Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
When I first started reading and learning about Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, I realised that this small union territory holds a big story of courage, culture, and change. In this article, I am sharing my understanding and learnings in a simple, story-like way so that students, travellers, and curious readers can feel connected to this unique region of India.
If you want to explore more about the administrative structure of India, you can also read my detailed article on Union Territories of India (internal link).
Overview of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
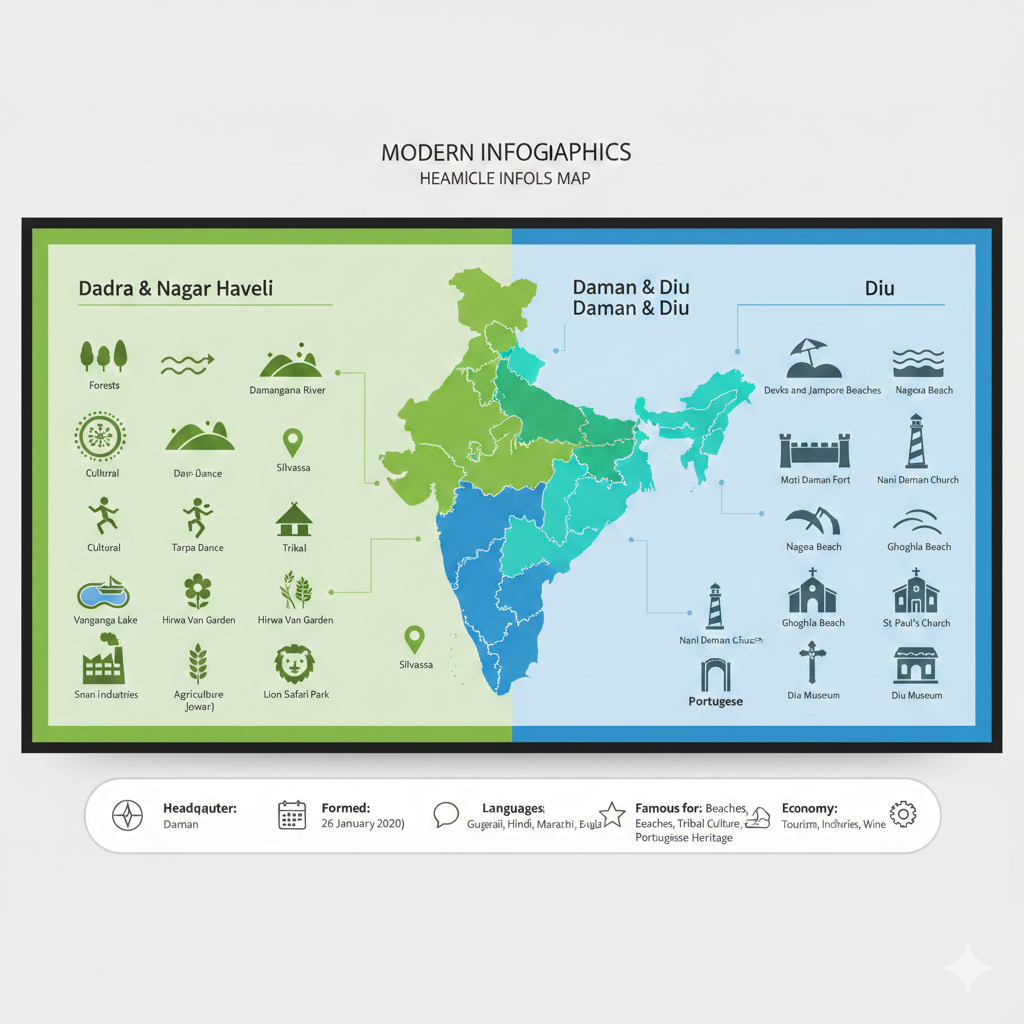
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is a union territory of India. It came into existence after the merger of two earlier union territories – Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu – on 26 January 2020. After this merger, a single union territory was formed.
The administrative headquarters of this union territory is located in Daman. Despite its small size, the region reflects a beautiful blend of Indian and Portuguese influences, making it both historically significant and culturally rich.
Geographical Location
This union territory is situated on the western coast of India.
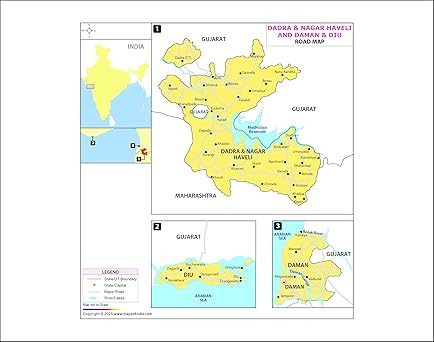
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli: A small land area located between the states of Gujarat and Maharashtra.
