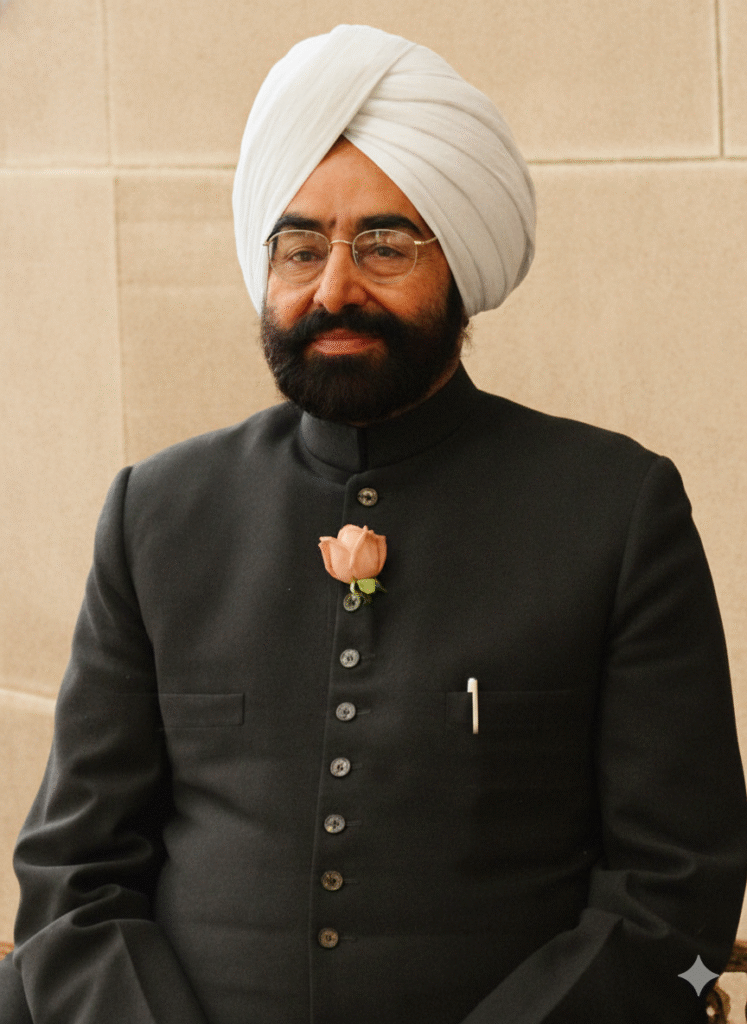
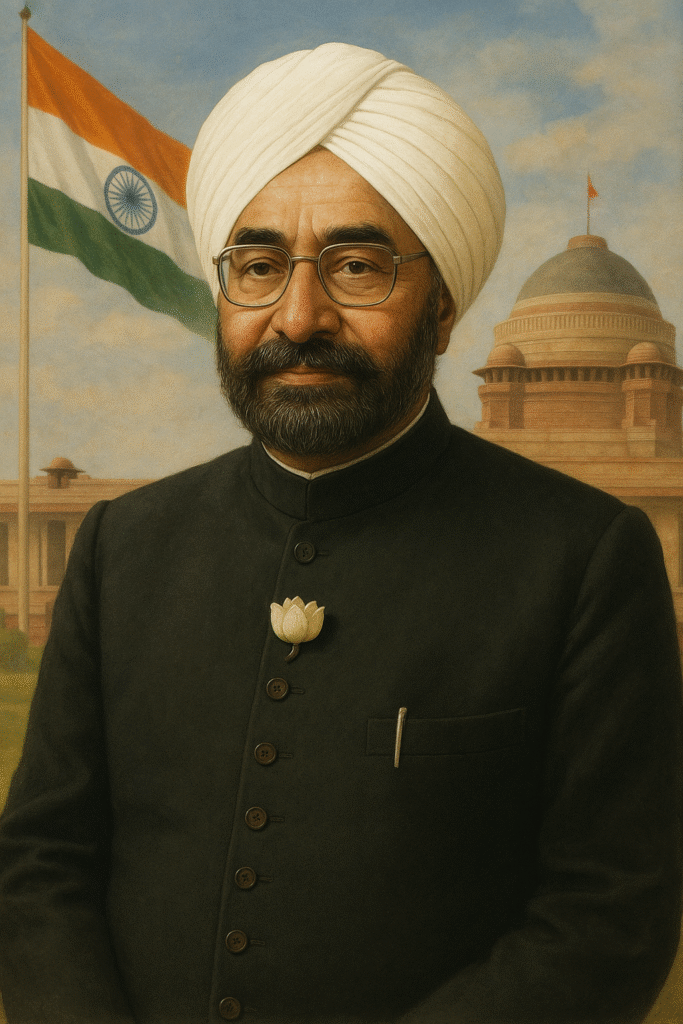
Biography of Giani Zail Singh
Introduction
Giani Zail Singh was the seventh President of India. He was the first Sikh to adorn the post of President of India. His life is a symbol of a true patriot, hardworking leader and social worker.
