
Detailed introduction of the Sultan of Deccan
The Deccan region has been an important landmass of the Indian subcontinent , extending over parts of present-day Maharashtra , Karnataka , Telangana , Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. This region was ruled by many powerful sultans , whose history is famous for culture , architecture , and administrative efficiency. The period of rule of the Deccan Sultans is mainly considered to be between the 14th and 17th centuries.
Rise of the Deccan Sultans
Independent states were formed in South India after the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate in the 14th century. The Bahmani Sultanate ( 1347-1527 ) was the first major Muslim empire in the Deccan. The sultanate came into existence as a result of the revolt against Muhammad bin Tughlaq. The Bahmani Sultanate established a strong base in the Deccan and its rulers made major contributions to the fields of art , music , and architecture.
Disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate and the formation of five independent Sultanates
After the disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate in the 16th century, five independent sultanates were formed in the Deccan , which were called Deccani Sultanates It is said that these five sultanates were:
- Bidar Sultanate
- Bijapur Sultanate
- Golconda Sultanate
- Ahmednagar Sultanate
- Berar Sultanate
These sultanates established power in their respective regions and engaged in wars , alliances and competition with each other.
Cultural Achievements of the Deccan Sultans
The Deccan sultans developed a unique cultural and architectural heritage in the region.
- Architecture : Gol Gumbaz of Bijapur , Golconda Fort , and Ahmednagar Fort are excellent examples of their architecture.
- Art and Music : The Deccan sultans encouraged the integration of Persian and Deccani culture. Deccani Urdu developed during the reign of these sultans.
- Literature : Literature in Persian , Urdu , and Telugu languages was encouraged in the courts of the Deccan.
Major Sultans and their Contributions
- Ali Adil Shah (Bijapur) : He promoted art and architecture.
- Qutb Shahi Rulers (Golconda) : They developed the diamond trade and strengthened the Golconda Fort.
- Nizam Shah (Ahmednagar) : He made Ahmednagar a cultural and commercial centre.
Fall of the Deccan Sultans
17th century, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb included all the sultanates of the Deccan in his empire. After this, the independent sultanates of the Deccan ceased to exist.
conclusion
The Deccan sultans have left a deep mark on Indian history and culture. Their statecraft , architecture , and cultural contributions still make us feel their greatness.
Detailed Introduction of The Sultan of Deccan

The history of the Deccan Sultans is an important chapter in the expansion of Islamic rule and the development of culture in the central and southern region of the Indian subcontinent. The Deccan region covers parts of Maharashtra , Karnataka , Telangana , Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in modern India. The sultans ruled from the 14th to the 17th centuries and enriched the region culturally , politically and economically.
Rise of the Deccan Sultans
Islamic rule in the Deccan began in the 14th century , when regional power centres began to emerge after the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate. The establishment of the Bahmani Sultanate in 1347 laid the foundation of a strong Islamic empire in the Deccan. Hasan Gangu Bahmani founded this sultanate and made Gulbarga (Kalburgi) its capital.
Growth and disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Sultanate remained the dominant power in the Deccan for about two centuries. Its administration and military system were considered excellent. But in the 16th century this Sultanate split into five independent states , which are called the Deccani Sultanates:
- Ahmednagar Sultanate (1490)
- Bijapur Sultanate (1490)
- Golconda Sultanate (1518)
- Bidar Sultanate (1528)
- Berar Sultanate (1490)
Cultural Achievements of the Deccan Sultans
The Sultans of Deccan made major contributions in the fields of architecture , music , literature and art.
- architecture :
- of Bijapur Gol Gumbaz : It is an example of amazing architecture.
- Charminar ( Golconda): Reflects the excellence of Qutub Shahi rulers.
- Golconda Fort : Its security system and grandeur are world famous.
- Literature and Language :
- Dakhni Urdu developed during the reign of these sultans.
- Persian , Arabic and Telugu literature received patronage.
