional urban planning, greenery, and modern lifestyle. Let us understand various aspects of Chandigarh in detail.
1. History
Chandigarh is named after the goddess Chandi, a form of Goddess Durga. The Chandi Temple, located near the city, is believed to be the origin of its name. After the partition of India, Punjab required a new capital, and Chandigarh was chosen. The city was planned in the 1950s by the renowned French architect Le Corbusier.
2. Geographical Location
Elevated Location
Chandigarh is situated in North India at the foothills of the Shivalik Hills, at an elevation of about 321 meters above sea level.
Climate
The climate here is semi-tropical. Summers are hot, winters are cold, and monsoons bring moderate rainfall.
3. City Planning
Chandigarh is known as India’s first planned city, divided into 47 sectors.
Road Network
The roads are designed using the “7V” system, ensuring smooth traffic flow and regulation.
Green Areas
The city is rich in greenery and is often called the greenest city of India.
4. Major Attractions
Rock Garden
Created by Nek Chand, this beautiful garden is made from waste and recycled materials.
Sukhna Lake
A man-made lake known for its peaceful environment and water sports activities.
Rose Garden
Asia’s largest rose garden showcasing hundreds of varieties of roses.
Capital Complex
This area houses the Secretariat, High Court, and Legislative Assembly buildings.
Chandi Temple
A popular religious and tourist spot dedicated to Goddess Chandi.
5. Culture and Lifestyle
Language
Hindi and Punjabi are the primary languages spoken here.
Festivals
Baisakhi, Lohri, and Diwali are the major festivals celebrated with enthusiasm.
Food
The cuisine of Chandigarh reflects the rich flavors of Punjab and North India. Butter-loaded parathas, sarson ka saag, and makki ki roti are among the favorite dishes.
6. Education and Development
Chandigarh is one of India’s most developed and academically advanced cities. Major institutions include:
- Panjab University
- PGIMER (Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research)
- Chandigarh Engineering College
7. Transport and Connectivity
Airport
Chandigarh International Airport connects the city to major national and international destinations.
Railways
The Chandigarh Railway Station is well-connected to major cities across India.
Bus Services
Direct bus services operate to major cities in Haryana and Punjab.
8. Unique Features
India’s Cleanest City
Chandigarh has received multiple awards for cleanliness and environmental management.
Wellness City
The city is known for its wellness-oriented lifestyle, with numerous parks, open spaces, and fitness facilities.
Chandigarh beautifully blends modernity, tradition, and nature. It stands not only as a model city for India but also as a major center of tourism, culture, and education.
History of Chandigarh
The history of Chandigarh is rich and diverse, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern urban development. The region holds significant historical, cultural, and religious importance. Let us understand this journey in detail.
Ancient Period
Influence of the Indus Valley Civilization
- Remains of the Indus Valley Civilization have been discovered in Chandigarh and nearby areas.
- Evidence from sites like Rakhigarhi and Ropar suggests the region was part of an ancient civilisation.
- Artifacts such as pottery and tools indicate flourishing trade and agriculture.
Rigvedic Age
- The area was a center of Vedic culture.
- The Saraswati River is believed to have flowed through the region, adding spiritual significance.
Medieval History
Maurya Empire
- The region held strategic importance under the Mauryas.
- Buddhism prospered during this era.
- Stupas and monasteries highlight the area's Buddhist heritage.
Gupta and Post-Gupta Period
- The region flourished as a cultural and economic hub.
- Temple architecture and sculpture developed significantly.
Mughal Empire
- The region came under Mughal administration.
- Agriculture and trade grew during this period.
- After Mughal decline, local rulers gained prominence.
Modern Period
Influence of the Sikh Empire
- The region became part of Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s Sikh Empire.
- Agriculture and security improved during this period.
- Several Gurdwaras were established in the area.
British Rule
- Chandigarh gained administrative importance.
- While not heavily developed, agriculture and trade continued.
Partition and Creation of Chandigarh
Partition of India (1947)
- Punjab was divided, and Lahore—the then capital—went to Pakistan.
- A new capital was required for Indian Punjab, leading to the selection of Chandigarh.
Construction of Chandigarh (1950s)
- Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru envisioned Chandigarh as the “face of modern India.”
- Le Corbusier designed the city’s master plan.
- Construction began in 1952 and continued into the 1960s.
- Chandigarh became India’s first fully planned city.
Present Era
Joint Capital (1966)
- After Haryana was formed, Chandigarh became the shared capital of Punjab and Haryana.
- It was declared a Union Territory.
Modern Development
- Chandigarh is now one of India’s cleanest and greenest cities.
- It is a hub for education, healthcare, and tourism.
- Rock Garden, Sukhna Lake, and Rose Garden are internationally known attractions.