Birth and Early Life
Basic Details
- Birth: 5 May 1916
- Place: Sandhwan village, Faridkot, Punjab (British India)
- Full Name: Giani Zail Singh
- Father's Name: Kishan Singh
- Religion: Sikh

Recommended Product on Amazon
High-quality product with excellent reviews. Trusted by users and available at the best price on Amazon.
👉 Buy on AmazonGiani Zail Singh was religious since childhood. He studied Gurmukhi and Sikh scriptures deeply, due to which he received the title of “Giani”.
Education
Giani Zail Singh had limited formal education, but he developed deep religious and social understanding through self-study. He took religious education and gave kirtan and sermons in gurudwaras.
Political Career
Participation in Freedom Struggle
- Zail Singh took part in the movement against British rule and went to jail several times.
- He was also associated with the “Praja Mandal Movement”, which fought for democratic rights in the princely states.
State-Level Politics
- Joined the Congress Party in 1949.
- Became a member of the Punjab Legislative Assembly in 1956.
He launched many schemes for social reforms, Dalits and backward classes in Punjab.
Chief Minister of Punjab
- He was the Chief Minister of Punjab (1972–1977).
He initiated reforms in education, agriculture and the industrial sector.
Union Minister
- He became the Home Minister in Indira Gandhi's government in 1980.
President of India (1982–1987)
Tenure
- 25 July 1982 – 25 July 1987
Important Achievements
- He became the first Sikh President of India.
- While serving as President, he expressed his independent opinion many times to protect secularism and democracy.
1984 Riots and Operation Bluestar
- The anti-Sikh riots that followed Operation Bluestar and the assassination of Indira Gandhi in 1984 affected him deeply.
- He publicly expressed grief and concern over these events.
Death
- Death: 25 December 1994
- Cause: Due to serious injuries sustained in a car accident
Honors and Memory
- He was posthumously awarded the Padma Vibhushan by the Government of India in 1995.
- Many places and institutions have been named after him in his honour.
Conclusion
Gyani Zail Singh was a leader who placed secularism, honesty and public service above all else in Indian politics. His life is an inspiring example of patriotism, service and struggle.
Giani Zail Singh: Introduction
Giani Zail Singh was a prominent political leader of India and the seventh President of the country, who adorned this highest constitutional post from 1982 to 1987. He was the first Sikh President of India and his life was a symbol of national service, simplicity and integrity. He has made a deep contribution to Sikhism, Indian culture and politics.
Before joining politics, he received religious education and earned popularity among the people through social service. He also participated in the freedom struggle and after independence, joined the Congress Party and played an important role in Punjab politics.
Giani Zail Singh served the country as the Chief Minister of Punjab, Union Home Minister, and then President. Many historic events took place during his tenure, such as Operation Bluestar and the assassination of Indira Gandhi. Even in these difficult times, he protected constitutional values and national unity.
His life was dedicated to India’s democracy, secularism and social harmony.