- Music and art :
- The Deccani musical style was developed.
- Dancing and singing were encouraged in the courts.
Major Deccani Sultans and their Contributions
- Ibrahim Adil Shah II ( Bijapur) :
- He was a lover of art and music. He wrote “Kitab-e-Navras” , in which music and devotion were given importance.
- Qutub Shahi Rulers(Golconda) :
- These rulers encouraged the diamond trade.
- Nizam Shahi dynasty (Ahmednagar) :
- Made Ahmednagar a strong and cultural centre.
Fall of the Deccan Sultans
17th century, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb invaded the Deccan and annexed all these sultanates into his empire. Thus, the independent sultanates of the Deccan came to an end.
conclusion
Indian history. They not only ruled but also made unique contributions to art , culture and architecture. The monuments , forts and architecture built by them still bear testimony to their glorious past.
Rise of the Deccan Sultans

The rise of the Deccan Sultans is an important chapter in Indian history. It is associated with the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate in the 14th century and the emergence of regional powers in South India. Islamic rule in the Deccan region began with the formation of the Bahmani Sultanate , which created the first organized Muslim power in the region.
Formation of the Bahmani Sultanate ( 1347)
The rise of the Deccan Sultans begins with the Bahmani Sultanate. When the Tughlaq dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate weakened, rebellions began in the provinces of the Deccan.
- Hasan Gangu A soldier named Alauddin Bahman Shah , who later assumed the title of Alauddin Bahman Shah , founded the Bahmani Sultanate in 1347 .
- First capital of the Bahmani Sultanate Gulbarga ( Kalburgi) was created , which was later shifted to Bidar.
Features of the Bahmani Sultanate
- Creation of independent power : This Sultanate emerged as an independent power instead of remaining subordinate to the Delhi Sultanate.
- Administrative Efficiency : The Bahmani Sultans created a strong administrative system.
- Cultural Development : Persian and Deccani cultures assimilated during the Bahmani rule.
Disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate and the rise of the Deccani Sultanates
The Bahmani Sultanate began to break down in the 16th century due to internal conflicts and administrative weaknesses. This resulted in the emergence of five independent sultanates , known as the Sultans of Bahmani Sultanate. Deccani Sultanates It is said:
- Ahmednagar Sultanate (1490)
- Bijapur Sultanate (1490)
- Golconda Sultanate (1518)
- Bidar Sultanate (1528)
- Berar Sultanate (1490)
Mutual struggle and development of the Deccani Sultanates
On one hand these sultanates fought among themselves , but on the other hand they also became the reason for regional cultural and economic development.
- Bijapur and Golconda : Famous for their architectural and cultural contributions.
- Ahmednagar : Emerged as a military power and commercial centre.
Major Contributions of the Sultans of Deccan
- Deccani architecture , such as that of Bijapur Gol Gumbaz and Golconda’s Castle .
- Development of Dakhni Urdu in literature and music.
- Expansion of trade and economy in the Deccan region.
conclusion
The rise of the Deccan Sultans was not only a political change , but it also symbolized cultural and social development. The Bahmani Sultanate and the subsequent Deccan Sultanates gave a new dimension to Indian history and transformed the Deccan into a prosperous and multi-cultural region.
Disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate and the formation of five independent Sultanates
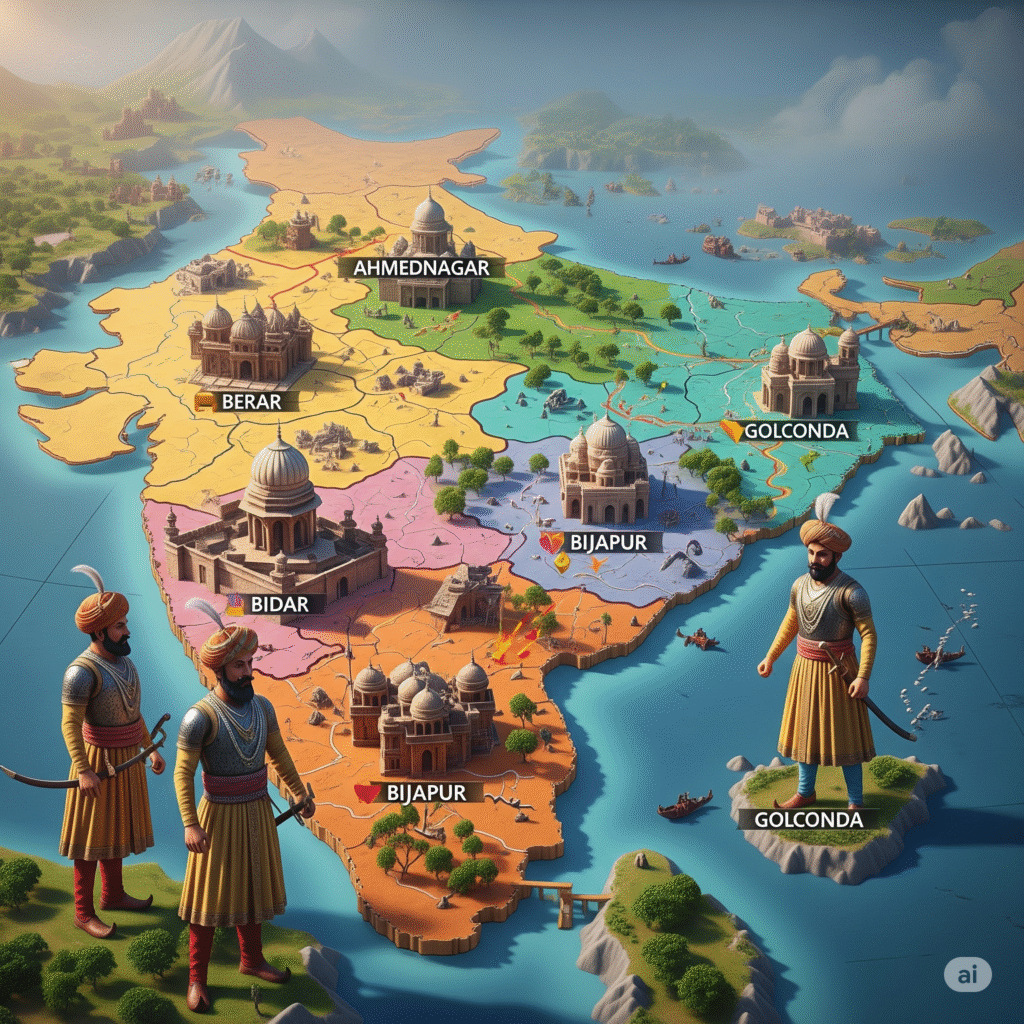

The Bahmani Sultanate , which was established in 1347 AD by Hasan Gangu Bahman Shah , was the first organized Muslim power in South India. This sultanate ruled the Deccan region for about two centuries. But in the early 16th century , the Bahmani Sultanate began to decline due to internal conflicts , power struggles and weak administration. As a result of this disintegration , five independent sultanates were formed in the Deccan region.
Disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate
- Internal conflict :
- The Bahmani Sultanate was a power struggle between Turkish , Persian , and Deccani elites.
- the ” Afaqi” (foreign) and “Deccani” (local) elites weakened the Sultanate.
- Political instability :
- Succession struggles among rulers and weak sultans weakened the administrative structure.
- The burden of an expansive empire :
- The inability to effectively govern such a large empire also led to the collapse.
- Shifting of capitals :
- Shifting the capital from Gulbarga to Bidar was also a sign of the weakness of the central power.
Formation of five independent sultanates
1500 AD, the Bahmani Sultanate split into small areas. This led to the rise of five independent sultanates in the Deccan region , which were called Deccani Sultanates It is said:
- Ahmednagar Sultanate (1490 AD)
- Founder: Malik Ahmad Nizam Shah.