- Daman and Diu: Two separate coastal areas on the western seaboard.
- Daman: Situated to the south of Gujarat, along the Arabian Sea.
- Diu: An island located near the Saurashtra region of Gujarat.
Historical Background
The history of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is closely linked with Portuguese rule. The Portuguese captured these areas in the 16th century, and the region remained under their control for a long time.
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli was liberated in 1954.
- In 1961, the Indian Army liberated Daman and Diu from Portuguese rule under “Operation Vijay”.
- In 1987, Goa was made a separate state, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu continued as union territories.
- On 26 January 2020, the two union territories were merged into a single union territory.
This journey from colonial rule to freedom and administrative reorganisation shows how even a small region can carry a big historical story.
Culture and Language
The culture of this union territory is diverse and colourful. Here, local tribal traditions, Indian customs, and Portuguese influences come together to create a unique cultural identity.
- Major languages: Gujarati, Hindi, Marathi, English, and local tribal dialects.
- Folk music and dance form an important part of the cultural heritage.
- Traditional arts, festivals, and local customs reflect the harmony of different communities.
Natural Beauty and Major Tourist Places
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu are known for serene beaches, green landscapes, wildlife, and historical monuments. The calm environment and natural charm make it an attractive destination for tourists.
Daman – Beaches and Heritage
- Devka Beach: A peaceful and scenic beach, ideal for quiet walks and relaxation.
- Jampore Beach: Known for its calm waves and water sports activities.
- Fort St. Jerome (Nani Daman Fort): A historic fort representing Portuguese architecture and defence.
- Lighthouse: Offers a spectacular view of the sea and the surrounding area.
Diu – Island of Calm and Culture
- Nagoa Beach: Famous for swimming and water sports.
- Diu Fort: A major historical site with strong Portuguese influence.
- St. Paul’s Church: Known for its beautiful carvings and European-style architecture.
- Ghoghla Beach: A relatively calm and less crowded beach, ideal for those seeking peace.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli – Greenery and Adventure
- Wildlife Sanctuary: A haven for nature and wildlife lovers.
- Water Sports: Various activities at lakes and rivers for adventure enthusiasts.
- Wanganga Lake: A scenic lake where visitors can enjoy boating and nature views.
Economic Situation
The economy of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is mainly based on industry and tourism. Many small and large industries operate here, supported by favourable policies.
- Industrial units provide employment and contribute to economic growth.
- Tourism, driven by beaches, forts, churches, wildlife, and natural beauty, is a major source of income.
The peaceful atmosphere, business opportunities, and growing tourism together make this region economically significant despite its small size.
Key Features of the Union Territory
- Famous for its natural beauty, beaches, forts, churches, and cultural heritage.
- Administratively, it comes under the direct control of the Central Government of India.
- The combination of tribal culture, Portuguese legacy, and modern development makes it unique.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is one of those regions of India where a unique confluence of culture, history, and modernity can be seen together.
Introduction to Dadra and Nagar Haveli
Dadra and Nagar Haveli is a small and beautiful part of this union territory, located on the west coast of India. It lies between Gujarat and Maharashtra and is famous for its natural beauty, tribal culture, and greenery. For learners and travellers, this region offers a chance to experience both nature and culture very closely.
Geographical Location of Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Location: Situated between the Valsad district of Gujarat and the Palghar district of Maharashtra.
- Area: Approximately 491 square kilometres.
- Major towns: Silvassa (capital), Dadra.
- River: The Damanganga River is the major river of this region, providing important natural resources.
Historical Background
- From 1779 to 1954, the region remained under Portuguese rule.
- In 1954, it became independent from Portuguese control.
- In 1961, it was officially incorporated into India and given the status of a union territory.
Culture of Dadra and Nagar Haveli
The culture of Dadra and Nagar Haveli is mainly based on tribal traditions and folk arts. Several tribal communities such as the Warli, Kokna, and Dodhia live here.
- Folk dance and music: Tarpa dance and Warli painting are the cultural identity of this region.
- Major festivals: Diwali, Holi, and the folk festivals of the Warli tribal communities.
Languages Spoken
- Major languages: Gujarati, Hindi, Marathi, and tribal dialects.
Tourist Spots in Dadra and Nagar Haveli
Silvassa
Silvassa is the capital of Dadra and Nagar Haveli. It has many gardens and museums that showcase the culture and natural beauty of the region.
Wanganga Lake Gardens
A beautiful lake and garden area where visitors can enjoy boat rides and spend peaceful time in nature.
