Detailed introduction of Sri Lanka
1. General Introduction
Sri Lanka , officially known as The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is an island country located in the Indian Ocean . It is located southeast of India and is bordered by India. Palk Strait And Gulf of Mannar Separates them.
2. Historical background
The history of Sri Lanka is thousands of years old. It was established in ancient times Lanka Or Sinhala Island It was known as and is mentioned in Hindu scriptures Ramayana It is also available in.
- In ancient times here Sinhalese and Tamil Civilizations developed.
- here in the 16th century The Portuguese arrived , then Dutch and finally The British ruled on it.
- On 4 February 1948 it Independence from British rule Happened.
- In 1972 it was renamed Ceylon by changing from Sri Lanka Was kept.
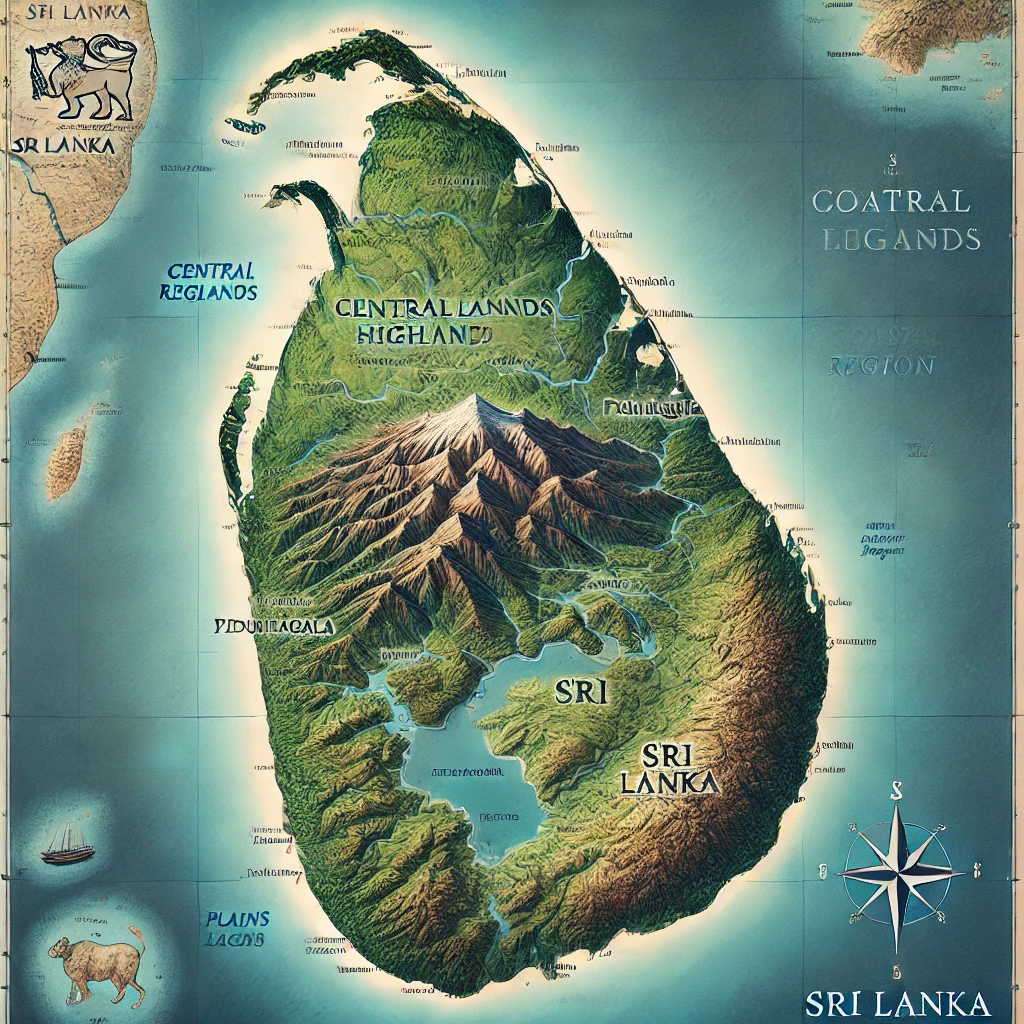
3. Geography and Climate
- Sri Lanka is one Island nation whose total area is 65,610 sq km Is.
- Main geographical parts of the country:
- The central mountainous region ( the highest peak here Pidurutalagala , with a height of 2,524 metres )
- Coastal region ( surrounded by beaches)
- Plains area
- The country has a tropical climate , with two main monsoon seasons.