- Capital: Ahmednagar.
- This Sultanate was famous for its military power and cultural richness.
- Bijapur Sultanate (1490 AD)
- Founder: Yusuf Adil Shah.
- Capital: Bijapur.
- Bijapur was famous for architecture , such as Gol Gumbaz , which is world famous.
- Golconda Sultanate (1518 AD)
- Founder: Qutub Shah.
- Capital: Golconda.
- This sultanate is known for diamond trade and architecture like Charminar.
- Bidar Sultanate (1528 AD)
- Founder: Qasim Bareed.
- Capital: Bidar.
- This sultanate was limited to a small area but was significant in cultural and literary contributions.
- Berar Sultanate (1490 AD)
- Founder: Fathullah Imad Shah.
- Capital: Achalpur.
- This Sultanate was considered the weakest and was soon annexed by other Sultanates.
Relations between these sultanates
- These sultanates were often in conflict with each other.
- Sometimes they formed alliances with each other , such as Battle of Talikota ( 1565 AD) , in which Bijapur , Golconda and Ahmednagar together defeated the Vijayanagara Empire.
Significance and impact
- These independent sultanates made the Deccan region culturally , politically and economically prosperous.
- Deccani architecture , literature and music developed during these sultanates.
- However , their internal conflicts helped the Mughals to conquer the Deccan.
conclusion
The disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate was a symbol of a major change in the political landscape of the Deccan region. The formation of five independent sultanates not only signalled the establishment of regional power centres , but also marked the beginning of a new phase of cultural and architectural development in the Deccan. But due to internal conflicts, these sultanates could not remain independent for long and eventually became part of the Mughal Empire.
Cultural Achievements of the Deccan Sultans

The Deccan Sultans not only established their political influence in Indian history but also contributed significantly to art , literature , music , architecture and cultural development. These Sultans made the Deccani region a centre of cultural prosperity. A unique synthesis of Persian , Turkish and local Indian traditions can be seen during their reign.
1. Architecture
The Deccan sultans built magnificent buildings , forts , tombs and mosques. Their architecture was a mixture of Indian and Islamic styles.
- Gol Gumbaz (Bijapur) :
- Built by the Sultans of Bijapur , it is one of the largest domes in the world.
- The sound resonance feature inside it makes it unique.
- Charminar (Golconda) :
- A contribution of the Qutb Shahi sultans , it is a fine example of Indian and Persian architecture.
- Golconda Fort (Golkonda) :
- This fort is famous for its strong security system and grandeur.
- Bidar Fort :
- It was built by the Bidar Sultans. It is a wonderful example of Deccani architecture.
2. Literature and language
The Sultans of Deccan gave great encouragement to literature. Persian and Deccani Urdu languages developed during their reign.
- Rise of Dakhni Urdu :
- This language was a mixture of Persian , Arabic , and local languages.
- Dakhni Urdu was used extensively in poetry and literature.
- Persian Literature :
- Persian literature found patronage in the courts of the Deccan.
- The poets and writers of the Sultans used to write compositions in Persian.
- Major literary works :
- Ibrahim Adil Shah II ( Bijapur) wrote an important work called “Kitab-i-Navras” , which describes music , devotion and love.
3. Music and dance
The Sultans of the Deccan also encouraged music and dance.
- Deccani style of music :
- The sultans developed a new style by mixing Indian and Islamic musical styles.
- Ibrahim Adil Shah II :
- He is considered a patron of music.
- He encouraged a style of music called “Navras” , which consisted of ragas of devotion and love.
- Dancing and singing events were regularly organised in the courts.
4. Art and Painting
The Deccan sultans encouraged paintings and handicrafts.
- Meenakari and Metal Art :
- Meenakari and metal crafts developed in Bijapur and Golconda.
- Persian Style Painting :
- There was a wonderful fusion of Persian and Indian paintings in the courts of the Deccan.
