Location and Extent of India
Whenever I look at the map of India, I realise how its location, shape and boundaries have shaped our history, climate, trade and culture. In this article, I am sharing my learnings about the location and extent of India in a simple, story-like way so that students and readers can easily understand and remember these concepts.
If you want to explore further, you can also read my detailed article on Geographical importance of India , which is closely related to this topic.
Location of India
India is a subcontinent located in the southern part of the continent of Asia. The country is famous for its geographical location, natural diversity and historical importance. Its position has made it a bridge between different regions of Asia and the world.
Latitude and Longitude of India
India is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Latitudinal extent of India: from 8°4′ North latitude to 37°6′ North latitude.
- Longitudinal extent of India: from 68°7′ East longitude to 97°25′ East longitude.
Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ North latitude) passes almost through the middle of India. It divides the country into two almost equal parts – the northern half and the southern half.
Sea Condition and Peninsular Shape
The southern part of India stretches into the Indian Ocean, giving it the appearance of a peninsula. A peninsula is a piece of land surrounded by water on three sides.
- To the west lies the Arabian Sea.
- To the east lies the Bay of Bengal.
- To the south lies the Indian Ocean.
Border and Extent of India
Total Area of India
The total area of India is 32,87,263 square kilometres, which makes it the seventh-largest country in the world.
Land Boundary
- India’s land boundary is about 15,200 kilometres long.
- India shares its borders with seven countries.
Countries Sharing Land Borders with India
- In the north and north-west: Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- In the north: China, Nepal and Bhutan.
- In the east: Myanmar and Bangladesh.
Maritime Boundary
India’s maritime boundary (coastline including islands) is approximately 7,516.6 kilometres long.
- It includes the mainland coastline.
- It also includes the coasts of the Lakshadweep and Andaman–Nicobar islands.
States Sharing International Borders
India has 28 states and 8 union territories. Out of these, 17 states share international borders with neighbouring countries.
Some examples are:
- Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat – share borders with Pakistan.
- Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh – share borders with China.
- West Bengal, Assam – share borders with Bangladesh.
Natural Boundaries of India
Himalayas in the North
- The Himalayan mountain range forms a strong natural wall in the north.
- It provides natural protection and acts as a geographical division between India and China.
Sea in the South
- India is surrounded by water on three sides in the south, making it a peninsular country.
- Kanyakumari is situated at the southernmost tip of mainland India.
Western and Eastern Boundaries
- West: The Thar Desert and the region around the Indus River.
- East: The region around the Brahmaputra River and the Eastern Ghats.
Unique Features of India’s Geographical Position
- India’s location makes it a natural centre of trade and cultural exchange with countries in Asia, Africa and Europe.
- Its position in the Indian Ocean makes it strategically important for maritime trade and security.
- This wide geographical expanse and variety of boundaries make India a diverse and culturally rich nation.
Latitude and Longitude – Basic Concepts
Before understanding India’s location, I found it helpful to revise the basic concepts of latitude and longitude. These are the main components of the geographic coordinate system, used to show the exact position of any place on Earth.
1. Latitude
Definition: Latitudes are imaginary lines that measure the position of a place north or south of the Equator.
- They are measured in degrees (°).
- The Equator is considered as 0° latitude.
Main Features of Latitudes
- Latitude lines run horizontally from west to east.
- They divide the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
- There are a total of 180 lines of latitude:
- From 0° to 90° North (up to the North Pole).
- From 0° to 90° South (up to the South Pole).
Important Latitudes
- 0° – Equator
- 23.5° North – Tropic of Cancer
- 23.5° South – Tropic of Capricorn
- 66.5° North – Arctic Circle
- 66.5° South – Antarctic Circle
Latitudinal Position of India
The latitudinal extent of India is from 8°4′ North to 37°6′ North.
2. Longitude
Definition: Longitudes are imaginary lines drawn from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- They are also measured in degrees (°).
- The Prime Meridian passing through Greenwich (London) is considered as 0° longitude.
Main Features of Longitudes
- Longitude lines run vertically from pole to pole.
- They divide the Earth into the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.
- There are a total of 360 lines of longitude:
- 180° East
- 180° West
- Longitude plays an important role in determining time.
Important Longitudes
- 0° – Prime Meridian
- 180° – International Date Line
Longitudinal Position of India
The longitudinal extent of India is from 68°7′ East to 97°25′ East.