4. Administrative set up
- Governance System: Republican presidential system
- President: Ranil Wickremesinghe (until 2025 )
- Prime Minister: Dinesh Gunawardene
- Parliament: Unicameral ( 225 members)
- National Capital: Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte ( formal capital) , Colombo ( economic capital)
5. Economy
- Major Industries: Tea , Textiles , Tourism , Gems and Minerals , Coconut Products , Fisheries
- currency: Sri Lankan Rupee ( LKR)
- Major Export Items: Tea , textiles , gems , spices , rubber
- Tourism: Natural beauty , Beach , Historical sites , Buddhist temple
6. Population and culture
- Population: approx 2.2 crore ( 2024 estimate)
- Major language: Sinhala and Tamil
- Religion:
- Buddhism ( 70%) population)
- Hinduism ( 13% ),
- Islam ( 10% ),
- Christianity ( 7% )
- National sport: Volleyball ( Popular Sport – Cricket)
- National Flower: Blue Water Lily
- National Animal: Sri Lankan Elephants
7. Important places and tourism
- Sigiriya ( ancient rock fort)
- Buddha’s Tooth Temple in Kandy
- Galle Fort ( built by the Dutch)
- Adams Peak
- Yala National Park
- Gangaramaya Temple in Colombo
8. Major Challenges
- Economic crisis ( problem of foreign debt and inflation)
- Political instability
- Historical impact of the Tamil–Sinhalese conflict
- Environmental problems ( climate change and deforestation)
conclusion Sri Lanka is a country rich in historical , cultural and natural heritage. It is famous for its Buddhist culture , beautiful beaches , tea plantations and biodiversity. However , it is currently facing many economic and political challenges.
General Introduction of Sri Lanka
General Introduction of Sri Lanka (in detail)
Sri Lanka , officially known as Sri Lanka, also known as the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka , is an island country in South Asia . It is located in the Indian Ocean and is shared with India. Palk Strait And Gulf of Mannar separates it. It has an important place from historical , cultural and economic point of view.
1. Name and identity
- Official name : Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
- Old name : Ceylon
- Popular Name : Moti Dweep ( Pearl of the Indian Ocean)
The name of Sri Lanka is a Sanskrit word ” Shri” ( auspicious , prosperous) and It is derived from the word ” Lanka” ( island) , meaning “prosperous island”.
2. Geographical location
- Continent : Asia
- Location : An island in the Indian Ocean, south of the Indian subcontinent
- Maritime Boundaries :
- In the north India
- the south , east, and west Indian Ocean
- Area : 65,610 sq km (equal in size to Himachal Pradesh)
- Important Islands : Jaffna Island , Mannar Island , Pungeri Island
size of sri lanka Looks like a tear drop (Teardrop of India) .
3. Historical perspective
The history of Sri Lanka is very ancient and it is mentioned in Hindu scriptures Ramayana It is found in Ravana’s temple. Lanka It is believed.
- Ancient period : Development of Sinhalese and Tamil civilisations
- Medieval Period : Spread of Buddhism
- colonial period :
- 1505: Arrival of the Portuguese
- 1658: Dutch rule
- 1796: British rule
- Independence : 4 February 1948 ( from Britain)
- Declared a Republic : 1972 ( then the name was changed from ‘ Ceylon ‘ to ‘ Sri Lanka ‘ )
4. Administrative set up
- System of Government : Republican Democracy
- Capital :
- Official capital : Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte
- Economic Capital : Colombo
- President : Ranil Wickremesinghe
- Prime Minister : Dinesh Gunawardene
- Parliament : unicameral ( 225 members)
Administration of Sri Lanka presidential system It is based on the Constitution of India , in which the President has executive powers.
5. Population and culture
- Total population : about 22 million ( 2024 estimate)
- Main ethnic groups :
- Sinhalese ( 75%)
- Tamil ( 15%)
- Muslim ( 9%)
- Others ( 1%)
- Main religions :
- Buddhism ( 70%)
- Hinduism ( 13%)
- Islam ( 10%)
- Christianity ( 7%)
- Official languages : Sinhala and Tamil
- Culture : Deep influence of Buddhist culture , traditional dance , art and Ayurveda are famous.
6. Economy and industry
- Currency : Sri Lankan rupee ( LKR)
- GDP : about $ 90 billion ( 2024 )
- main industries :
- Tea production (Sri Lankan tea is famous in the world)
- clothing industry
- Tourism
- Gems and Minerals
- Fisheries and Coconut Products
- Major Export Items :
- Tea , textiles , spices , rubber , jewelry
The economy of Sri Lanka is mainly Agriculture , tourism and textile industry resting on.
7. Major tourist destinations
Sri Lanka is famous for its natural beauty and cultural heritage.
- Sigiriya – Ancient Rock Fort
- Kandy – Temple of the Tooth of Buddha
- Galle Fort – Historical fort built by the Dutch
- Adams Peak – The Holy Mountain
- Yala National Park – For wildlife lovers
- Nuwara Eliya – Beautiful tea plantations and mountains
8. Climate and environment
- Climate : Tropical
- Main seasons :
- Yala Monsoon (May – August)
- The Great Monsoon (October – January)
- Important rivers : Mahaweli , Kelani , Walawe
- Natural wealth : Elephant , leopard , peacock , rare aquatic animals
Sri Lanka is famous for its biodiversity and is home to elephants , leopards , and many rare birds.