Giani Zail Singh: Birth and Early Life
Giani Zail Singh was born on 5 May 1916 in Sandhwan village, Faridkot district, Punjab (then British India). His real name was Jarnail Singh. His father’s name was Kishan Singh, who was a simple farmer. He belonged to a Sikh family and adopted a religious and simple lifestyle since childhood.
From childhood, he was inclined towards Sikh scriptures and religious thoughts. He studied in traditional schools as well as studied Gurumukhi and Sikh history in depth. Due to his deep interest and scholarship in religious education, he was given the title of “Gyani”, which later became a part of his name.
Although his formal education was limited, he made his mark among the people through self-study and religious preaching. He often used to do kirtan and discourses in gurdwaras, which made him popular in the society. This is where the foundation of his social life and entry into politics was laid.
Giani Zail Singh’s early life was full of struggle, but his religious upbringing, honesty, and spirit of service led him to become a mass leader.
Giani Zail Singh: Education
Giani Zail Singh’s formal education was limited, as his childhood was spent in a rural environment during British rule, where facilities for higher education were very limited. However, he received his early education from the local school, where he studied Gurmukhi, Punjabi, and religious scriptures.
His main focus of studies was Sikhism, Gurbani, and Sikh history. He studied Sri Guru Granth Sahib and other religious books in depth since childhood. It was this religious knowledge and spiritual understanding that earned him the title of “Gyani”, which later became a permanent part of his name.
Although he did not receive a higher degree from any university, his religious, cultural and social knowledge was very deep. He did not limit education to bookish knowledge, but adopted it as a practice and service. He was self-educated, intelligent and an impressive speaker, who used education as a tool in his life – to serve and improve society.
This characteristic of his connected him with the common people and established him as a popular leader.
Giani Zail Singh: Political Career
Giani Zail Singh’s political career began during the Indian freedom struggle and led him to the highest constitutional post of India – the President. His entire political journey was based on patriotism, public service and truth.
Participation in the Freedom Struggle
- Giani Zail Singh raised his voice against the British rule in his youth.
- He joined the Praja Mandal movement, which was being run to demand democratic rights in the princely states.
- He also went to jail several times for participating in this movement.
Entry into the Congress Party
- In the year 1949, he joined the Indian National Congress.
- He worked for the welfare of rural areas, especially Dalits, backward and farmers.
- His popularity and organization ability took him to great heights.
Punjab Legislative Assembly Member and Minister
- Elected as a member of the Punjab Legislative Assembly for the first time in 1956.
- He then became a Minister of State and held the responsibility of several important departments, such as:
- Public Works Department
- Health Department
- Agriculture Department

Top Rated Amazon Product
Trusted and popular product with strong customer reviews. Available at the best price on Amazon.
👉 Check Price on AmazonChief Minister of Punjab (1972–1977)
- Gyani Zail Singh became the Chief Minister of Punjab in 1972.
- During his tenure, he:
- Promoted rural development
- Expanded education and health services
- Introduced welfare schemes for scheduled castes and backward classes
Union Home Minister (1980–1982)
- In 1980, Indira Gandhi appointed him as the Home Minister in her government.
- While in this position, he:
- Played an important role in maintaining internal security, law and order, and communal harmony in the country.
- Paid special attention to the rehabilitation of displaced Sikh families after Partition.
President of India (1982–1987)
- In 1982, Giani Zail Singh was elected the seventh President of India.
- He became the first Sikh President of India.
- Many serious incidents took place during his tenure:
- Operation Bluestar (1984)
- Assassination of Indira Gandhi
- Anti-Sikh riots
- In these difficult times, he acted with restraint while protecting the Constitution and secularism.
Characteristics of Political Life
- He was a leader of the masses – had direct communication with the common people.
- He considered politics a means of service, not a means of power.
- He always gave priority to secularism, dignity of the Constitution, and democratic values.