Summary
The history of Chandigarh reflects a remarkable transformation—from ancient civilizations to a symbol of modern urban planning. Known for its architecture, culture, and natural beauty, Chandigarh remains one of India’s most unique and harmonious cities.
Geographical Location of Chandigarh
The geographical location of Chandigarh plays a major role in defining its beauty, orderliness, and climate. Located in the north-western part of India, the city has a unique identity due to its physical and natural features. Let us understand it in detail.
Location and Boundaries
Situation
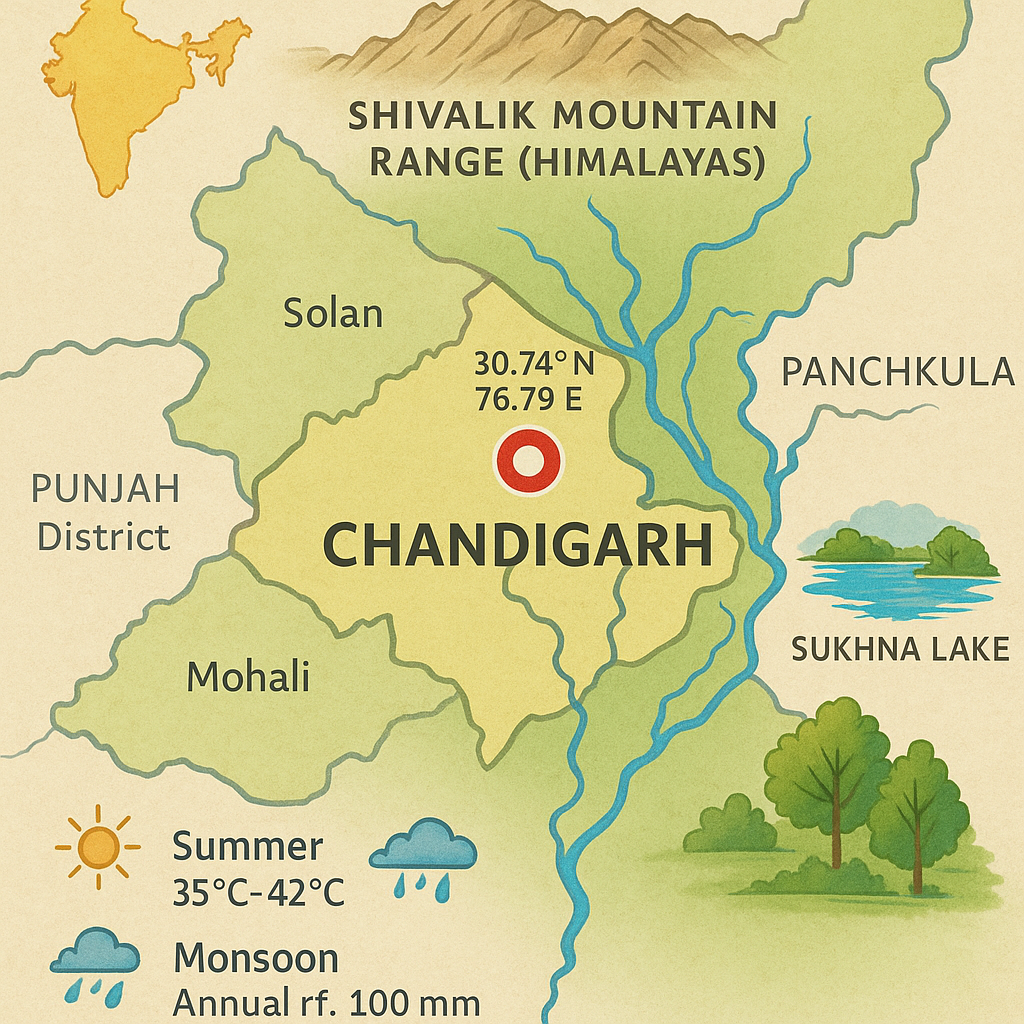
- Chandigarh is located at 30.74° North latitude and 76.79° East longitude.
- It is situated in the foothills of the Shivalik mountain range, a part of the Himalayas.
- The city lies between the Indian states of Punjab and Haryana.
Boundaries
- North: Solan district of Himachal Pradesh
- South: Panchkula district of Haryana
- West: Mohali district of Punjab
Area and Size
The total area of Chandigarh is approximately 114 sq. km. The city is divided into a sector system consisting of 47 sectors. Each sector is designed as an independent unit with markets, parks, and residential areas.
Physical Characteristics
Mountainous Terrain
Due to its proximity to the Shivalik Hills, Chandigarh has a combination of hilly and plain regions. The hills in the northern part help regulate the city’s temperature.
Water Resources
- Sukhna Lake: The main reservoir of the city, created by damming the Sukhna River.
- Several small streams and reservoirs support irrigation and water supply.
Soil and Agriculture
The soil of Chandigarh is fertile, mainly sandy loam. However, due to rapid urbanization, agricultural land has become limited.