The Indian Standard Time (IST) is based on 82°30′ East longitude, which passes near Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh.
Importance of Latitude and Longitude
- Positioning: They give the exact location of a place on Earth.
- Climate and Time: Latitude affects climate zones, while longitude determines time zones.
- Map Making and Navigation: They are essential for maps, GPS and navigation.
Because of its latitudinal and longitudinal position, India experiences a diverse climate and supports rich biodiversity.
Tropic of Cancer and India
The Tropic of Cancer is one of the most important latitude lines on Earth. It helps us understand climate, seasons and the distribution of heat from the Sun.
What Is the Tropic of Cancer?
- It is located at 23.5° North latitude.
- It represents the places on Earth where the Sun can be seen directly overhead (at a 90° angle) once a year.
Position of the Sun on the Tropic of Cancer
Around 21st or 22nd June every year (Summer Solstice in the Northern Hemisphere), the Sun shines directly overhead at the Tropic of Cancer.
Importance of the Tropic of Cancer
- It marks the northern boundary of the tropics.
- The region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn is known for its generally hot climate.
Tropic of Cancer and India
India is one of the countries through which the Tropic of Cancer passes. It divides India into almost two equal halves – the northern and southern parts.
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the following eight states of India:
- Gujarat: Through areas of Jasod (Kutch) and Ahmedabad districts.
- Rajasthan: Through Sirohi and Dungarpur districts.
- Madhya Pradesh: Through Ratlam, Ujjain and Vidisha districts.
- Chhattisgarh: Through Jashpur and Ambikapur regions.
- Jharkhand: Through Ranchi district.
- West Bengal: Through Durgapur and Jalpaiguri.
- Tripura: Through Unnakoti and Dhalai districts.
- Mizoram: Through Champhai district.
Natural and Cultural Impacts of the Tropic of Cancer
Effect on Climate
- Areas near the Tropic of Cancer generally have a hot climate.
- During summer, days are longer and the Sun’s rays are more direct and intense in these regions.
Farming and Lifestyle
- Due to the tropical climate, there is a high diversity of crops and vegetation in these areas.
- The influence of the monsoon is also strong here.
Geographical Identification
- At many places in India, monuments and markers have been built to indicate the Tropic of Cancer.
Thus, the Tropic of Cancer is important not only from a geographical point of view, but also for its impact on climate, agriculture and culture.
Sea Condition and Maritime Position of India
When I studied India’s map more closely, I realised how powerful our sea condition is. It refers to the maritime position of India, which makes it a peninsula surrounded by sea on three sides. This maritime location is extremely important from strategic, commercial and cultural angles.
Maritime Status of India
Surrounded by Sea on Three Sides
- West: Arabian Sea
- East: Bay of Bengal
- South: Indian Ocean
Length of Sea Border
- India has a maritime border of approximately 7,516.6 km.
- This includes the coastline of the mainland as well as that of the Andaman–Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands.
Oceanic Expanse
- India is located in the northern part of the Indian Ocean, which makes it very important for international maritime trade.
- Its position makes it a hub of trade routes connecting Asia, Africa and Europe.
Importance of India’s Sea Condition

Premium Smart Gadget
High quality product with latest technology. Perfect for daily use and long durability.
Buy on AmazonTrade and Transport
- India’s maritime position has made it a major centre for sea trade since ancient times.
- Major ports like Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kochi and Kandla play a crucial role in international trade.
Strategic Strength
- India’s location in the Indian Ocean provides a strong strategic advantage in maritime security and naval operations.
- India has several naval bases that protect its maritime interests.
Effect on Weather and Climate
- The surrounding seas greatly influence India’s climate.
- The southwest monsoon, which is vital for Indian agriculture, depends largely on the winds coming from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Cultural and Historical Influence
- The seas provided India with opportunities for cultural and trade exchanges with other regions such as Rome, Greece and Southeast Asia in ancient times.
- India’s naval power was impressive during the Chola and Maurya empires.
Fisheries and Blue Economy
- India’s vast maritime area supports a strong fisheries and marine products industry.
- The concept of a blue economy highlights how India benefits from marine resources, energy and coastal activities.
Islands and India’s Maritime Position
Lakshadweep
- Located in the Arabian Sea.