Lion Safari Park
Located near Kilvani village, it is an ideal place for wildlife lovers who wish to see animals in a natural environment.
Hiran Garden
This garden is famous for its greenery and attractive waterfalls, making it a good spot for family outings and photography.
Religious and Natural Places
Balaji Temple, Satmalia Deer Park, and the scenic surroundings of Vanganga Lake together create a mix of religious and natural attractions that draw tourists throughout the year.
Economy of Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Agriculture: The main livelihood here. Paddy, jowar, and rice are the primary crops.
- Industry: Silvassa has many industrial units. Due to tax exemption and favourable policies, many big industries have been established here.
- Tourism: Natural beauty, greenery, and a peaceful environment make tourism an important part of the local economy.
The region is famous for its tribal culture, dense forests, greenery, and rivers, which make it environmentally rich. It is not only known for its beauty and cultural heritage but is also an important area for business and industry due to its tax benefits and strategic location.
Introduction to Daman and Diu
Daman and Diu was a beautiful union territory of India, which was merged with Dadra and Nagar Haveli on 26 January 2020 to form the present union territory. The region is famous for its natural beauty, beaches, Portuguese architecture, and cultural heritage. Although Daman and Diu are geographically located in different places, they are connected through history and culture.
Daman – Location and Features
Location
- Daman is located on the southern coast of Gujarat, along the Arabian Sea.
- It is situated close to the Valsad district of Gujarat.
Geographical Features
- Area: About 72 square kilometres.
- Major river: The Damanganga River divides Daman into two parts – Moti Daman and Nani Daman.
Historical Background of Daman
- Daman came under the control of the Portuguese in 1559.
- It remained under Portuguese rule until 1961.
- In 1961, it was liberated by India under “Operation Vijay”.
Tourist Places in Daman
- Devka Beach: A calm and beautiful beach that attracts tourists for its peaceful environment.
- Jampore Beach: Known for its calm waves, soft sand, and water sports.
- Moti Daman Fort: A historic fort built by the Portuguese, important from a defence and architectural point of view.
- Nani Daman Church: Reflects the Portuguese architectural style and religious heritage.
- Lighthouse: Offers a spectacular view of the sea and surrounding landscape.
Diu – Island of History and Calm
Location
- Diu is a small island located to the south of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat.
- It lies between the Gulf of Khambhat and the Arabian Sea.
- It is separated from the mainland by the Diu Creek.
Geographical Features
- Area: About 40 square kilometres.
- Its island nature and coastal setting give it a unique landscape and climate.
Historical Background of Diu
- Diu came under Portuguese control in the 16th century.
- It was liberated by the Indian Army in 1961.
Tourist Places in Diu
- Diu Fort: A major historical site representing the legacy of Portuguese rule.
- Nagoa Beach: Popular for swimming, relaxing, and water sports.
- Ghoghla Beach: A relatively calm and less crowded beach, ideal for peaceful walks.
- St. Paul’s Church: Known for its intricate carvings and European-style architecture.
- Diu Museum: Preserves antiquities and artefacts related to the Portuguese period.
Culture of Daman and Diu
The Portuguese influence can be clearly seen in the culture of Daman and Diu. At the same time, Indian traditions are also deeply rooted here.
- Major languages: Gujarati, Hindi, English, and Portuguese.
- Traditional folk dance and music are important parts of local celebrations.
- Christian festivals like Christmas and Easter are celebrated with great enthusiasm and devotion.
Economy of Daman and Diu
- Tourism: The main pillar of the economy. Beaches, forts, churches, and heritage buildings attract tourists from across India and abroad.
- Fisheries: Fishing is carried out on a large scale and supports local livelihoods.
- Wine production: The wine production industry is relatively well developed here, adding to the economic diversity.
Daman and Diu, despite their small geographical size, hold great importance for India from a historical, cultural, and natural point of view. Every corner of this region offers a new story, a unique experience, and a quiet lesson in how different cultures can live together in harmony.
FAQ about Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
Q1. What is Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu?
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu is a union territory of India. It was formed on 26 January 2020 after the merger of the two earlier union territories – Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu.
Q2. What is the capital of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu?
The administrative headquarters of the union territory is located in Daman.
Q3. Why is this union territory historically important?
The region was under Portuguese rule for several centuries. Dadra and Nagar Haveli was liberated in 1954, while Daman and Diu were freed in 1961 under “Operation Vijay”. This colonial past and the struggle for liberation make it historically important.
Q4. What are the main tourist attractions in Daman and Diu?
Major tourist attractions include Devka Beach, Jampore Beach, Moti Daman Fort, and the Lighthouse in Daman, and Diu Fort, Nagoa Beach, Ghoghla Beach, St. Paul’s Church, and Diu Museum in Diu.