Climate
Semi-Tropical Climate
Chandigarh experiences three main seasons:
- Summer (April–June): Hot and dry, temperature ranges between 35°C and 42°C.
- Monsoon (July–September): Heavy rainfall with an annual average of about 1100 mm.
- Winter (October–February): Cool and pleasant, with temperatures between 3°C and 20°C.
Wind and Humidity
- Heat waves occur during summer.
- Humidity increases substantially during monsoon.
- Cold north-western winds blow in winter.
Natural Vegetation and Greenery
Green Cover
- Chandigarh is known as “the greenest city of India.”
- The city contains extensive trees, shrubs, and grasslands.
- Common trees include Neem, Peepal, and Gulmohar.
Parks and Gardens
- Rock Garden: Made entirely from waste and recycled materials.
- Rose Garden: The largest rose garden in Asia.
- Other major gardens include the Terrace Garden and Botanical Garden.
Geological Structure
The region is composed mainly of alluvial soil and river erosion deposits. The Shivalik base consists of sandstone and rocks. Chandigarh lies in an earthquake-prone zone, but its buildings are designed to withstand seismic activity.
Geographical Role in Transport and Connectivity
Central Position
The city is located between major cities of North India—Delhi, Amritsar, and Shimla—making it a significant strategic and commercial hub.
Road and Rail Network
- Good roads connect Chandigarh to all nearby regions.
- National Highways NH-5 and NH-7 pass through the city.
- Chandigarh Railway Station provides connectivity across India.
Features
Conservation of Shivalik Region
The foothills of Shivalik near Chandigarh have protected biodiversity with wildlife sanctuaries and natural habitats.
Pleasant Environment
The presence of greenery and water reservoirs maintains environmental balance, keeping pollution levels lower than in other major Indian cities.
Conclusion
The geographical location of Chandigarh sets it apart from other Indian cities. Its strategic position, lush greenery, and organized structure make it a model city and an excellent example of environmental harmony.
City Plan of Chandigarh
Chandigarh is known as India’s first planned city. Its systematic and modern layout is admired worldwide. To understand the city’s structure and design, we must study its planning in detail.
History of City Planning
The Purpose of Establishing Chandigarh
- After the partition of India in 1947, Lahore—the capital of Punjab—went to Pakistan.
- A new capital was needed for Indian Punjab, leading to the selection of Chandigarh.
- The city was envisioned as an administrative center and a symbol of modern India.
Contribution of Le Corbusier
- The famous French architect Le Corbusier was chosen to design the city in the 1950s.
- He designed Chandigarh like a human body, with each part serving a specific function.
- The plan emphasized modernity, greenery, and functionality.
Structure of the City
City Planning as a Human Body
- Head: Capitol Complex — includes the Secretariat, Legislative Assembly, and High Court.
- Heart: Sector 17 — the main commercial hub.
- Lungs: Open spaces, gardens, and parks.
- Spine: The road network.
- Parts: Individual sectors functioning as different organs.
Sector System
- Chandigarh is divided into 47 sectors.
- Each sector measures approximately 800 m × 1200 m.
- Each sector includes residential areas, markets, parks, and public services.
- Pedestrian and vehicular zones are separated for safety.
“Seven V” Road Network
- V1: National highways and major city roads.
- V2: Main sector-connecting routes.
- V3: Sector’s internal main roads.
- V4: Market and internal residential roads.
- V5 & V6: Local lanes.
- V7: Dedicated pedestrian pathways.
This network ensures smooth and controlled traffic movement.
Greenery and Open Spaces
Green Belts and Parks
Greenery is an essential element of Chandigarh’s planning. Each sector has well-designed parks and green spaces. Large parks like Rock Garden, Rose Garden, and Sukhna Lake contribute to the city’s natural beauty.
Environmental Planning
Different species of trees were planted along each road with thoughtful planning. Nearly 40% of the city consists of green and natural areas.
Social and Urban Amenities
Residential Areas
Each sector includes housing for different social groups. Clean surroundings, parks, and basic amenities are provided within walking distance.
Commercial and Business Centres
Sector 17 is the city’s main business hub. Every sector also has its own local markets.
Educational and Health Facilities
- Panjab University
- PGIMER
- Many schools and hospitals in each sector
Cultural and Entertainment Centres
- Museums, art galleries, and theatres
- Sukhna Lake and Rock Garden serve as major recreation points
Traffic and Transportation System
Well-Maintained Roads
Chandigarh’s roads are wide, straight, and well-organized. Traffic lights and roundabouts help regulate movement.
Facilities for Pedestrians
Separate pedestrian paths and vehicle-free zones ensure safety and convenience.
Features
Schematic Design
The city is designed so that workplaces, homes, and recreational areas are close to each other. Essential services are available in every sector.