5. Syncretism of religion and culture
The Sultans of the Deccan adopted a policy of coordination between different religions and cultures.
- Hindu-Muslim cultural coordination :
- The Sultans also patronised Hindu artists , poets and architects.
- Ibrahim Adil Shah II was called “Jagat Guru” , as he showed keen interest in Hinduism and music.
6. Trade and crafts
The Deccan sultans encouraged trade and crafts.
- Diamond Trade :
- The Golconda Sultanate was world famous for its diamond mines and trade.
- Weapons and Metal Crafts :
- Deccani weapons and craftsmanship were famous throughout India.
conclusion
The cultural achievements of the Deccan sultans were an important part of their ruling style. They enriched architecture , literature , music , and art and turned the Deccan into a cultural hub. Today their legacy survives in the form of their magnificent buildings , literary works, and cultural syncretism.
Major Sultans of Deccan and their Contributions

The Deccan Sultans contributed to politics , administration , art , architecture and cultural prosperity during their reign. The policies and actions of these Sultans gave a special identity to the Deccan region. Below are described some of the prominent Deccan Sultans and their important contributions.
1. Hasan Gangu Bahman Shah ( 1347-1358)
- Founder of the Bahmani Sultanate :
- Hasan Gangu founded the Bahmani Sultanate and gave himself the title “Ala Uddin Bahman Shah”.
- Construction of the capital :
- Made Gulbarga (Kalburgi) his capital.
- Administrative Reforms :
- Created a strong administrative structure and stabilised the foundations of the Sultanate.
2. Mahmud Gawan ( 1463-1481)
- Great Prime Minister (Vazir) :
- Mahmud Gawan was the Prime Minister during the Bahmani Sultanate and made significant contributions to the Sultanate’s administrative , military and cultural progress.
- Mahmud Gawan Madrasa :
- He established a huge madrasa (Islamic learning centre) at Bidar , which is a masterpiece of Bahmani architecture.
- Military and financial reforms :
- He increased the military strength of the Sultanate and reformed the revenue system.
3. Yusuf Adil Shah ( 1490-1510)
- Founder of Bijapur Sultanate :
- He established the Bijapur Sultanate in 1490 , becoming independent from the Bahmani Sultanate.
- religious tolerance :
- Yusuf Adil Shah was a proponent of religious tolerance and tried to bring together Hindu and Muslim cultures.
- Architecture :
- The architecture of Bijapur began to develop during his reign.
4. Ibrahim Adil Shah II (1580-1627)
- The great ruler of Bijapur :
- He was called “Jagatguru” because he promoted Hindu and Islamic cultural syncretism.
- Interest in music and literature :
- He wrote a treatise called “Kitab-e-Navras” , in which special emphasis was laid on music and devotion.
- Architectural Development :
- During his reign grand structures like the “Gol Gumbaz” were planned.
5. Qutb Shahi dynasty ( 1518-1687)
Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah ( 1580–1612)
- Rulers of the Golconda Sultanate :
- He built Charminar , which is the symbol of Hyderabad.
- Establishment of Hyderabad :
- He founded the city of Hyderabad in 1591 .
- Literary Contribution :
- Encouraged Persian , Urdu and Telugu literature.
6. Ahmad Nizam Shah ( 1490-1510)
- Founder of Ahmednagar Sultanate :
- He broke away from the Bahmani Sultanate and founded the Ahmednagar Sultanate.
- Military reforms :
- He created a strong military system to protect his empire.
- Architecture :
- Many mosques and palaces were constructed in Ahmednagar.
7. Mohammed Adil Shah ( 1627-1656)
- Sultans of Bijapur :
- He developed the Bijapur Sultanate as a cultural and architectural centre.
- Construction of Gol Gumbaz :
- , which is a unique example of Indian architecture, was completed .
8. Qasim Barid ( 1492-1504)
- Founder of Bidar Sultanate :
- He founded the Barid Shahi dynasty.