9. Key problems and challenges
- Economic crisis – foreign debt and inflation are increasing.
- Political instability – Governments have changed in recent years.
- Tamil-Sinhalese conflict – Ethnic conflict has a long history.
- Environmental threats – Climate change , deforestation and pollution are increasing.
10. Interesting Facts
- Sri Lanka is the world’s Largest tea exporter is one of the countries.
- The Sigiriya Fort here world Heritage Sites Is included in.
- sri lanka colombo port of asia The busiest ports Is one of.
- It is the first country that has Woman Prime Minister ( Sirimavo Bandaranaike , 1960) .
- National game of Sri Lanka Volleyball but the most popular game is Cricket Is.
conclusion Sri Lanka is a country rich in historical , cultural and natural heritage. It is famous for its Buddhist culture , beautiful beaches , tea plantations and biodiversity. However , at present it is facing many problems. economic and political challenges India is facing many problems. If these problems are solved properly , then this country will be able to make a name for itself again. Prosperous and stable It can be made.
Historical background of Sri Lanka
Historical background of Sri Lanka (in detail)
, dynasties , foreign invasions and cultural exchange since ancient times . Its history is known as the Ancient period , Medieval period , Colonial period and Modern period can be divided into.
1. Ancient period (about 500 BC – 1200 AD)
(A) Vedic and Ramayana period
- Sri Lanka is mentioned in Hindu epics Ramayana It has been done in.
- This Lanka and it was called Rakshasaraj Ravana It is considered to be the city of.
- It is believed that Lord Rama used this weapon to reach Lanka Ram Sethu (Adam’s Bridge) was built.
(B) Sinhalese Civilization and the First Dynasty
- The Sinhalese people came to Sri Lanka from India in 543 BC.
- King Vijaya (Prince Vijaya) in Sri Lanka Sinhalese Kingdom was established.
- The Sinhalese people adopted Buddhism and laid the foundation of a strong state in Sri Lanka.
(C) Advent of Buddhism
- In the 3rd century BCE Emperor Ashoka Son of Mahendra and daughter Sanghamitra Propagated Buddhism in Sri Lanka.
- King Devanampiyatis ( 250-210 BC) The influence of Buddhism increased during his reign.
- Many Buddhist monasteries , stupas and temples were built in Sri Lanka.
(D) Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa Kingdom
- Anuradhapura (377 BC – 1017 AD) – The first great kingdom of Sri Lanka.
- King Dutugamunu (161–137 BC) defeated the Tamil king Elara and ruled over the entire island.
- Polonnaruwa Kingdom (1070-1200 AD) – Sri Lanka became most powerful during the reign of King Parakramabahu ( 1153-1186) .
2. Medieval Period ( 1200-1500 AD)
(A) Chola and Tamil rule
- In the 10th century South Indian Chola Empire invaded Sri Lanka.
- King Rajaraja Chola and Rajendra Chola Occupied many parts of Sri Lanka.
- the 13th century, Tamil influence increased in northern Sri Lanka.
(B) Re-establishment of Sinhalese dynasties
- Sinhalese kings ruled over southern Sri Lanka Dambadeniya , Gampola and Kotte Like new states were established.
- King in the 15th century Parakramabahu VI (1412–1467) United Sri Lanka again.
3. Colonial Period ( 1505-1948 AD)
(A) Portuguese rule ( 1505-1658)
- Portuguese traders in 1505 Lorenzo de Almeida Reached Sri Lanka.
- The Portuguese Colombo Port Took control and started the business.
- He fought battles with Sinhalese kings and preached Christianity.
(B) Dutch Rule ( 1658-1796)
- in 1658 Dutch Defeated the Portuguese and captured Sri Lanka.
- The Dutch Spices and Cinnamon took control of the business of.
- built canals , roads and forts in Sri Lanka .
(C) British Rule ( 1796-1948)
- in 1796 British East India Company Defeated the Dutch and captured Sri Lanka.
- In 1815 The British also captured Kandy, the last Sinhalese state .
- 1833 Sri Lanka was given a Colonial territories It was made.
- , coffee and rubber plantations in Sri Lanka was established.
- The British forced the Tamil people to for labour from India started bringing Sri Lanka , which Conflict between Sinhalese and Tamils Increased.
- in 1919 Sri Lanka National Congress was formed and the independence struggle against British rule began.
4. Modern period ( 1948- present)
(A) Independence and establishment of the Republic ( 1948-1972)
- 4 February 1948 Sri Lanka was liberated from British rule on I got freedom .
- 1972, Sri Lanka declared itself Republic declared and adopted a new constitution.
- Name of the country Changed from Ceylon to “Sri Lanka” Was kept.