Greenery and Environmental Balance
Large green belts and parks make Chandigarh a symbol of a clean and green environment.
Earthquake-Resistant Structures
Buildings in the city follow earthquake-resistant designs to ensure safety.
Conclusion
The city plan of Chandigarh is a model for India. Its modernity, greenery, and well-organized structure make it an ideal urban example where lifestyle and environment exist in perfect harmony.
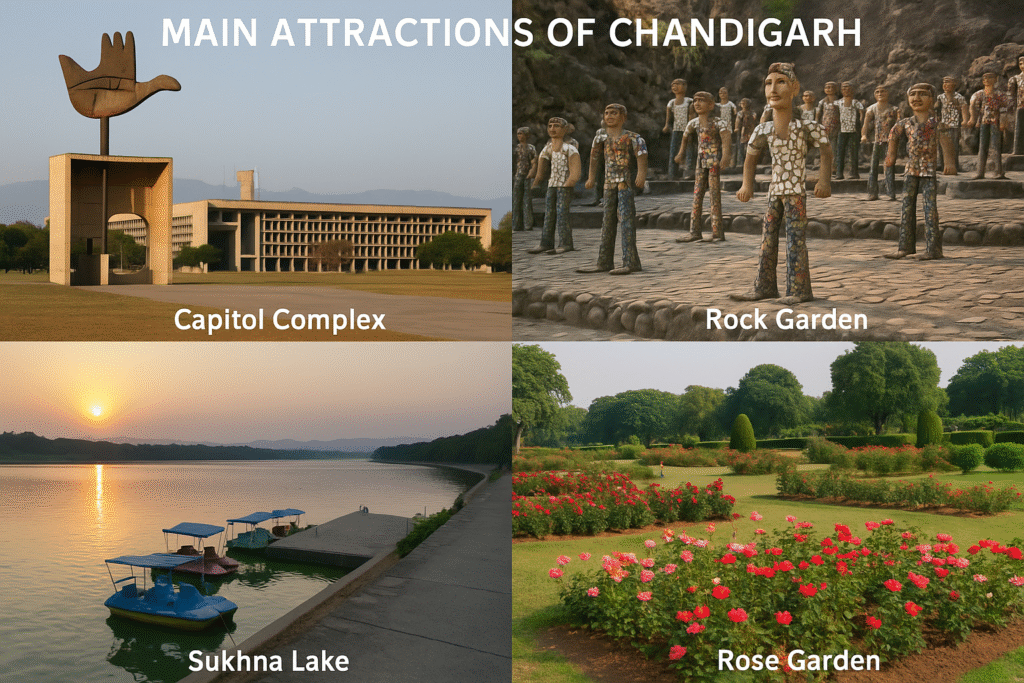
Main Attractions of Chandigarh
Chandigarh, also known as the “City Beautiful”, is admired for its well-organized layout, greenery, and modern architecture. It is one of India’s most attractive and tourist-friendly cities. Let us explore its major attractions in detail.
1. Capitol Complex
Description
- A UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Designed by Le Corbusier, showcasing the modern architectural identity of Chandigarh.
Main Structures
- Secretariat: Administrative building.
- Assembly Hall: Houses the Punjab and Haryana Legislative Assemblies.
- High Court: Punjab and Haryana High Court.
- Open Hand Monument: Symbol of Chandigarh representing the spirit of “open to give and open to receive.”
2. Rock Garden
Location: Sector 1
Description
- Created by Nek Chand using waste and recycled materials.
- Features stunning sculptures made from broken ceramics, tiles, glass, and industrial waste.
- Spread across 40 acres of artistic landscape.
3. Sukhna Lake
Location: Foothills of the Shivalik Range
Description
- A man-made lake formed by damming the Sukhna River.
- Activities include boating, paddling, yoga, and bird watching.
- Migratory birds visit the lake during monsoon and winter.
4. Rose Garden (Zakir Hussain Rose Garden)
Location: Sector 16
Description
- The largest rose garden in Asia.
- Spread across 30 acres with over 1600 varieties of roses and medicinal plants.
- Hosts the annual Rose Festival in February–March.
5. Elante Mall
Location: Industrial Area
Description
- One of the largest and most modern malls in North India.
- Offers premium shopping, dining, and entertainment experiences.
6. Panjab University
Location: Sector 14
Description
- One of India’s oldest and most prestigious universities.
- Known for its museums, libraries, and art galleries.
- Several campus buildings were designed by Le Corbusier.
7. Terraced Garden
Location: Sector 33
Description
- Spread across 10 acres, designed in a terraced layout.
- Famous for flower varieties and musical fountains.
- Hosts the annual Garden Festival.
8. Chandigarh Museum and Art Gallery
Location: Sector 10
Description
- Divided into three sections: Art Gallery, Aviation Museum, and Archaeological Museum.