- Consists of about 36 small islands.
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Located near the meeting point of the Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean.
- They are extremely important from a strategic and defence point of view.
Due to this unique maritime position, India is often called the “Jewel of the Indian Ocean”. Its role is central in sea trade among Asia, Africa and Europe, and its blue economy adds to its economic and geographical importance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Location and Extent of India
1. What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India?
India extends from 8°4′ North to 37°6′ North latitude and from 68°7′ East to 97°25′ East longitude. This wide extent gives India a great variety in climate and natural conditions.
2. Why is India called a peninsular country?
India is called a peninsular country because it is surrounded by water on three sides – the Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, while the north is connected to the Asian mainland.
3. Through how many states of India does the Tropic of Cancer pass?
The Tropic of Cancer passes through eight Indian states – Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram.
4. What is the total area and land boundary of India?
The total area of India is about 32,87,263 square kilometres, making it the seventh-largest country in the world. India’s land boundary is about 15,200 kilometres long and it shares borders with seven neighbouring countries.
5. How does India’s maritime location help in trade?
India’s central position in the Indian Ocean makes it a natural hub for international sea trade. Important ports like Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kochi and Kandla connect India with Asia, Africa and Europe. This location supports exports, imports, fisheries and the blue economy.
6. On which longitude is Indian Standard Time (IST) based?
Indian Standard Time (IST) is based on the longitude 82°30′ East. This standard meridian helps maintain a uniform time across the whole country.
The Border of India (Boundary of India)
India is a vast and diverse country whose borders are extremely important from geographical, cultural, historical, and strategic points of view. India’s boundary is connected to both land and sea, linking the country with South Asia, Central Asia, Southeast Asia, and major global trade routes.
While studying India’s boundaries, I realised how borders are not just lines on a map, but living spaces where cultures meet, trade flows, and security challenges emerge. For a broader understanding, you may also read my article on Location and Extent of India .
Expansion of India’s Borders
Total Area of India
The total area of India is approximately 32,87,263 square kilometres, making it the seventh-largest country in the world.
Geographical Extent
India extends from 8°4′ North latitude to 37°6′ North latitude and from 68°7′ East longitude to 97°25′ East longitude.
Total Length of India’s Borders
- Total land border length: approximately 15,200 kilometres.
- Total maritime border length: approximately 7,516.6 kilometres.
International Borders of India
India shares its international land borders with seven countries. Each border has its own geographical, political, and cultural significance.
1. India–Pakistan Border
- Border length: approximately 3,323 kilometres.
- Location: North-western India.
- Indian states sharing the border: Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat.
- Important boundary line: The Radcliffe Line, drawn in 1947 during the partition of India and Pakistan.
2. India–China Border
- Border length: approximately 3,488 kilometres.
- Location: Northern India, passing through the Himalayan mountain range.
- Indian regions sharing the border: Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh.
Important Border Disputes
- Aksai Chin and parts of Arunachal Pradesh are disputed territories.
- The India–China war of 1962 was fought over these regions.
3. India–Nepal Border
- Border length: approximately 1,751 kilometres.
- Location: Northern India.
- Indian states sharing the border: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal, Sikkim.
- India and Nepal share close cultural and social ties, often described as a “Roti and Beti” relationship.
4. India–Bhutan Border
- Border length: approximately 699 kilometres.
- Location: North-eastern India.
- Indian states sharing the border: Sikkim, West Bengal, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam.
5. India–Bangladesh Border
- Border length: approximately 4,096 kilometres.
- Location: Eastern India. This is India’s longest international land border.
- Indian states sharing the border: West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram.
Important Feature
In 2015, India and Bangladesh signed the Land Boundary Agreement, which successfully resolved long-standing border disputes.
6. India–Myanmar Border
- Border length: approximately 1,643 kilometres.
- Location: Eastern India.
- Indian states sharing the border: Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland.
7. India–Afghanistan Border
- Border length: approximately 106 kilometres.
- This border lies in the region of Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (POK).
- It is associated with the Durand Line.
Maritime Boundary of India
India also has an extensive maritime boundary, connecting it to major oceans and global sea routes.
Seas and Ocean Surrounding India
- West: Arabian Sea
- South: Indian Ocean
- East: Bay of Bengal
Island Groups Forming Maritime Boundaries
- Lakshadweep Islands: Located in the Arabian Sea.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Located between the Indian Ocean and the Bay of Bengal.