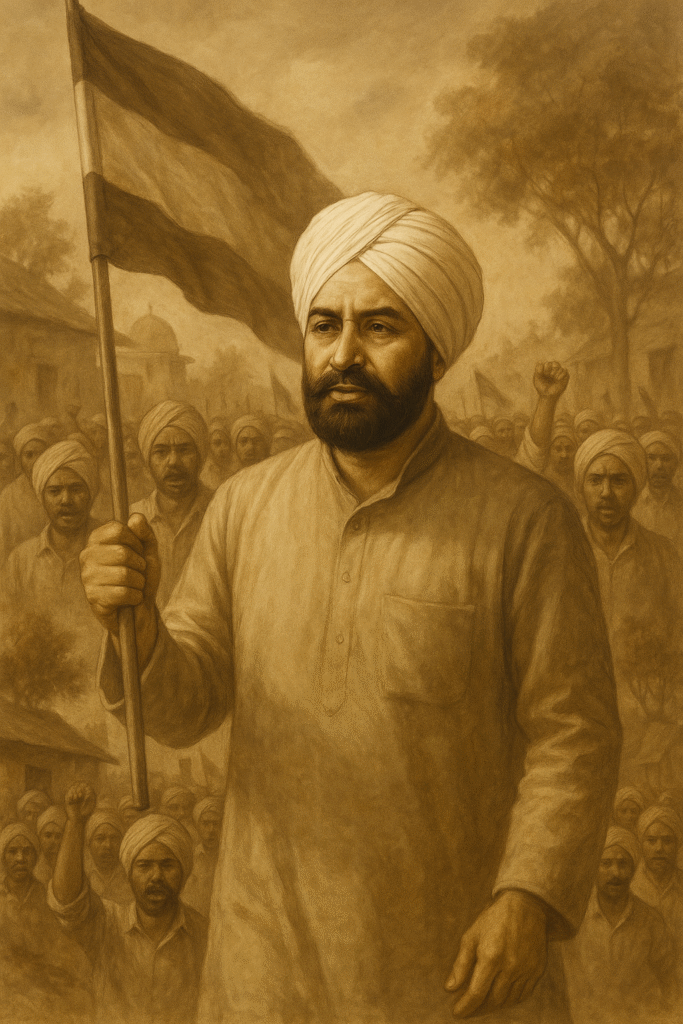

Giani Zail Singh: Participation In The Freedom Struggle
Giani Zail Singh played an active role in India’s freedom struggle, especially in the movements launched in the princely states of Punjab against British rule. His contribution was particularly visible through the Praja Mandal movement, which was launched to demand democratic rights and public participation in the princely states.
Participation in Praja Mandal Movement
- At that time, many parts of Punjab were not independent, but they were princely states of kings and nawabs.
- Giani Zail Singh led a movement demanding democratic reforms in these monarchical regimes.
- He was a pioneer in making the public aware, opposing princely atrocities and raising his voice against the princely states which became puppets of the British Empire.
Imprisonment and Struggle
- Due to his views and movements, he was also sent to jail several times by the British government.
- He continued the struggle in non-violent ways even while suffering atrocities.
- His struggle was mainly for social justice, religious freedom and Indian unity.
Participation in Mass Movement
- He went from village to village and organized people and explained the importance of independence.
- He was inspired by the principles of Mahatma Gandhi and Congress, and worked to instill enthusiasm in the public against the British rule.
Conclusion
Gyani Zail Singh may not have been publicized as a great freedom fighter, but his contribution to the struggle against the princely states at the local level, public awakening, and establishment of democracy was important and inspiring. This experience of his later helped him to become a responsible and sensitive politician.
Giani Zail Singh: State Level Politics

Best Selling Amazon Product
Popular and reliable product with strong customer trust. Available now with fast delivery on Amazon.
👉 View on AmazonAfter active participation in the freedom struggle, Giani Zail Singh entered the politics of Punjab after independence. He gradually emerged as a popular leader and became the Chief Minister of Punjab, serving in many important positions in state politics.
Entry into Punjab Assembly
- After independence, Giani Zail Singh formally started his political career by joining the Indian National Congress.