(B) Sri Lankan Civil War ( 1983-2009)
- 1983 , conflict between Sinhalese and Tamils escalated.
- Tamil rebel groups Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam ( LTTE) demanded a separate Tamil nation in northern Sri Lanka.
- In Sri Lanka Civil war lasted for 26 years walked.
- In 2009 The Sri Lankan Army defeats the LTTE , ending the civil war .
(C) Present time ( 2010- till now)
- After the Civil War ended Sri Lanka took steps towards development .
- In 2019 Terrorist attack in Colombo Which increased the threat to the security of the country .
- in 2022 Sri Lanka’s economic crisis Which increased inflation and unemployment .
- To improve the situation in 2023-24, the government Economic reforms and international aid Took.
conclusion History of Sri Lanka Conflicts , foreign invasions and cultural prosperity It is full of. In ancient times it was a Great Buddhist Center Sri Lanka was a British colony , but during the colonial period it faced the rule of various European powers. Despite facing challenges like civil war and economic crisis after independence , Sri Lanka established itself as a strong nation. An important Asian nation has been established as .
Geography and Climate of Sri Lanka
Geography and Climate of Sri Lanka (in detail)
Sri Lanka , which is also called the Indian subcontinent Also known as the Teardrop of India , it is an island country. It is famous for its Varied geographical features , tropical climate and rich biodiversity It is famous for.
1. Geographical location and size
- Continent : Asia
- Location : South of the Indian subcontinent Indian Ocean located in
- Latitude and Longitude : 5°55′ to 9°51′ North Latitude and 79°41′ to 81°53′ East Longitude
- Total area : 65,610 square kilometers
- Size : This island tear drop It appears shaped like .
- Maritime Boundaries :
- In the north India
- the south , east, and west Indian Ocean
- Nearest country : India (separated by the Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar)
(A) Important topographical features
- Central Highlands
- The central part of Sri Lanka is hilly and high.
- Here Mount Pidurutalagala (2,524 m ) is the highest peak in Sri Lanka.
- There are many waterfalls and deep forests located in this area.
- Fertile Plains
- The rivers originating from the hills bring fertile soil to the plains.
- Extensive agricultural land is found in northern and eastern Sri Lanka.
- Coastal Region
- Sri Lanka’s coastline is approximately 1,340 km He is tall.
- There are many beautiful beaches and ports here , such as Colombo , Galle , Trincomalee .
- Islands
- There are some small islands near Sri Lanka , such as Mannar Island , Pungeri Island, and Jaffna Island .
- in the southern part Ram Sethu ( Adam’s Bridge) , which is situated in the shallow waters between India (Tamil Nadu) and Sri Lanka.
2. Climate
Climate of Sri Lanka Tropical Climate , which means it is hot and humid all year round.
(A) Major climatic regions
- Lowland tropical region – Hot and humid climate is found in the coastal and plain areas.
- Mountainous regions – have a cold climate , especially Nuwara Eliya and the surrounding area.
- Dry region – The northern and eastern parts receive less rainfall and have a dry climate.
(B) Major seasons
- Yala Monsoon (May – August)
- due to south-west monsoon western and southern parts There is heavy rainfall in.
- The Great Monsoon (October – January)
- Causes of Northeast Monsoon the northern and eastern parts It rains in.
- Hot and dry season (February – April)
- During this period the temperature increases throughout the country and rainfall decreases.
(C) Temperature
- In coastal areas : average temperature 27-32°C
- In mountainous regions : Average temperature 15-20°C
- Temperatures in winter at high altitudes like Nuwara Eliya 0°C It can fall up to.
3. Major rivers and water sources
Most of the rivers in Sri Lanka They originate from mountainous regions and meet the sea .
(A) Major rivers
- Mahaweli River
- of Sri Lanka Longest river (335 km).
- It originates from the central hills Trincomalee It meets the sea in.
- Kelani River
- Meets the sea near Colombo.
- Kalu Ganga
- It is situated in the south-west and brings lots of water during the rains.
- Malvathu Oya
- It flows northwards and is important in the Tamil areas.
(B) Major lakes and reservoirs
- Parakrama Samudra – An ancient reservoir built by King Parakramabahu.
- Bolgoda Lake – The largest natural lake in Sri Lanka.
- Beira Lake – A beautiful lake located in the centre of Colombo city.
4. Natural vegetation and biodiversity
Sri Lanka has its Rich biodiversity It is known for its wildlife and various types of forests and animals are found here.
(A) Major vegetation area
- Evergreen rainforests- such as Sinharaja Forest (UNESCO World Heritage Site).
- Dry forest area : Dry forests are found in the north and east due to less rainfall.
- Mangrove vegetation – found in coastal areas.
(B) Major wildlife
- Elephants – Sri Lankan elephants are famous around the world.
- Sri Lankan leopard – rare species , which can be seen in Yala National Park.
- Nilgiri Langur – This is a unique monkey found in the forests of Sri Lanka.