Best Quality Smart Product
Trusted Amazon product with excellent performance and long-lasting durability. Perfect for daily use.
Buy on AmazonNatural Boundaries of India
Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayas form a strong natural boundary between India and China, Nepal, and Bhutan.
River Boundaries
Rivers such as the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Sutlej flow along or near the borders of several neighbouring countries.
Thar Desert
In the west, the Thar Desert forms a natural division between India and Pakistan.
Geographical and Strategic Importance of India’s Borders
Cultural and Economic Exchange
India’s borders act as gateways for cultural interaction and economic exchange with neighbouring countries.
Security Importance
Many border areas are strategically sensitive. The Border Security Force (BSF) and the Indian Army play a crucial role in protecting India’s borders.
Trade and Transportation
Both land and sea borders are essential for international trade, transport, and connectivity.
Conclusion
India’s borders connect the country with a wide range of natural landscapes, cultures, and nations. From the Himalayas in the north to the seas in the south, India’s boundaries are vital for its security, trade, cultural exchange, and global relations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Boundary of India
1. How many countries share land borders with India?
India shares its land borders with seven countries: Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
2. Which country shares the longest border with India?
Bangladesh shares the longest international land border with India, with a length of about 4,096 kilometres.
3. What is the total length of India’s maritime border?
India’s maritime border is approximately 7,516.6 kilometres long, including island territories.
4. Why are the Himalayas important for India’s borders?
The Himalayas act as a natural protective wall, separating India from several northern countries and influencing climate and defence.
5. What was the Radcliffe Line?
The Radcliffe Line was drawn in 1947 to demarcate the borders between India and Pakistan during partition.
Total Area of India
The total area of India is approximately 32,87,263 square kilometres. This vast geographical size makes India the seventh-largest country in the world by area. While studying India’s size, it becomes clear how its large extent contributes to its diversity in landforms, climate, vegetation and cultures.
Geographical Extent of India
Latitudinal Extent
India stretches from 8°4′ North latitude to 37°6′ North latitude. This wide latitudinal range is one of the main reasons for the country’s varied climate, from tropical conditions in the south to temperate regions in the north.
Longitudinal Extent
The longitudinal extent of India lies between 68°7′ East longitude and 97°25′ East longitude. This east–west spread influences sunrise and sunset timings across different parts of the country.
Physical Dimensions of India
Distance from North to South
The approximate length of India from north to south is 3,214 kilometres.
Distance from East to West
The approximate width of India from east to west is 2,933 kilometres.
India’s Global Position by Area
India occupies about 2.4% of the total land area of the Earth. In terms of area, India ranks after the following countries:
- Russia
- Canada
- China
- United States of America
- Brazil
- Australia
This ranking highlights India’s importance as one of the world’s largest nations.
Area Distribution among States and Union Territories
Largest State of India
Rajasthan is the largest state in India by area. It covers about 10.4% of India’s total area, which is approximately 3,42,239 square kilometres.
Smallest State of India
Goa is the smallest state of India by area. It accounts for nearly 0.11% of the total area, with about 3,702 square kilometres.
Largest Union Territory
Ladakh is the largest union territory of India by area, contributing a major share of the total area among union territories.

Top Rated Amazon Product
High performance, durable and trusted by customers. Ideal choice for quality lovers.
Buy on AmazonSmallest Union Territory
Lakshadweep is the smallest union territory of India, with an area of only 32 square kilometres.
Land and Maritime Boundaries
Terrestrial (Land) Boundary
India has a land boundary of approximately 15,200 kilometres, connecting it with several neighbouring countries.
Maritime Boundary
India’s maritime boundary is about 7,516.6 kilometres long. This includes the coastline of the mainland as well as island territories such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.
Conclusion
India’s vast area makes it a country rich in geographical diversity, climatic variation and natural resources. Its large size, combined with a strategic location and regional variety, gives India a unique place on the global map and plays a crucial role in its economic, cultural and environmental significance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Total Area of India
1. What is the total area of India?
The total area of India is approximately 32,87,263 square kilometres.
2. What is India’s rank in the world by area?
India is the seventh-largest country in the world in terms of total area.