- He won the election for the first time as a member of the Punjab Legislative Assembly in the year 1956.
- As an MLA, he paid special attention to public welfare, rural development and social equality.
Work as a Minister of State
- In the 1950s and 60s, he was a minister in various ministries in the Punjab government.
- He handled departments like Public Works Department, Health, Agriculture, and Social Welfare.
- During this time he worked on the development of roads, health facilities and irrigation system in rural areas.
Efforts for Dalits and Backward Classes
- Gyani Zail Singh’s entire political life was dedicated to the upliftment of Dalits, backward classes and poor farmers.
- He tried to bring these classes into the mainstream in the field of reservation, employment and education.
Chief Minister of Punjab (1972–1977)
- Gyani Zail Singh was appointed Chief Minister of Punjab in 1972.
Main Features of His Tenure
- Development in agriculture sector: Adopted new technologies and schemes to advance the Green Revolution.
- Industrialization: Implemented favorable policies for setting up industries in the state.
- Education and Health: Established schools, colleges and health centers in rural areas.
- Social Harmony: Tried to maintain communal harmony and take all sections along.
Conclusion
Gyani Zail Singh was recognized as a strong, down-to-earth and public-spirited leader in state politics. He served the people not only from an administrative point of view but also with human sensibilities. Due to his work and image, he started playing a prominent role in national politics as well, which later resulted in him becoming the Home Minister of India and then the President.
Giani Zail Singh: Chief Minister Post (1972 – 1977)
Giani Zail Singh’s tenure as the Chief Minister of Punjab was an important and influential chapter in his political life. He became the Chief Minister of Punjab on 17 March 1972 and served in this post for about 5 years. His leadership was a concrete effort towards social justice, development and harmony.
Background of Becoming Chief Minister
- In 1972, the Congress Party got a majority in the Punjab Assembly elections.
- Giani Zail Singh was elected to the post of Chief Minister on the basis of his organization ability, popularity and strong leadership.
- He was considered a strong supporter of Dalits, backward classes and farmers.
Major Works and Achievements as Chief Minister
Rural Development and Agricultural Reform
- He ensured better facilities of roads, electricity and irrigation in the rural areas of Punjab.
- The availability of seeds, fertilizers and agricultural equipment to farmers was made easy.
- The state government’s schemes played an important role in making the Green Revolution successful.
Improvement in the Field of Education and Health
- New schools, colleges and technical institutes were opened during his tenure.
- Health services were made accessible by setting up primary health centers in rural areas.
- Special assistance was given to children of scheduled castes and poor families for education.
Social Harmony and Dalit Upliftment
- He implemented many schemes for the Dalit society such as:
- Free housing scheme
- Scholarship scheme
- Effective implementation of reservation in government jobs
- His administration constantly strived to maintain ethnic and religious harmony.
Industry and Employment
- Industrial policies were formulated to encourage small and medium industries.
- Job fairs and technical training programs were started for the youth.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Separatism was emerging in some areas of Punjab, which the government faced challenges in controlling.
- The opposition also criticized the government over allegations of corruption.
- Governance became difficult due to political instability and pressure from opposing groups.
Conclusion
Gyani Zail Singh’s tenure as Chief Minister was development-oriented, public welfare and social justice based. He created his image as a leader who could become the voice of the people of the lower class. His work style took him to greater heights in national politics, which resulted in him becoming the Home Minister of India and later the President.
Giani Zail Singh: Tenure as Union Minister (1980 – 1982)
After a successful tenure as the Chief Minister of Punjab, Giani Zail Singh got the opportunity to reach heights in national politics. When Indira Gandhi returned to power once again in 1980, she expressed confidence in Giani Zail Singh and appointed him as the Home Minister of the Government of India.
Background of Becoming Home Minister
- The Congress Party won a big victory in the 1980 general elections.
- Indira Gandhi included experienced and reliable leaders in her cabinet, in which Giani Zail Singh’s name was prominent.