- Sea turtles – found on the southern coasts.
(C) Major National Parks
- Yala National Park – Famous for leopards and elephants.
- Wilpattu National Park – It is the largest national park in Sri Lanka.
- Udawalawe National Park – There are a large number of elephants here.
5. Natural disasters
Sri Lanka is also affected by natural disasters , the major ones being:
- Cyclones – Cyclones originating in the Indian Ocean sometimes affect Sri Lanka.
- Floods – Many areas suffer heavy floods during monsoon.
- Drought – Water is sometimes scarce in arid areas.
- Tsunami – Sri Lanka suffered massive losses in the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami.
conclusion
Sri Lanka is a unique country because of its diverse geographical features and climate. Lush green mountains , beautiful beaches , dense forests and rich wildlife It is included among the most beautiful countries in Asia. Although it is affected by natural disasters and climate change , efforts are being made towards its biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Administrative System of Sri Lanka
Administrative system of Sri Lanka (Detailed description)
Sri Lanka is one Constitutional democracy And There is a Republic where Presidential System is in force. Here the government Executive , Legislature and Judiciary Sri Lanka’s administrative system has been influenced by British rule and has been reformed from time to time.
1. Structure of Government
The government of Sri Lanka is mainly divided into three parts:
- Executive – President , Prime Minister and Council of Ministers
- Legislature – Parliament
- Judiciary – courts and legal institutions
2. Executive – Government system
(A ) President
- President of Sri Lanka Head of State, Head of Government and Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces It happens.
- to the President direct election by the people and his term of office 5 year What happens?
- Near the President special executive powers There are , such as:
- Appointment of ministers
- Power to dissolve Parliament
- Making decisions related to defence and foreign affairs
- proposing changes to the constitution
(B) Prime Minister
- Prime Minister The second most important position after the President It happens.
- President Appointment of Prime Minister This is done by the leader of the majority in the Parliament.
- The Prime Minister coordinates between the Parliament and the Government and is assisted by the Council of Ministers.
(C) Council of Ministers
- In this Cabinet ministers , ministers of state and deputy ministers are included.
- work to implement government policies , run various ministries and remain accountable to the Parliament.
- in key ministries Defence , Finance , Education , Health , Foreign Policy , Agriculture , Tourism and Transport Are included.
3. Legislature – Parliamentary System
- In Sri Lanka Unicameral Parliament occurs , which ” Parliament of Sri Lanka” It is said.
- In Parliament 225 members There are.
- Election of members of parliament direct voting by the people Through For 5 years It is done.
- Making legislation , passing the budget, and supervising the actions of the President The work is done by the Parliament.
(A) Functions of the Parliament
- Creation and amendment of new laws
- overseeing the financial affairs of the government
- Supervising the work of the President and the Council of Ministers
- controlling national security and foreign policy
(B) Key positions in Parliament
- Speaker – Presides over the meetings of the Parliament .
- Parliamentary Committees – Review the policies of various ministries.
4. Judiciary – Judicial system
The judiciary of Sri Lanka is independent and protected by the Constitution. This judiciary protects the rights of citizens and exercises judicial review of the actions of the government.
(A) Major Courts
- Supreme Court –
- This is the highest court of Sri Lanka.
- Hears constitutional matters , appeals and cases involving fundamental rights.
- Chief Justice heads the Supreme Court.
- Court of Appeal –
- It hears appeals against decisions of lower courts.
- High Court –
- It hears serious crimes and civil cases.
- District Courts and Magistrate Courts –
- They hear small cases at the local level.
(B) Legal system
- is influenced by British law , Roman-Dutch law and local traditions.
- it Organized legal framework Ensures that every citizen gets justice.
5. Administrative Divisions
Sri Lanka is administratively divided into 9 Provinces and 25 Districts It is divided into.
(A) 9 major provinces
- Western Province – Colombo
- Central Province – Kandy
- Southern Province – Galle
- Northern Province – Jaffna
- Eastern Province – Trincomalee
- North Western Province – Kurunegala
- North Central Province – Anuradhapura
- Sabaragamuwa Province – Ratnapura
- Uva Province – Badulla
(B) District Administration
- Each district is headed by a District Secretary He does.
- Under the district administration Various departments , local councils and government agencies is coordinated.
(C) Local Government
Local administration in Sri Lanka is divided into three levels:
- Municipal Councils – For bigger cities and municipalities.
- Urban Councils – For medium sized towns.
- Village Councils ( Pradeshiya Sabhas) – For rural areas.
6. Political system and major political parties
In Sri Lanka Multi-Party Democracy , where several political parties are active.
(A) Major political parties
- Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna ( SLPP) – Currently the largest party.
- United National Party ( UNP) – traditionally a major party.
- Sri Lanka Freedom Party ( SLFP) – Historically strong party.
- Tamil National Alliance ( TNA) – The main party of the Tamil community.
- Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna ( JVP) – A party with leftist ideology.
7. Law and civil rights
- Constitution of 1978 to citizens under Liberty , equality, and religious freedom has been given the right to.
- In Sri Lanka Fundamental Rights A petition can be filed in the Supreme Court for protection of.
- In the country Human Rights Commission is employed.
conclusion Administrative system of Sri Lanka based on presidential system There is a clear balance between the executive , legislature and judiciary in the country. However , sometimes there is a lot of political instability in the country . Political instability and administrative challenges are seen. But , the government local administration , judicial reforms and maintaining democratic values is constantly striving for.
Economy of Sri Lanka

Economy of Sri Lanka (Detailed Description)
Economy of Sri Lanka Growing and Diversifying , which is mainly Agriculture , Industry , Services and Tourism It is based on. It has also been an important trading center of South Asia. However , in recent years Economic crisis , foreign debt and currency devaluation Due to this, Sri Lanka’s economy has faced serious challenges.
1. Structure of Economy
Sri Lanka’s economy can be divided into three major sectors:
- Agriculture Sector – Production of tea , rubber , coconut and spices.
- Industrial Sector – Textile manufacturing , petrochemicals , and food processing.
- Service Sector – Tourism , banking , IT and transportation services.
2. Gross Domestic Product ( GDP) and Economic Growth
- of Sri Lanka Total GDP About $ 80-90 billion It has been around.
- Per Capita Income It is higher than other countries in South Asia , but has been declining recently.
- Main economic challenges – foreign debt crisis , inflation and currency devaluation.
(A) Contribution of major sectors in GDP
- Service Sector – 55-60%
- Industry Sector – 25-30%
- Agriculture Sector – 8-12%
3. Major Economic Sectors
(A) Agriculture & Plantation Economy
Agriculture is the biggest factor in Sri Lanka’s economy Spine and it is the country’s Foreign Exchange Reserves It is also a major source of.
(i) Major agricultural products
- Tea-
- Sri Lanka is the world’s 4th largest tea exporter Is.
- ” Ceylon Tea” is famous in the international market.
- Rubber-
- Source of raw materials for tires and other rubber products.
- Coconut-
- Sri Lanka is one of the top coconut producing countries in the world.
- Spices-
- Sri Lanka in particular Cinnamon , cardamom and black pepper It is famous for its export.
- Rice-
- Rice is the staple food of Sri Lanka and is cultivated extensively in the country.
(ii) Challenges of the agricultural sector
- By the government in 2021 ban on chemical fertilizers Due to this, agricultural production declined.
- Climate change and uncertainty of monsoon also affect the region.
(B) Industry & Manufacturing
Sri Lanka’s industrial sector is slowly growing , but it is still small compared to other Asian countries.
(i) Major Industries
- Textile & Apparel –
- Sri Lanka’s textile industry Over 40% of the country’s exports Contributes.
- Sri Lankan clothing is in great demand in Europe and America.
- Food Processing –
- tea , spices and coconut based products.
- Petrochemicals –
- Crude oil is imported for fuel and gas production.
- Cement & Construction –
- The sector is experiencing growth due to Sri Lanka’s developing infrastructure.
- IT & Software Industry –
- Colombo and other major cities IT Hubs and Startups are developing rapidly.
(C) Service Sector
Sri Lanka’s services sector is the largest segment of its economy.
(i) Tourism Industry
- Sri Lanka has its Beautiful beaches , historical sites and national parks It is famous for.
- tourism to sri lanka major source of foreign exchange reserves Is.
- Major tourist places-
- Sigiriya
- Galle Fort
- Kandy and Buddhist Temples
- Yala National Park
(ii) Banking & Finance
- In Sri Lanka Public and private banking system is developing.
- to attract foreign investment Colombo International Financial City is being set up.
(iii) Transport & Logistics
- Colombo Port It is one of the busiest ports in South Asia.
- Sri Lankan Road , railway and air routes also play an important role in export-import.
4. Trade & Foreign Investment
- Sri Lanka is mainly Tea , textiles , spices and marine products exports of .
- Main trading partners- India , China , USA , UK and Japan .
- Sri Lanka has Trade Agreements with India and China ( Free Trade Agreements – FTA) have done.
5. Economic Challenges & Crisis
In recent years, Sri Lanka has severe economic crisis have had to face.
(A) Major economic problems
- Foreign Debt Crisis –
- on Sri Lanka in 2022 Foreign debt of more than 50 billion dollars Was.
- included loans taken from China , India and other countries.
- Currency Depreciation –
- Srilankan The rupee weakened , making imports expensive.
- Inflation and Food Crisis –
- Inflation rates reached over 50% , making living difficult.
- Energy Crisis –
- to Sri Lanka fuel and power crisis had to face.
(B) Improvements and Solutions
- Financial assistance from IMF (International Monetary Fund) and India Was taken.