Q5. What is special about the culture of Dadra and Nagar Haveli?
The culture of Dadra and Nagar Haveli is strongly influenced by tribal traditions. Communities like the Warli, Kokna, and Dodhia live here. Warli painting, Tarpa dance, and local festivals are important parts of its cultural identity.
Q6. Which languages are commonly spoken in this union territory?
Gujarati, Hindi, Marathi, English, Portuguese (in some areas), and various tribal dialects are commonly spoken across Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
Conclusion
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu may look small on the map, but in reality it is a region of big stories and rich experiences. From tribal culture to Portuguese architecture, from peaceful beaches to dense forests, from industry to tourism – everything here shows how history, nature, and modern life can come together.
For me, learning about this union territory has been like reading a living storybook of India – full of struggle, diversity, and hope. If you ever get a chance to visit, or even study this region in detail, you will surely feel that it is not just a place, but an experience that stays with you.
Geographical Location and History of Daman and Diu
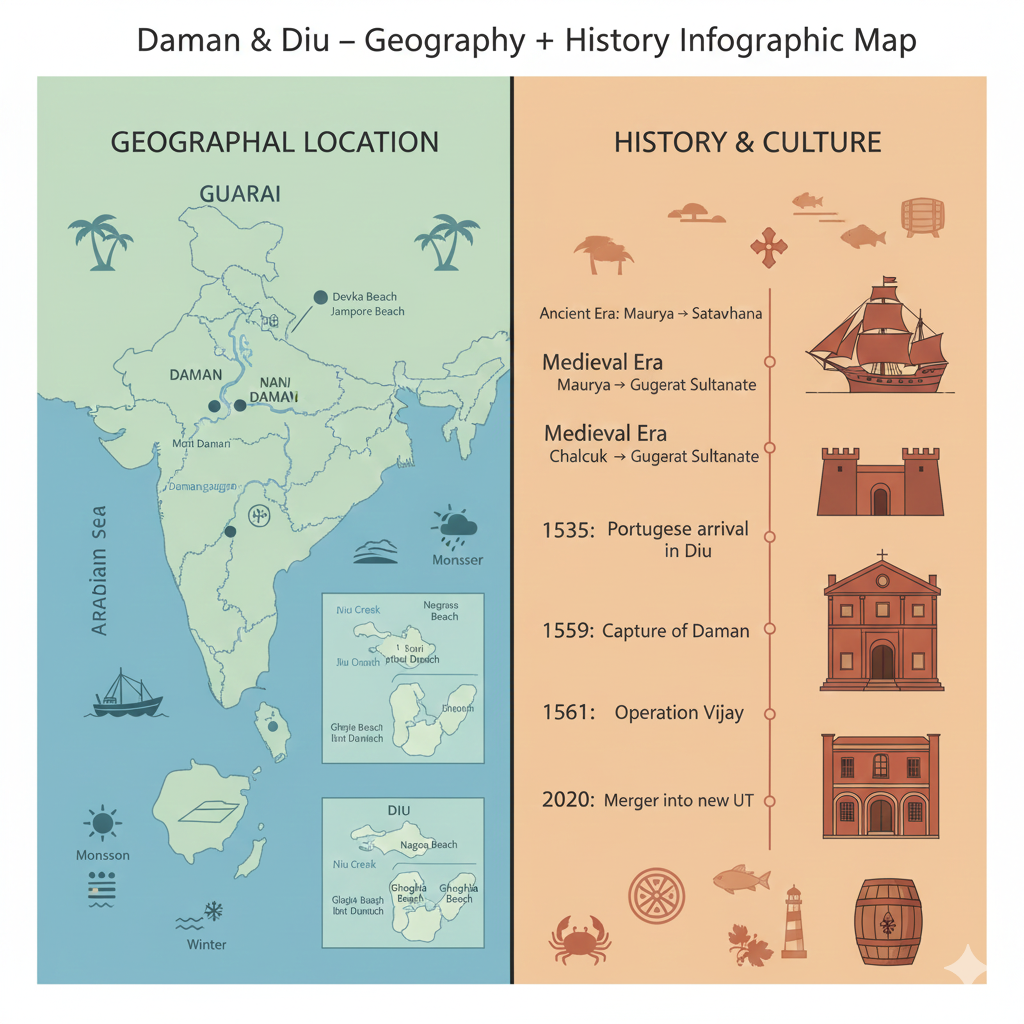
Daman and Diu is a small and beautiful region located on the west coast of India. Surrounded by the Arabian Sea and situated near Gujarat, this union territory is geographically divided into two parts. Despite being a single administrative unit, the geographical locations of Daman and Diu make them unique.