- He was appointed the Union Home Minister of India on 18 January 1980.

Highly Recommended Amazon Product
Quality product with positive customer feedback. Check availability and latest offers on Amazon.
👉 Check Price on AmazonMajor Works and Achievements as Home Minister
National Security and Internal Peace
- He made many efforts to strengthen the internal security, communal harmony, and law and order of the country.
- Extremism and separatist activities were increasing in India at that time, especially in the northeastern states and Punjab.
- Gyani Ji strengthened coordination between the central and state governments to establish peace in these areas.
Maintaining Law and Order
- As Home Minister, he emphasized on police reforms.
- Started the process of equipping the central paramilitary forces with modern technology and training.
- Special strategies were made to deal with riots and terrorist incidents.
Security of Weaker Sections of Society
- Priority was given to protecting the rights of Dalits, minorities and backward classes.
- He laid special emphasis on maintaining religious freedom and communal harmony.
Administrative Efficiency
- His administrative style was firm but democratic.
- He used to communicate directly with the officers and showed efficiency in decision making.
Challenges
- Sikh fundamentalism and separatism were gradually increasing in Punjab, which he took seriously.
- It was a big challenge to deal with communal tension and Naxalite activities in many places in the country.
- During the Home Ministry, he had to take decisions on many sensitive issues which had a profound impact on future politics.
Conclusion
Gyani Zail Singh showed firm, sensitive and patriotic leadership as Home Minister. He gave priority to the internal security and social unity of the country and made a mark as a visionary politician. Seeing his work and dedication, the Congress leadership appointed him as the President of India in the year 1982.

Giani Zail Singh: President of India (1982 – 1987)
Giani Zail Singh was the seventh President of India and held the highest constitutional post from 1982 to 1987. He was the first Sikh President of India. His presidential tenure came at a very important and sensitive time, when the country was going through many social, political and communal crises.
Assumption of President
- Giani Zail Singh became the President of India on 25 July 1982.
- He pledged to protect the Constitution and maintain the unity and integrity of all Indians.
Major Events and Works as President
Protecting the Constitution and Supporting Democracy
- Giani Zail Singh always protected constitutional values as President.
- He supported the dignity of democracy, secularism, and independence of the judiciary.
Operation Bluestar (1984)
- In 1984, the government launched Operation Bluestar to put an end to terrorism and separatist activities in the Golden Temple of Amritsar, Punjab.
- During this operation, many Sikh devotees were killed, leading to tension across the country.
- Giani Zail Singh attempted to maintain restraint and peace within constitutional limits.
Assassination of Indira Gandhi and Subsequent Riots (1984)
- On 31 October 1984, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated by her Sikh security guards.
- After this, riots broke out against Sikhs across the country, especially in Delhi.
- As President, Giani Zail Singh attempted to establish peace and ensure the safety of the affected.
National Integration and Communal Harmony
- He appealed on several occasions to promote communal harmony and ethnic harmony in the country.
- Encouraged dialogue between various social and political parties to maintain national unity.
His Personality and Approach as President
- Giani Zail Singh’s personality was simple, humble and sensitive.
- He was a hardworking, disciplined and loyal person to the Constitution.
- His communication style was not only peaceful but also inspiring.
Conclusion
Giani Zail Singh’s presidential tenure came at a complex and challenging period in Indian history. He played an important role in maintaining the unity and integrity of the country while respecting constitutional dignity. His life and tenure are still a source of inspiration for Indian politics and society.
1984 Riots and Operation Bluestar
During Giani Zail Singh’s presidential tenure (1982-1987), India faced two major and sensitive incidents: Operation Bluestar and the 1984 anti-Sikh riots.
Operation Bluestar (June 1984)
Background
- Sikh separatist and terrorist activities began to increase in Punjab in the 1980s.
- Their center was the Golden Temple, which is the holiest religious place of the Sikhs.
- Some extremist terrorists were hiding inside there, whose armed activities were deteriorating the law and order in the state.