- Public finance reform and changes in the tax system Are being done.
- Efforts to increase new investments and production in agriculture and industries Are happening.
conclusion Sri Lanka’s economy is based on agriculture , industry and service sectors. However , in recent years the country has faced difficulties due to foreign debt and inflation. The government is now economic reform , foreign investment and reviving tourism The government is working hard to make a sustainable economy. If the right policies are adopted , Sri Lanka’s economy can become stable and prosperous again in the future.
Population and Culture of Sri Lanka
Population and culture of Sri Lanka (detailed description)
Sri Lanka is one Multicultural , multilingual and multi-religious It is a country whose population is made up of diverse communities. The culture here is based on Buddhist , Hindu , Muslim and Christian traditions Sri Lanka Music , dance , art , food and festivals Its cultural richness is reflected in it.
1. Population ( Population of Sri Lanka)
(A) Total population and density
- Total Population – Approx. 2.2 crore ( 22 million) people .
- Population density is about 340 persons per sq. km .
- Urban and rural divide –
- About 20-25% people live in urban areas I live in.
- Balance 75-80% population lives in rural areas She resides in.
- major city –
- Colombo ( the capital and largest city)
- Kandy ( Cultural Centre)
- Galle ( historic coastal city)
- Jaffna ( Tamil majority area)
(B) Ethnic Groups of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is home to various ethnic communities , with distinct cultural and linguistic identities.
| Ethnic Groups | Percentage | Main areas |
| Sinhalese | 75% | Throughout Sri Lanka , especially the south and central regions |
| Lankan Tamil | 11% | Northern and Eastern Provinces (Jaffna , Trincomalee) |
| Indian Tamil | 4.5% | Tea plantation areas (Kandy , Nuwara Eliya) |
| Muslims ( Sri Lankan Moors) | 9.5% | Colombo , Eastern Province , Kandy |
| Burger and others | 0.5% | Small communities in Colombo and Galle |
(i ) Sinhalese
- of Sri Lanka The largest ethnic group (75%) .
- their main religion Buddhism (Theravada Buddhism) Is.
- Language – Sinhalese .
(ii) Sri Lankan Tamil
- This community in particular Northern and Eastern Sri Lanka I live in.
- their main religion Hinduism But there are some Tamil Christians too.
- Language- Tamil .
(iii) Indian Tamil
- During British rule in the 19th century tamil laborers from india Children of.
- mainly People working in tea plantation areas .
(iv) Muslims ( Sri Lankan Moors)
- Sri Lankan Muslims are mostly from the business community.
- their main religion Islam Is.
- Main languages- Tamil and Sinhalese .
(v ) Burger
- Mixed descendants of Europeans (mainly Dutch and Portuguese) and local Sri Lankans.
- Mainly Christianity do follow.
- Language- English , Sinhalese and Tamil .
(C) Religions in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is a religiously diverse country , where many religions co-exist.
| Religion | Percentage | Main follower groups |
| Buddhism | 70% | Sinhalese |
| Hinduism | 12% | Tamil |
| Islam | 9.5% | Muslim (Moor) |
| Christianity | 8.5% | Tamil and Burgher communities |
- Buddhism – the main religion of Sri Lanka , mainly Theravada Buddhism is followed.
- Hinduism – Mainly followed by Sri Lankan Tamils , and there are many ancient Hindu temples.
- Islam – mainly Sunni Muslim Population.
- Christianity – specifically Catholic and Protestant communities It is followed by.
2. Culture of Sri Lanka
(A) Languages ( Languages of Sri Lanka)
There are primarily two official languages in Sri Lanka:
- Sinhala – the main language , which is 75% people I say it.
- Tamil – almost 25% people This is called this.
- English – Widely used in business , administration and education .
(B) Art and Music
Sri Lanka’s art and music show Indian , South Asian, and European influences.
- Kandyan Dance – Traditional Sinhalese Buddhist dance.
- Bharatanatyam – practiced by the Tamil Hindu community .
- Perahera Festival – Buddhist religious festival featuring traditional dances.
- Sri Lankan folk music – sung accompanied by drums and traditional instruments.
(C) Food ( Cuisine of Sri Lanka)
Sri Lankan food is spicy and delicious , influenced by South Indian and Southeast Asian cuisine.
Famous Dishes
- Rice & Curry – Staple food of Sri Lanka.
- Hoppers – Thin pancakes made from coconut milk and rice .
- Kiribath – Special rice made with coconut milk .
- Kottu Roti – A dish made of sliced parathas and spices.
- Seafood – prawns , fish and crabs .
(D) Major festivals ( Festivals of Sri Lanka)
A variety of festivals are celebrated in Sri Lanka due to the different ethnic and religious communities.
- Vesak – Major festival of Buddhism.
- Diwali – Festival of lights celebrated by the Hindu community.
- Islamic Eid – Celebrated by the Muslim community.