Geographical Location of Daman
Place
- Daman is located on the west coast of India.
- It lies to the south of Gujarat and close to the Maharashtra border.
- The region is situated near the Valsad district.
Area
The total area of Daman is approximately 72 sq. km.
Rivers and Bays
The Damanganga River is the main river of this region.
- Moti Daman – Major administrative and historical area.
- Nani Daman – Residential and commercial area.
Beaches
Daman lies along the Arabian Sea and is home to popular beaches such as:
- Devka Beach
- Jampore Beach
Climate
Daman has a coastal climate with three major seasons:
- Summer: Temperature rises up to 35°C.
- Winter: Cool climate around 20°C.
- Monsoon: Receives heavy rainfall.
Geographical Location of Diu
Place
- Diu is located near the Saurashtra region of Gujarat.
- It lies between the Gulf of Khambhat and the Arabian Sea.
- Diu is separated from the mainland by the Diu Creek.
Area
The total area of Diu is approximately 40 sq. km.
Rivers and Water Bodies
- Diu is an island territory with several small creeks and water channels.
- It is surrounded by the Arabian Sea, making it important for maritime trade and tourism.
Beaches
Diu is famous for its calm and scenic beaches such as:
- Nagoa Beach
- Ghoghla Beach
- Jallandhar Beach
Climate
- Summer: Temperature remains around 30–34°C.
- Winter: Approximately 20°C.
- Monsoon: Moderate to heavy rainfall.
Geographical Features of Daman and Diu
Coastal Areas
Both Daman and Diu are coastal regions bordering the Arabian Sea. Their beaches are lined with golden sand and coconut trees.
Soil and Vegetation
- Fertile coastal soil.
- Coconut, betel nut, and other coastal vegetation are commonly grown.
Terrain
The region is mostly flat and plain with no major mountains.
Marine Biodiversity
Due to proximity to the Arabian Sea, marine life such as fish, crabs, and other aquatic species thrive here.
Geographical Importance
Trade and Transport
Daman and Diu have historically been important for maritime trade due to their coastal location.
Tourism
The beaches, bays, calm atmosphere, and historical charm make the region a major tourist destination.
Natural Resources
The region is rich in coastal resources such as fish, coconut, and other sea-based products.
Conclusion
The geographical location of Daman and Diu enhances its historical and cultural value. Its coastal beauty, natural resources, and pleasant climate attract tourists, traders, and researchers from across the world.
History of Daman and Diu
The history of Daman and Diu is filled with deep cultural, political, and maritime developments. The region remained under Portuguese rule for centuries, which shaped its architecture and traditions.
Ancient and Medieval History
Ancient Period
- Daman and Diu were known for maritime trade in ancient India.
- The region connected India with western countries through sea routes.
- It was part of the Maurya Empire and later the Satavahana Empire.
Medieval Period
- Influenced by the Chalukyas and the rulers of Somnath.
- Became an important port for Arab and Persian traders.
- During the 14th and 15th centuries, it was under the Gujarat Sultanate.
Portuguese Rule
Arrival of the Portuguese
- The Portuguese arrived in India via sea route in the 16th century.
- In 1535, Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat allowed the Portuguese to build a military base in Diu.
- The Portuguese eventually captured Diu and then expanded control.
Capture of Daman
In 1559, the Portuguese also captured Daman and developed it as a major trading and strategic center.
Characteristics of Portuguese Rule
- Construction of forts, churches, and Portuguese-style buildings.
- Daman and Diu became known as part of "Portuguese India".
- Spread of Christianity and establishment of churches like St. Paul’s Church and Bom Jesus Church.
British and Maratha Challenges
The Maratha Empire challenged the Portuguese several times, but the Portuguese maintained control despite British expansion in India.
Movement for Merger with India
Indian Independence Struggle
- Even after India’s independence in 1947, Daman and Diu remained under Portuguese rule.
- Local people and freedom fighters started movements against colonial rule.
Operation Vijay (1961)
In 1961, the Government of India launched “Operation Vijay,” liberating Goa, Daman, and Diu. The Portuguese were defeated, and the region was annexed to India.
Post-Independence History
Union Territory Status
- In 1961, Goa, Daman, and Diu were made a single union territory.
- In 1987, Goa became a state, and Daman and Diu became a separate union territory.
Merger with Dadra and Nagar Haveli
On 26 January 2020, Daman and Diu was merged with Dadra and Nagar Haveli to form a new union territory.
Cultural Influences
The influence of Portuguese culture is very evident in Daman and Diu. Churches, forts, and architecture still showcase European heritage.
Main Historical Sites
- Diu Fort: A major Portuguese fort located along the Arabian Sea.