- Exhibits include ancient manuscripts, artefacts, and modern art.
9. The Japanese Garden
Location: Sector 31
Description
- Designed based on Japanese architecture and aesthetics.
- Features an artificial lake, bridges, and traditional Japanese pavilions.
- A perfect place for meditation and peace.
10. Leisure Valley
Location: Sector 10
Description
- An 8-km-long green belt running across multiple sectors.
- Includes gardens like the Botanical Garden and the Garden of Bougainvillea.
- Hosts yoga sessions, walkathons, and cultural activities.
11. International Dolls Museum
Location: Sector 23
Description
- A popular attraction for children and families.
- Showcases dolls and toys from different countries.
- Special attraction: dolls representing Indian folk traditions.
12. Fun City and Water Park
Location: Chandigarh–Panchkula Road
Description
- One of North India’s largest amusement and water parks.
- Offers water rides, thrill rides, and children’s play zones.
13. Botanical Garden
Location: Sector 1 and Sector 14
Description
- Home to rare plant species and medicinal flora.
- Promotes awareness about nature and environmental conservation.
14. Bird Park Chandigarh
Location: Near Sukhna Lake
Description
- A paradise for bird watchers.
- Hosts various species in a serene and green atmosphere.
15. Shanti Kunj
Location: Sector 16
Description
- A peaceful natural park known for tranquility and greenery.
- Has a variety of trees, flowers, and medicinal plants.
Conclusion
The main attractions of Chandigarh highlight its architecture, greenery, modern lifestyle, and deep cultural balance. It is an ideal destination for both residents and tourists.
Culture and Lifestyle of Chandigarh
Chandigarh is not only a planned city but also a vibrant blend of rich Indian culture and modern living. It harmoniously combines Punjabi traditions with contemporary lifestyles. This cultural richness is reflected in its people, food, festivals, music, and daily life.
1. A Confluence of Traditional and Modern Culture
Influence of Punjabi Culture
- The city is deeply influenced by Punjabi values and traditions.
- People are known for their warmth, openness, and enthusiastic lifestyle.
- Traditional dances like Bhangra and Giddha define the cultural identity of the region.
Modern Lifestyle
- Chandigarh is among the most modern and progressive cities of India.
- Residents embrace fashion, technology, and contemporary trends.
- Café culture and nightlife are highly popular among the youth.
2. Art and Music
Music
- Punjabi folk music such as Bhangra, Giddha, and Sufi songs are deeply rooted in the city's culture.
- Artists like Gurdas Maan, Hans Raj Hans, and Diljit Dosanjh are widely celebrated.
- Classical and Bollywood music also have strong influence.
Art
- The Museum and Art Gallery in Sector 10 houses ancient and modern artworks.
- Nek Chand’s artistic creations in the Rock Garden attract art lovers globally.
3. Food and Catering
Punjabi Cuisine
- Punjabi cuisine forms the heart of Chandigarh’s food culture.
- Popular dishes include butter-loaded parathas, sarson ka saag, makki di roti, chole-bhature, and lassi.
- Local dhabas are famous for their authentic taste.
Modern Food Culture
- Indian, Italian, Chinese, and Continental cuisines are easily available.
- Sector 17 and Elante Mall are major food hubs.
4. Festivals and Celebrations
Main Festivals
- Lohri: Celebrated with bonfires, music, and traditional dance.
- Baisakhi: Harvest festival celebrated with great enthusiasm.
- Diwali and Holi: Celebrated with lights, colours, and joy.
Cultural Programs
- The Rose Festival, Music Festival, and Dance Festival are major annual events.
- Artists from India and abroad participate in these events.
5. Clothing and Fashion
Traditional Clothing
- Women commonly wear salwar-kameez and dupatta.
- Men wear kurta–pyjama and turban, representing Punjabi identity.
Modern Fashion
- Youth prefer branded clothing and trendy outfits.
- Sector 17 and Elante Mall are major fashion destinations.
6. Social Life
Friendly People
- Residents are warm, welcoming, and community-oriented.
- Family values play an important role in daily life.
Nightlife
- Chandigarh has one of the most vibrant nightlife scenes in North India.
- Clubs, bars, cafés, and lounges are popular meeting spots.
7. Sports and Fitness
Importance of Sports
- Sports are highly valued in Chandigarh.
- Popular sports include hockey, cricket, football, and athletics.
- Panjab University and various playgrounds encourage sports activities.
Fitness Culture
- Sukhna Lake and sector gardens are popular for morning walks and exercise.
- Yoga, meditation, and gym workouts are trending among residents.
8. Education and Progressive Attitude
Level of Education
- Panjab University, PGIMER, and other institutes provide top-class education.
- The city gives high importance to academic and technical learning.
Progressive Approach
- The people of Chandigarh have an open-minded and progressive outlook.
- Women and men participate equally in society, education, and work.