- Christmas – Celebrated by the Christian community.
- Sinhala & Tamil New Year – Celebrated in April.
conclusion
Sri Lanka’s population and culture are full of diversity. Here we can see the integration of various ethnic groups , languages and religions. Sri Lanka’s rich traditions , art , music , food and festivals make it a Culturally rich country Let’s make it.
Important places and tourism in Sri Lanka

Important places and tourism in Sri Lanka (detailed description)
Sri Lanka Natural beauty , historical sites and religious importance It is famous for ” The Pearl of Asia” And ” Paradise of the Islands” It is also called the Beaches , Mountains , Forests , Historical Temples and National Parks It is a centre of attraction for tourists.
1. Major Tourist Attractions in Sri Lanka
Tourism in Sri Lanka can be divided into different categories:
- Historical and cultural sites
- Natural and wildlife tourist destinations
- Beaches and coastal tourist destinations
- Religious places
1. Historical and cultural sites
Sri Lanka has many ancient historical sites , some of which can be UNESCO World Heritage Site has got the status of.
(A) Sigiriya ( Sigiriya – Lion Rock)
- it The most famous historical sites of Sri Lanka Is.
- It was built as a fort by King Kashyapa in the 5th century .
- here on the rocks Ancient Frescoes , Water Garden and Lion ‘s Gate Are.
- This ” The Eighth Wonder of the World” It is also called.
(B ) Anuradhapura
- this is sri lanka’s ancient capital Thi and is a major Buddhist religious site.
- here are several Buddhist stupas , temples and ancient relics Are.
- Major landmarks:
- Ruwanweli Saya Stupa ( Ruwanwelisaya Stupa)
- Mahabodhi Tree ( Jaya Sri Maha Bodhi) – This is the same sacred tree under which Lord Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Isurumuniya Temple
(C ) Polonnaruwa
- this is from sri lanka The second oldest city Is.
- 11th and 12th century temples here. Ancient ruins , statues and temples Are.
- Major landmarks:
- Gal Viharaya – Giant Buddha statue.
- Rankot Vihara
(D) Galle Fort
- it Dutch colonial era It is an excellent example of the architecture of .
- This UNESCO World Heritage Site Has the status of.
- This fort Dutch , Portuguese and British architecture It is a mixture of.
2. Natural and wildlife tourist destinations
Sri Lanka has its Lush green hills , tea plantations and wildlife safaris It is famous for.
(A ) Ella
- It is one of the most beautiful hill stations in Sri Lanka.
- From here one can see a wonderful view of the lush green mountains and tea gardens.
- Major landmarks:
- Nine Arches Bridge
- Adams Peak ( Little Adam’s Peak)
(B) Nuwara Eliya
- This ” Little England of Sri Lanka” It is said.
- , waterfalls and cool climate here make it an ideal tourist destination.
- Major Attractions:
- Horton Plains National Park
- ‘s End View Point
(C) Yala National Park
- it Sri Lanka’s most famous wildlife sanctuary Is.
- Here Asian elephant , leopard , crocodile and various birds Are found.
- it Wildlife Safari The best place for.
(D) Minneriya National Park
- here every year ” Elephant Gathering “ It can be seen.
- This place is also a centre of attraction for bird lovers.
3. Beaches and coastal tourist spots
Sri Lanka has its beautiful beaches and blue waters It is famous for.
(A ) Mirissa
- Here Whale and Dolphin Watching can be enjoyed.
- This is a calm and beautiful beach.
(B ) Unawatuna
- This is from Sri Lanka The most popular beaches Is one of.
- Here Scuba diving , snorkelling and water sports Can be done.
(C ) Bentota
- this beach Luxury Resorts and Water Sports It is famous for.
(D) Pasikuda & Arugam Bay
- Pasikuda – Clear waters and calm beaches.
- Arugam Bay – one of the best places in the world for surfing .
4. Religious places
Sri Lanka is home to several major religious sites , significant to followers of Hinduism , Buddhism , Islam, and Christianity.
(A) Sri Dalada Maligawa ( Temple of the Tooth, Kandy)
- this is from sri lanka The most sacred Buddhist temple Is.
- Lord Buddha’s temple is here Tooth Relic has been kept safe.
- it UNESCO World Heritage Site is also there.
(B) Munneswaram Temple
- This is a Ancient Hindu Temple , which is dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- This temple is believed to be associated with Ramayana.
(C) Nagadeepa Temple
- This is a famous Buddhist and Hindu pilgrimage sites Is.
(D) Kataragama Temple
- This temple is God Murugan (Karthikeya) is devoted to.
- Hindus , Buddhists and Muslims all consider this temple sacred.
conclusion Sri Lanka is one A paradise for travel lovers It is. Here Historical sites , beaches , mountains , wildlife and religious places Making it a wonderful travel destination. Whether you are interested in history , nature , adventure or spirituality , there is so much to explore in Sri Lanka!