- Moti Daman Fort: Built near the Damanganga River, showcasing Portuguese military architecture.
- St. Paul’s Church: Located in Diu, famous for its Portuguese-style design.
- Nagoa Beach: Developed during the Portuguese era and a major tourist attraction.
Conclusion
The history of Daman and Diu reflects ancient maritime trade, foreign colonialism, and India’s freedom struggle. The region’s cultural and architectural heritage, especially from Portuguese rule, continues to attract visitors from around the world.
Culture and Language of Daman and Diu
Daman and Diu, located on the western coast of India, is a region where various cultures beautifully merge. The culture here reflects Portuguese influence, Gujarati traditions, and local customs. Along with marine life, festivals, and religious beliefs, the diversity of this region is seen in its language, art, food, and daily lifestyle.
Culture
The culture of Daman and Diu is rich, diverse, and historically influenced by multiple communities.
1. Religious Influence
- Hinduism: Hinduism has a strong presence here, with several ancient temples such as Somnath Mahadev Temple and Hanuman Temple.
- Christianity: Christianity spread during Portuguese rule. Important churches include St. Paul’s Church and Bom Jesus Church.
- Islam: A small Muslim population also contributes to the cultural fabric of the region.
2. Architecture and Art
- The Portuguese influence is clearly visible in local architecture.
- Forts, churches, and coastal structures represent Portuguese-style construction.
- Folk art and traditional handicrafts are part of the local heritage.
3. Music and Dance
- Folk music and dance form an important part of cultural traditions.
- Popular dance forms include Mando and Decani, which blend Portuguese and local styles.
- Sea songs and religious hymns are commonly sung.
4. Festivals and Celebrations
- Navratri: Celebrated with great enthusiasm due to Gujarati influence. Garba and Dandiya are performed widely.
- Christmas and Easter: Major Christian festivals celebrated with church decorations and prayer services.
- Diu Festival: An annual event featuring music, dance, and cultural programs for tourists.
5. Food and Dishes
- Seafood plays a central role in local cuisine—fish, shrimp, and crab dishes are common.
- Gujarati dishes like dhokla, fafda, and khandvi are popular.
- Portuguese dishes such as vindaloo and fish stew are also part of the food culture.
Language
Daman and Diu showcases linguistic diversity shaped by local culture and historical influences.
1. Gujarati
Gujarati is the primary language, widely used in administration, business, and daily communication.
2. Hindi
Hindi is also commonly spoken and helps in communication between locals and tourists.
3. Portuguese
Due to centuries of Portuguese rule, the influence of the Portuguese language still exists, especially among older generations and Christian communities.
4. English
English is mainly used in tourism, business, and hospitality due to the increasing number of visitors.
Cultural Mix
Daman and Diu represents a unique blend of Gujarati, Portuguese, and local coastal traditions.
Gujarati Influence
Visible in folk dances like Garba and in vegetarian cuisine.
Portuguese Influence
Seen in Christianity, church architecture, and maritime lifestyle.
Local Traditions
The customs and festivals of fishing communities play an important role in local culture.
Importance of Culture and Language
The culture and language of Daman and Diu reflect its rich historical and social heritage. The region symbolizes India’s unity in diversity, where multiple languages, traditions, and religions coexist peacefully. Tourism plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting this culture internationally.
Conclusion
The culture and language of Daman and Diu represent its historical legacy, Portuguese influence, and Indian diversity. The lifestyle, traditions, architecture, and linguistic richness make this region unique, vibrant, and culturally significant.
Natural Beauty and Tourist Places of Daman and Diu
Daman and Diu is famous for its natural beauty, serene atmosphere, and coastal charm. The beautiful beaches, historical forts, churches, and greenery make it one of the most attractive tourist destinations in India. Its unique blend of natural and historical elements draws tourists throughout the year.
Natural Beauty
Beaches
- Beaches here are known for clean sand, coconut trees, and clear water.
- The calm and clean environment makes them ideal for relaxation and leisure.
Lush Green Vegetation
- Daman and Diu has abundant greenery, gardens, and coconut trees.
- The scenic views of nature and landscapes make it visually captivating.
Birds and Marine Life
- The region is home to various species of sea birds and fish.
- Marine life viewing and coastal biodiversity attract nature enthusiasts.
Tourist Places in Daman
1. Devka Beach
One of the most famous beaches of Daman, known for its beautiful sand and mesmerising sunset views. Amusement parks and recreational facilities make it ideal for families.
2. Jampore Beach
An excellent beach for swimming and picnics. Tourists enjoy water sports, camel rides, and peaceful surroundings.