9. Environment and Green Lifestyle
Green City
- Chandigarh is one of the cleanest and greenest cities in India.
- Residents are conscious about cleanliness and environmental protection.
Harmony with Nature
- People enjoy spending time in gardens, parks, and open spaces.
- The city promotes sustainability and eco-friendly living.
Conclusion
The culture and lifestyle of Chandigarh beautifully blend tradition with modernity. With its festivals, food, art, community spirit, and progressive outlook, the city offers a unique and inspiring experience for both residents and visitors.

Education and Development in Chandigarh
Chandigarh is one of India’s leading cities in the fields of education and development. Its high-quality educational institutions, modern infrastructure, and innovation-based initiatives make it an educational and progressive hub. The city excels in traditional, vocational, and technical education.
1. Importance of Education and Infrastructure
Importance of Education
- Education is considered the primary means of social and personal growth.
- The educational standard here is higher than the national average.
- The literacy rate is around 86%, making Chandigarh one of India’s most literate cities.
Educational Infrastructure
- The city has a large number of government and private schools.
- Schools like Kendriya Vidyalaya, DAV, St. John’s, and St. Anne’s contribute to quality education.
- Several top universities and institutions offer higher education.
2. Major Educational Institutions
(a) School Education
Government Model Schools
- Provide quality education at affordable fees.
- Encourage students in academics, sports, arts, and scientific learning.
Private Schools
- Offer world-class infrastructure and modern teaching methods.
- Smart classrooms and digital learning are widely adopted.
(b) Higher Education
Panjab University
- One of India’s oldest and most prestigious universities.
- Provides higher education in science, arts, management, engineering, and other fields.
- Its libraries and research centers rank among the best in the country.
PGIMER
- The Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research is a premier medical institution.
- It has international recognition in medical research and health education.
Chandigarh University
- A leading private university providing excellence in technical and management education.
UIET
- The University Institute of Engineering and Technology (UIET) is a top center for engineering and technical studies.
3. Vocational and Technical Education
Industrial Training Institutes (ITI)
- Provide technical and industrial skill training.
- Courses include automobile, mechanical, electronics, and manufacturing skills.
Chandigarh College of Architecture (CCA)
- One of India’s premier architectural institutes.
- Provides excellent education and training in architecture and planning.
Innovation and Startups
- Chandigarh hosts several innovation centers and startup hubs.
- Students are encouraged to take up entrepreneurship and innovative projects.
4. Contribution of Technology in Education
- Smart classrooms and e-learning facilities are widely available.
- Digital libraries and online platforms make learning accessible.
- The Chandigarh Administration promotes digital education under “e-Governance” and the “Smart City Mission.”
5. Research and Development (R&D)
- Institutions like Panjab University and PGIMER contribute actively to research.
- Major fields include agriculture, science, and environmental studies.
6. Developments and Plans
(a) Urban Development
- Chandigarh’s infrastructure makes it one of the most well-organized cities in India.
- Roads, gardens, and government buildings are integral parts of its development plans.
(b) Smart City Mission
- Special projects to promote education, technology, and innovation.
- Skill development programs and smart technology initiatives in schools and colleges.
(c) Employment Opportunities
- Technical education and vocational training have increased job opportunities.
- IT parks, BPOs, and startups have made Chandigarh a growing employment hub.
7. Social and Cultural Contributions
- Education has made citizens socially and culturally aware.
- Focused efforts on women’s education, child education, and vocational programs.
8. Environmental Education
- Schools and colleges promote environmental protection and green lifestyles.
- Various awareness programs are organized throughout the year.
Conclusion
Chandigarh has made remarkable progress in education and development. With quality education, modern infrastructure, and sustainable planning, the city serves as a model for others. Here, education is not just learning—it is the foundation of social and economic development.
Transport and Connectivity in Chandigarh
Chandigarh is known for its well-planned transportation system and excellent connectivity. Its infrastructure makes travel smooth and accessible, both locally and nationally.
1. Local Transport
(a) Public Bus Service
- Chandigarh Transport Undertaking (CTU): The primary public transport service.
- Provides AC and non-AC buses connecting Chandigarh, Mohali, and Panchkula.
- Economical, accessible, and reliable.
(b) Auto Rickshaw and E-Rickshaw
- Popular mode of local travel.
- Eco-friendly e-rickshaws have been recently promoted.
(c) Cab and Taxi Services
- Ola, Uber, and local taxi services are available citywide.
- Convenient and time-efficient.
(d) Bicycles and Walking
- Dedicated lanes for cycling and walking across sectors and gardens.
- Promotes eco-friendly transportation.
2. Intercity Connectivity
(a) Bus Service
- ISBT Sector 17 and Sector 43: Provide direct buses to Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Delhi.
- Volvo, deluxe, and ordinary services are available.
- CTU and HRTC buses are widely used.