Operation Bluestar
- In June 1984, the central government launched a military operation to flush out the terrorists hiding in the Golden Temple.
- This operation took place under the leadership of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi and its aim was to remove armed terrorists from the religious place.
- The operation involved heavy firing and clashes, causing extensive damage to the Golden Temple and killing many people, including devotees.
Role of Giani Zail Singh
- As President, he supported the actions of the Central Government while staying within constitutional limits.
- At the same time, he urged to maintain peace and law and order in the country.
Anti-Sikh Riots of 1984
Background
- On 31 October 1984, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated by her two Sikh security guards.
- After this, fierce riots broke out against Sikhs across the country, especially in Delhi.
Effect of the Riots
- Thousands of Sikhs were killed, millions of families were affected.
- Deep resentment and pain spread among the Sikh community.
- There was a major impact on the social and political unity of the country.
Role of Giani Zail Singh
- Being a Sikh, this period was very sensitive and difficult for Giani Zail Singh.
- He made continuous efforts to maintain peace and law and order.
- During the riots, he kept trying to maintain a balance between the government and the public while following constitutional obligations.
Conclusion
Operation Bluestar and the 1984 riots are such dark chapters in the history of India which had a long-term impact on the country’s politics and society. Giani Zail Singh discharged the post of President by following restraint, sensitivity and constitutional decorum in these difficult circumstances. His efforts were aimed at maintaining peace and unity in the country, although the circumstances were very complex.
Death of Giani Zail Singh
Giani Zail Singh died on 3 December 1994. He was remembered as a distinguished and respected politician of India at that time. With his demise, Indian politics and society lost an experienced, sensitive and public-spirited leader.
Post-Death Highlights
- A large number of people attended his funeral, which reflected the deep respect of the public towards him.
Giani Zail Singh’s political and social service will always be remembered, especially his contribution to the upliftment of Dalits and backward classes in Punjab and all over India.
He became immortal in history as a true nationalist and constitution-loving leader.
Giani Zail Singh: Honour and Memory
The life and work of Giani Zail Singh is remembered as an important legacy in Indian politics and society. His service, leadership and struggle were honored in many ways and his memory was cherished.
Honors
Honor of Holding the Post of President of India
- He was the first Sikh and Dalit leader of India to get the honor of the highest constitutional post of the country.
- His taking over the presidency is considered a symbol of equality and inclusiveness in society.
Recognition at State and National Level
- Many felicitation ceremonies were organized for his contribution.
- He was remembered as an inspirational leader in the field of social justice and democracy by the Government of Punjab and the Government of India.
Honor Awards and Memorials
- Many institutions, roads and memorials have been built in his name.
- Institutions working for social justice and Dalit upliftment carry forward his ideals.
Memory
Memorials and Places
- Various memorials and public places have been established in Punjab in the name of Giani Zail Singh.
- Through these, his political journey and social contribution are remembered.
Literature and Research
- Many books and research work have been done on his life.
- His contribution is considered an important chapter in the study of Indian history and politics.
Social Programs and Annual Remembrance
- Many social and political organizations organize programs on his death anniversary.
- The story of his ideology and struggle inspires the new generation.
Conclusion
Giani Zail Singh is named among those leaders of India who made tireless efforts to protect the rights of the weaker sections of the society, empowerment of democracy, and national unity. His memory still shines like a guiding light in the struggle for social justice and equality.
Conclusion
Giani Zail Singh is remembered as a leader who upheld the dignity of the Constitution, protected democratic values, and worked tirelessly for social justice. His contribution to national unity, secularism, and the upliftment of the weaker sections of society continues to inspire future generations.

Popular Amazon Choice
Well-reviewed and trusted product preferred by many buyers. Check the latest price and offers on Amazon.
👉 View on AmazonReferences
- Books and biographies written on the life of Giani Zail Singh.
- Government records and archives related to the President of India.
- Historical documents on Indian politics and Punjab state politics.
- Newspaper reports and journals published during 1970–1990.
- Research papers and scholarly articles on Indian political history.