3. Which is the largest state in India by area?
Rajasthan is the largest state in India by area.
4. Which is the smallest union territory of India?
Lakshadweep is the smallest union territory, with an area of only 32 square kilometres.
5. How much of the Earth’s land area does India cover?
India covers about 2.4% of the total land area of the Earth.
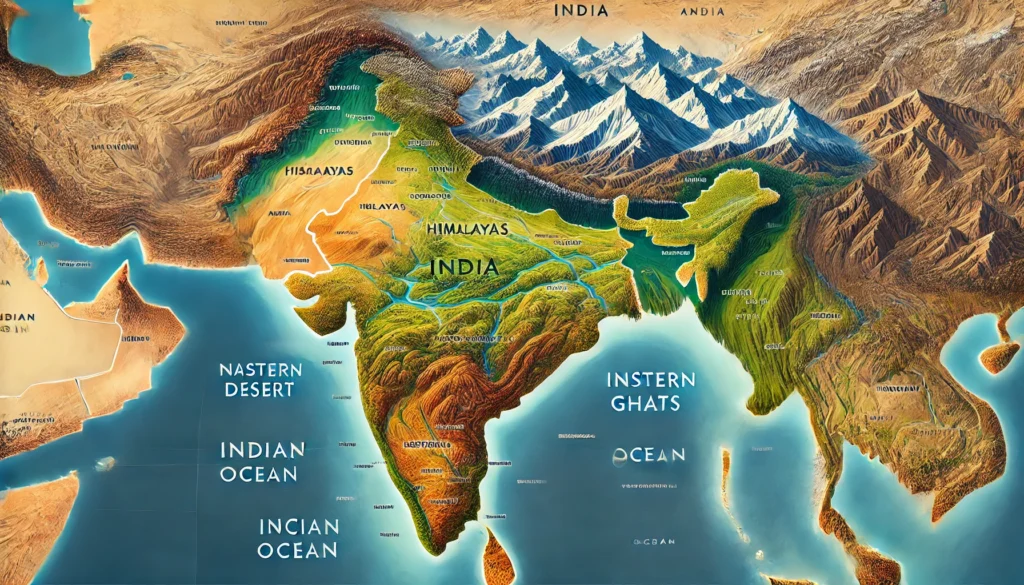
Natural Boundaries of India
India’s natural boundaries separate it from neighbouring countries and deeply influence its geography, climate, security and culture. These boundaries are formed by natural elements such as mountains, rivers, deserts and seas, which together shape India’s physical and human landscape.
1. Mountain Boundaries
The Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayan mountain range forms the most prominent natural boundary of India.
Location
The Himalayas separate India from China, Nepal and Bhutan.
Importance
- The Himalayas act as a natural wall that blocks cold northern winds.
- They are the source of major rivers such as the Ganga, Yamuna and Brahmaputra.
Main Himalayan Ranges
- Karakoram Range – located in Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Ladakh Range, Zaskar Range and Sivalik Hills.
Strategic Importance
The Himalayan ranges ensure natural security along the India–China and India–Nepal borders.
2. River Boundaries
Several international boundaries of India are also marked by rivers.
Indus River System
- Flows towards Pakistan.
- Main rivers include Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej.
Ganga River System
- Plays an important role along the borders with Nepal and Bangladesh.
- Tributaries like Kosi and Gandak demarcate the India–Nepal border.
Brahmaputra River
- Flows through Arunachal Pradesh and Assam before entering Bangladesh.
- Forms a natural division along parts of the India–Bangladesh border.
3. Desert Boundaries
Thar Desert
Location
The Thar Desert lies in the western part of India and forms a natural boundary with Pakistan.
States Covered
Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana and Punjab.
Importance
Due to low population density, this desert region holds significant strategic importance.
4. Maritime Boundaries
India is surrounded by sea on three sides, making it a peninsular country.
- West: Arabian Sea
- South: Indian Ocean
- East: Bay of Bengal
Role of the Sea
- Total maritime boundary length: 7,516.6 km.
- Crucial for trade, defence and economic development.
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep form an integral part of India’s maritime boundary.
5. Forests and Hilly Boundaries
Satpura and Vindhya Ranges
Located in central India, these ranges form a natural division between northern and southern India.
Eastern and Western Ghats
- Run parallel to India’s eastern and western coasts.