(b) Railway Service
- Chandigarh Railway Station: Well-connected to major Indian cities.
- Regular trains run to Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Amritsar, and Jammu Tawi.
- High-speed trains like Shatabdi and Vande Bharat make travel faster.
3. National and International Connectivity
(a) Air Service
- Shaheed Bhagat Singh International Airport: Serves Chandigarh, Mohali, and Panchkula.
- Direct flights to Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Kolkata, etc.
- International flights available to Dubai, Sharjah, and Abu Dhabi.
(b) Road Connectivity
- Connected to Delhi via NH-44 (old NH-1).
- Acts as a major gateway to Himachal destinations like Shimla, Manali, and Dharamsala.
(c) Inter-State Connectivity
- Excellent connectivity with Haryana, Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh.
4. Transport Infrastructure
(a) Roads and Sector Design
- Wide, clean, and organized roads.
- The sector-based grid pattern reduces traffic congestion.
(b) Flyovers and Underpasses
- Ensures smooth traffic movement within the city.
- Improves connectivity with nearby cities.
(c) Parking Facilities
- Multi-level parking available at Sector 17, Elante Mall, and major markets.
- Ensures convenient and hassle-free travel.
5. Eco-Friendly Transport
Bicycle Sharing System
- Public bicycle-sharing through mobile apps.
- Encourages healthy and green commuting.
Promotion of Electric Vehicles (EV)
- Initiatives to promote electric buses and vehicles.
- Charging stations being installed across the city.
6. Role of Smart City Mission
Smart Bus Shelters
- Equipped with digital screens and live bus tracking.
Integrated Traffic Management System (ITMS)
- Smart traffic lights and surveillance cameras for smooth traffic control.
7. Special Services for Tourism and Travel
- Tourist buses available for Rock Garden, Sukhna Lake, Rose Garden, and other attractions.
- Taxi tour services also available to cover major sightseeing spots.
8. Challenges and Solutions
Challenges
- Increasing traffic and pollution.
- Declining use of public transport.
Solutions
- Introduce more electric buses and green vehicles.
- Make public transport more affordable and user-friendly.
Conclusion
Chandigarh’s transport and connectivity systems are among its major strengths. With well-planned infrastructure, modern technology, and eco-friendly initiatives, the city offers convenience for residents and tourists alike. With the growing focus on smart and green transportation, Chandigarh continues to move toward a sustainable future.
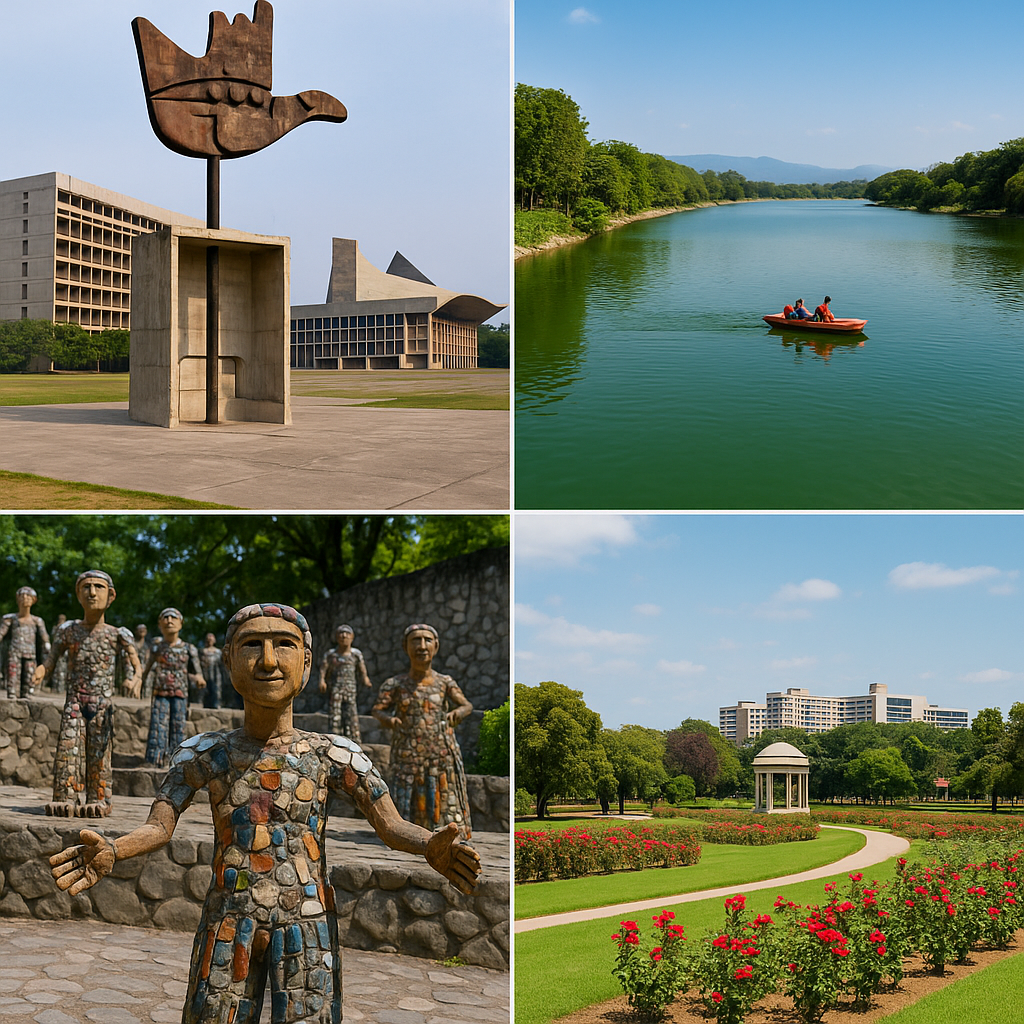

Features of Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a unique and special city of India, known for its beauty, well-organized structure, and progressive development. It is not only an administrative and educational hub but also famous for its cultural richness and modern lifestyle. The city’s key features can be understood in the following categories.