- Cultural Preservation :
- The Bidar Sultanate encouraged Persian literature and art.
- Development of Bidar Fort :
- The Bidar Fort was expanded during his reign.
9. Fathullah Imad Shah ( 1490-1510)
- Founder of Berar Sultanate :
- He founded the Berar Sultanate.
- Military organization :
- He strengthened the military system to keep his small empire stable.
conclusion
, art , music , literature and architecture in their respective regions . Due to their efforts, the Deccan region not only prospered politically , but also progressed culturally and socially. The legacy of these sultans is still reflected in their buildings , literary works and cultural integration.
Fall of the Deccan Sultans
The Deccan Sultans ruled over large parts of South India for about two centuries. After the disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate , five independent sultanates (Ahmednagar , Bijapur , Golconda , Bidar and Berar) were formed in the Deccan. These sultanates established many dimensions of cultural and political advancement. But due to internal conflicts , weak administration and external attacks, the Deccan Sultans declined by the end of the 17th century.
1. Internal conflict and political instability
- Conflicts after Independence :
- After their separation from the Bahmani Sultanate , there were constant internal conflicts among the Deccani Sultanates.
- Ahmednagar , Bijapur , and Golconda to capture territories and establish dominance.
- Battle of Talikota ( 1565) :
- The Deccani sultans united and fought against the Vijayanagara Empire and defeated it.
- However , this alliance was temporary , and after the battle they turned against each other again.
2. Weak administration and succession struggles
- Succession struggles among the Deccan sultanates increased internal instability.
- The administrative system became weak due to the rule of weak and incompetent sultans.
- The rulers of the Sultanates showed excessive dependence on foreign armies and ministers to maintain their power , which weakened internal power.
3. Intervention of the Mughal Empire
- Policies of Akbar and Aurangzeb :
- The Mughal emperor Akbar adopted strategic methods to weaken the Deccan sultanates.
- Aurangzeb invaded the Deccan Sultanates to expand the Mughal Empire into South India.
- Fall of Ahmednagar :
- Akbar invaded Ahmednagar , and annexed it to his empire in 1595 AD.
- Decline of Bijapur and Golconda :
- Aurangzeb conquered Bijapur in 1686 AD and Golconda in 1687 AD and made them a part of the Mughal Empire.
4. Rise of the Marathas
- The Maratha Empire rose in the 17th century under the leadership of Shivaji .
- The Marathas continuously attacked the Deccan Sultanates and took advantage of their weaknesses.
- Due to the increasing power of the Marathas the Sultanates of the Deccan became weaker and weaker.
5. Economic collapse
- Effect of internal conflicts and wars :
- Constant wars and internal conflicts worsened the economic condition of the Sultanates.
- Decline in Diamond Trade :
- The diamond trade of areas like Golconda , which was a major source of income , gradually weakened.
- Failure of the land revenue system :
- The land revenue system failed due to weak administration , leading to discontent among the peasants and the general public.
6. Foreign intervention
- The Deccan sultanates sometimes relied on the Portuguese and other foreign powers to maintain their power.
- The intervention of the Portuguese and other European powers further complicated local politics.
7. Cultural and social vulnerabilities
- Despite cultural development , the Sultanates did not take any concrete steps to remove social inequalities.
- Excessive centralisation of power and wealth and neglect of the common people also led to the downfall.
8. Failed alliances and lack of strategies
- The Deccan sultanates united against the Vijayanagara Empire , but they lacked a long-term alliance.
- Due to lack of a strong united front they could not stand against the Mughals and the Marathas.
conclusion
The decline of the Deccan sultans was a result of several factors—internal conflicts , weak administration , pressure from the Mughal Empire and the Marathas , economic instability, and foreign intervention. The Deccani sultanates collapsed by the end of the 17th century , and most of the region came under the control of the Mughals or the Marathas. However , the cultural and architectural heritage of these sultans survives to this day and bears testimony to their rich history.