- The Western Ghats are globally famous for their biodiversity.
Shillong Plateau and Patkoi Hills
- Located in north-eastern India.
- Define the boundaries of Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Nagaland and Assam.
- The Patkoi Hills form part of the India–Myanmar border.
6. Effect on Climate and Vegetation
- The Himalayas block cold winds and support the monsoon system.
- Deserts and seas contribute to climatic diversity.
- Maritime boundaries support fisheries, trade and mineral resources.
Conclusion – Natural Boundaries of India
India’s natural boundaries are important not only geographically, but also strategically, economically and culturally. They ensure national security and strongly influence the country’s climate, environment and natural resources.
Features of India
India is an ancient and diverse country, renowned worldwide for its geography, culture, history and economic contributions. These features together make India a truly unique nation.
1. Geographical Features
Expansion
- Total area: 32,87,263 square kilometres.
- Seventh-largest country in the world by area.
- Surrounded by the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean on three sides.
Natural Diversity
India includes high mountains like the Himalayas, major rivers such as the Ganga–Yamuna system, the Thar Desert and tropical rainforests. World Heritage sites like the Western Ghats and the Sundarbans Delta are also located here.
Climate
India experiences a wide range of climates, from cold Himalayan regions to tropical areas. The monsoon plays a crucial role in agriculture and weather patterns.
2. Cultural Features
Cultural Diversity
India is home to multiple religions, languages, traditions and festivals. Major religions include Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism and Jainism. India is often called the “Land of Religions”.
Languages
- 22 official languages.
- More than 1,600 dialects.
- Hindi and English are the major official languages.
Festivals
India is known as the “Land of Festivals”. Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas and Guruparva are widely celebrated.
Arts and Crafts
India is famous for classical music, dances like Bharatanatyam, Kathak and Kathakali, and traditional crafts such as Banarasi sarees and Kashmir shawls.
3. Historical Features
Ancient Civilization
India is one of the world’s oldest civilizations, with the Indus Valley Civilization, Maurya Empire and Gupta Empire.
Religious Centres
India is the birthplace of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism. Cities like Varanasi, Ayodhya, Haridwar and Bodh Gaya are spiritually significant.
Heritage Sites
The Taj Mahal, Khajuraho Temples, Qutub Minar and Ajanta–Ellora Caves are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
4. Economic Features
Agriculture-Based Economy
About 60% of India’s population depends on agriculture. Major crops include rice, wheat, sugarcane, tea and spices.
Industrial Development
India is a global leader in IT services and the pharmaceutical industry. Steel, automobile and textile industries are also important.
International Trade
Ports such as Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata are major centres of international trade. India is a leading exporter of spices, textiles and gems.
5. Social Features
Democracy
India is the largest democratic country in the world, with a parliamentary system and a written constitution.
Population
With a population of around 1.4 billion, India is the most populous country in the world.
Education and Science
Institutions like IITs, IIMs and ISRO are globally recognised. India has made remarkable progress in space science, IT and medicine.
Family Values
Joint family traditions and collective social values remain strong in Indian society.

Premium Quality Amazon Product
Highly rated product with excellent quality, durability and trusted customer satisfaction.
Buy on Amazon6. Strategic and Geographical Location
India is located in southern Asia and is surrounded by three oceans. Its position makes it a central link in trade routes between Asia, Africa and Europe.
7. Environmental and Biodiversity Features
Biodiversity
India hosts about 8% of the world’s species, including the Bengal tiger, Indian peacock and Ganges river dolphin.
National Parks and Sanctuaries
India has more than 100 national parks and over 500 wildlife sanctuaries. Kaziranga, Ranthambore and Sundarbans are among the most famous.
Conclusion – Features of India
The diverse features of India make it a unique nation. From ancient civilisation and cultural richness to rapid progress in science, technology and economy, India holds a significant and respected position on the global stage.
References
- NCERT, India – Physical Environment, Class IX & X, National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), New Delhi.
- NCERT, Contemporary India, Class IX, National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), New Delhi.
- Government of India, Official Portal of India, Geography and Administrative Information Section.
- Survey of India, Maps and Geographical Data of India, Government of India.
- World Atlas and standard geography reference books related to India’s natural boundaries and physical features.
- UNESCO and UNICEF educational resources on India’s natural heritage and cultural diversity.