1. Planned Architecture
(a) Design by Le Corbusier
- The strongest feature of Chandigarh is its planned architecture.
- The city was designed by Swiss–French architect Le Corbusier.
- The grid pattern and sector-based layout make it different from other Indian cities.
- Each sector includes essential facilities such as markets, parks, schools, and community spaces.
(b) Modern Architecture
- Buildings like the Legislative Assembly, Secretariat, and High Court represent exceptional modern architecture.
- The Open Hand Monument is the symbol of the city, representing freedom, peace, and openness.
2. Green City
Chandigarh is known as the “City Beautiful” because of its greenery and cleanliness.
- Rose Garden: Asia’s largest rose garden.
- Sukhna Lake: A man-made lake and popular recreational spot.
- Rock Garden: A unique sculpture garden made entirely from waste materials.
3. High Standard of Living
- Chandigarh offers a high standard of living with world-class infrastructure.
- Clean water, electricity, and well-maintained roads are available in every area.
- Residents are well-educated, disciplined, and environmentally aware.
4. Administrative Hub
- Chandigarh is the joint capital of both Punjab and Haryana.
- As a Union Territory, it is directly governed by the Central Government of India.
- The High Court, Secretariat, and various administrative departments are located here.
5. Education and Development
- Home to top educational institutions like Panjab University, PGIMER, and Chandigarh University.
- Prestigious schools like DAV, St. John’s, and St. Anne’s enhance the city’s academic excellence.
- The city leads in technological development and research.
6. Cultural Diversity
- Chandigarh reflects a blend of cultures from Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, and other states.
- Festivals such as Baisakhi, Lohri, and Diwali are celebrated with great enthusiasm.
- Cultural centres like Tagore Theatre host plays, exhibitions, and artistic performances.
7. Tourist Attractions
- Rock Garden: Created by Nek Chand using recycled materials.
- Sukhna Lake: Ideal for boating, strolling, and relaxation.
- Capitol Complex: A UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Open Hand Monument: A symbol of Chandigarh’s identity.
8. Transportation and Connectivity
- Chandigarh has a well-organized transport network.
- National highways, a modern international airport, and well-connected railway services link it to major Indian cities.
- Public transport is being upgraded under the Smart City Mission.
9. Environment Conservation
- Chandigarh is known as an eco-friendly city.
- Residents actively adopt solar energy, electric vehicles, and green initiatives.
- Extensive gardens and green belts help control pollution.
10. Healthcare Facilities
- The city has high-quality medical services.
- PGIMER is a leading institution for treatment, research, and medical education.
- Both private and government hospitals ensure excellent healthcare coverage.
11. Sports and Recreation
- The city has many stadiums such as PCA Stadium (Mohali) and Tau Devi Lal Stadium.
- Fitness and outdoor activities are popular among residents.
- Morning walks and yoga at Sukhna Lake and local parks are part of daily life.
12. Safety and Governance
- Chandigarh is one of the safest cities in India.
- The police administration is efficient and responsive.
- CCTV cameras and smart traffic systems enhance public safety.
13. Economic Progress
- IT parks and industrial areas are developing rapidly.
- The city is a major center for jobs in IT, BPO, and service sectors.
- It is also emerging as a hub for startups and new businesses.
14. A Blend of Modernity and Tradition
- Chandigarh showcases a perfect mix of modern living and traditional values.
- People follow contemporary lifestyles while maintaining cultural roots.
Conclusion
Chandigarh stands out as an ideal Indian city due to its planned design, greenery, high living standards, and cultural richness. Its unique features attract not only residents but also tourists and investors. The city holds immense potential for even greater progress in the future.