3. Moti Daman Fort
A historical fort built by the Portuguese, featuring old government buildings and gardens. A must-visit for history lovers.
4. St. Jerome Fort (Nani Daman Fort)
Located along the Damanganga River, this fort showcases classic Portuguese architectural style.
5. St. Paul’s Church
An iconic church built during Portuguese rule. The woodwork and carved ceilings are major attractions.
Tourist Places in Diu
1. Nagoa Beach
The most famous beach in Diu. Known for swimming, water sports, and beautiful coconut-tree surroundings.
2. Diu Fort
Built by the Portuguese in the 16th century, the fort provides stunning views of the Arabian Sea. Cannons, tunnels, and old structures highlight its historical importance.
3. Jalandhar Beach
Named after the mythological demon Jalandhar. A small temple here adds to its religious significance.
4. Ghoghla Beach
One of the largest and less crowded beaches in Diu. Popular for activities like swimming, parasailing, and surfing.
5. Bom Jesus Church
Famous for its Portuguese-style architecture and peaceful ambiance, attracting tourists and pilgrims alike.
Other Attractions
Diu Museum
Displays historical artifacts, relics, and items from the Portuguese era.
Ghelsar Lake
Known for natural beauty and offers boating facilities.
Panikota Fort
A small sea fort located in the middle of the water, accessible by boat.
Nature Activities and Adventure Sports
- Jet skiing, boating, and windsurfing on various beaches.
- Watching sunsets along the coastline.
- Bird watching opportunities in the coastal zones.
Importance of Natural Beauty
The natural beauty of Daman and Diu not only attracts tourists but also preserves the biodiversity and cultural identity of the region. It is ideal for peace lovers, nature enthusiasts, and history researchers.
Conclusion
Daman and Diu stands out as one of India’s most beautiful coastal tourist destinations. Its beaches, natural beauty, historical sites, and adventure activities create an unforgettable experience for every traveler.
Economic Condition of Daman and Diu
Daman and Diu, part of the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, has a strong economy supported by tourism, industries, fisheries, and limited agriculture. The region has grown significantly from the Portuguese era to modern times.
1. Major Economic Sectors
Tourism
- Daman and Diu is known for its natural beauty, beaches, and historical sites.
- Tourism is the main economic pillar, attracting thousands of visitors annually.
- Tourism supports the hotel industry, restaurants, transport, and local handicrafts.
- Government-organised events like the Diu Festival promote tourism.
Industry
- The region hosts many small and medium industries.
- Major industries include plastics, chemicals, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
- Industrial areas in Daman support national and international trade.
- Tax exemptions and government schemes encourage industrial growth.
- Industries provide significant employment to locals and migrants.
Fisheries
- A key component of the coastal economy.
- Fishing is a major source of income for local families.
- Fish and marine products are exported nationally and internationally.
Agriculture
- Agriculture is limited due to small land area.
- Coconut, rice, and fruits are cultivated in certain zones.
- Coconut-based products contribute to the economy.
2. Revenue Sources
Excise Duties and Taxes
Excise duties, business taxes, and industrial contributions are major sources of government revenue.
Alcohol Production and Sale
Daman and Diu is known for its alcohol production. Cheaper liquor also attracts tourists, contributing to revenue.
Income from Tourism
Hotels, resorts, entry fees, and tourism-related services provide substantial income to the government.
3. Trade and Transport
- The coastal location supports sea-based trade routes.
- Fish and marine product exports play a major role.
- Well-developed road and water transport support commercial activity.
4. Labour Force and Employment
- Tourism and fisheries provide local employment.
- Industries create jobs for workers from local and nearby regions.
5. Economic Challenges
Limited Resources
Due to small geographical size, the region has limited agricultural and industrial expansion possibilities.
Environmental Challenges
Coastal pollution is rising due to unchecked tourism and industrial activities.
Seasonal Dependence
Fishing and tourism are seasonal, affecting steady income generation.
6. Government Initiatives
- Promotion of tourism through events and beautification projects.
- Industrial incentives like tax exemptions.
- Environmental protection schemes for coastal greenery.
7. Effects of Economic Development
- Per capita income has increased due to tourism and industries.
- Improved infrastructure and higher living standards.
Conclusion
The economy of Daman and Diu is driven by tourism, industries, and fisheries. With rich natural resources and strategic coastal location, the region continues to grow economically. However, sustainable development is essential to balance environmental challenges and limited land resources.
Key Features of Daman and Diu
Daman and Diu, part of the integrated union territory “Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu,” is located in the western coastal region of India. Its historical, geographical, cultural, and economic characteristics make it unique. The region is widely known for its serene beaches, Portuguese heritage, and natural beauty.
1. Geographical Features
(i) Coastal Region
- Daman and Diu are located along the Arabian Sea.
- The region is famous for its beaches, bays, and marine life.
- The climate is tropical, with hot summers and pleasant winters.
(ii) Regional Division
- Daman: Located near the Valsad district of Gujarat. Known for tourism and industrial activities.
- Diu: Situated at the southern end of the Kathiawar Peninsula in Gujarat. The region is peaceful and full of natural beauty.
(iii) Marine Life and Biodiversity
- This coastal region is rich in marine biodiversity, with various species of fish, crabs, and sea birds.
2. Historical Features
(i) Portuguese Influence
- Daman and Diu remained under Portuguese rule for nearly 450 years.
- The Portuguese built impressive forts, churches, and architectural structures.
- Their influence is visible in religious places, food, music, and architecture.
(ii) Freedom Struggle and Merger with India
- The region was liberated in 1961 under India’s Operation Vijay.
- In 1987, after Goa became a state, Daman and Diu became a separate union territory.
3. Cultural Characteristics
(i) Religion and Traditions
- Communities following Hinduism, Christianity, and Islam live harmoniously here.
- Prominent religious sites include St. Paul’s Church, Somnath Mahadev Temple, and Hanuman Temple.
- Major festivals such as Navratri, Christmas, and Easter are celebrated with enthusiasm.
(ii) Language and Arts
- Gujarati, Hindi, and English are the major languages spoken.
- Portuguese influence still exists in some communities.
- Folk dance, music, and traditional handicrafts form the cultural identity of the region.
(iii) Festivals and Celebrations
- Diu Festival and Navratri Festival are key cultural events.
- Tourists actively participate in cultural and religious programs.
4. Characteristics of Tourist Destinations
Beaches
- Jampore Beach (Daman): Famous for peaceful surroundings and water sports.
- Nagoa Beach (Diu): Popular for water sports and scenic beauty.
- Devka Beach (Daman): Ideal for family outings and sunset views.
Historical Places
- Diu Fort: A grand example of Portuguese architecture.
- Moti Daman Fort: The main historical fort of Daman.
- St. Paul’s Church: Represents Portuguese architectural style and Christian tradition.
Museums and Other Sites
- Diu Museum: Showcases Portuguese-era heritage items.
- Panikota Fort: A historical sea fort accessible by boat.
5. Economic Characteristics
(i) Tourism-Based Economy
- Tourism is the main economic driver.
- Growing tourist arrivals boost local businesses and employment.
(ii) Industrial Activities
- Daman has many industries, including plastics, textiles, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
- Tax benefits make it an attractive destination for industrial investments.
(iii) Fisheries and Marine Trade
- Fishing is a major source of livelihood.
- Marine exports contribute significantly to trade.
6. Environmental Characteristics
(i) Coastal Protection
- Special initiatives are taken to maintain beach cleanliness and coastal conservation.
- The greenery and clean environment reflect successful environmental initiatives.
Biodiversity
- The region has rich coastal and marine biodiversity.
- It is ideal for bird watching and nature observation.
7. Social and Lifestyle Characteristics
Lifestyle
- The lifestyle here is simple, peaceful, and culturally vibrant.
- Seafood and Gujarati cuisine are integral to the local diet.
Education and Health
Education and healthcare facilities are developing steadily due to income from industries and tourism.
8. Modern Development and Government Initiatives
(i) Promotion of Tourism
- Government organises the Diu Festival and other cultural events.
- Tourist spots are being modernised and beautified.
(ii) Promotion of Industries
- Tax exemptions and infrastructure development attract industries.
Environmental Protection
- Special schemes are implemented to maintain environmental balance and beach cleanliness.
Conclusion
Daman and Diu is one of India’s most unique coastal regions, known for its natural beauty, historical heritage, and cultural diversity. Its geographical location, tourist attractions, and industrial growth make it economically and culturally significant. The region is a treasure for tourists, historians, nature lovers, and cultural explorers.
Conclusion
Daman and Diu stand out as one of the most unique and attractive regions of India due to their natural beauty, historical heritage, coastal lifestyle, and cultural diversity. Its peaceful beaches, Portuguese architecture, religious sites, and growing economic development make it significant both culturally and economically. The region beautifully balances tradition, modern progress, and environmental conservation, offering a rich experience for tourists, historians, nature lovers, and cultural enthusiasts. Thus, Daman and Diu remain a memorable destination that reflects the harmony of history, nature, and culture.
References
- Government of India – Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu Official Portal
- Daman and Diu Tourism Department – Tourist Information Resources
- Historical Records of Portuguese India – Public Archives
- Local Cultural Studies and Regional Geography Reports