Gujarat is a major state of India , located in the western part of the country. The state is famous for its rich cultural heritage , historical sites , and economic development. The capital of Gujarat Gandhinagar , while its largest city is Ahmedabad The state is located on the coast of the Arabian Sea and shares its borders with the states of Pakistan , Rajasthan , Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
History of Gujarat :
- The history of Gujarat dates back to ancient times. The region has been a part of the Indus Valley Civilisation and has archaeological sites such as Lothal , which was a major port at that time.
- This region has been ruled by the Maurya , Solanki , Mughal and Maratha empires.
- In modern times , Gujarat has been an important centre of the independence movement, being the birthplace of Mahatma Gandhi.
Geographical Location :
- Gujarat has a coastline of approximately 1,600 kilometres , making it important for maritime trade and fisheries.
- The climate here ranges from dry to semi-arid and tropical.
- The state is home to the Gir forest , the only natural habitat of the Asiatic lions.
Culture :
- The culture of Gujarat is known for its diversity and colorful traditions. Major festivals here Navratri , Uttarayan (Makar Sankranti) , and Diwali Are.
- Garba and Dandiya are the main folk dances here.
- Gujarati dishes , such as dhokla , khakhra , fafda , and thepla , are famous throughout India.
Economic Development :
- Gujarat is one of the most prosperous and industrially developed states of India.
- is famous for chemicals , petroleum , textiles , and diamond cutting industries.
- The Kandla and Mundra ports in Gujarat are among the busiest ports in India.
Tourist Places :
- Ahmedabad – Sabarmati Ashram , Akshardham Temple
- Gir National Park – Home of the Asiatic Lions
- Dwarka – The City of Lord Krishna
- Saputara – the only hill station
- Rann of Kutch – White Desert and Rann Utsav
Important Persons :
- Mahatma Gandhi
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Dinkar Rao Makrand
Gujarat is a major state of India due to its cultural , historical and economic characteristics.
History
The history of Gujarat is very rich and diverse , which is associated with many important events and civilizations from ancient times to modern times. Its history reaches from the Indus Valley Civilization , Rajput dynasty , Muslim rulers , Mughals , Marathas and British rule to the freedom struggle. Let us understand it in detail:
Ancient period :
- Indus Valley Civilization (c. 2500–1700 BCE) :
- Lothal , Dholavira and Rangpur in Gujarat were part of the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- Lothal is considered to be the most developed port of the ancient world.
- Dholavira was an advanced city , where amazing examples of water management and architecture have been found.
- Epic Period (Ramayana and Mahabharata) :
- According to mythology , Dwarka is considered to be the city of Lord Krishna. It is mentioned in the Mahabharata.
- The remains of Dwaraka submerged in the sea have been discovered by modern archaeology.
- Maurya Empire ( 321–185 BCE) :
- Gujarat was part of the Maurya Empire during the time of Chandragupta Maurya and Ashoka.
- Buddhism spread during this period.
- Rule of Shakas and Kushans :
- After the fall of the Mauryas , the Shaka (Scythian) and Kushan dynasties ruled Gujarat.
- During this period, trade and culture developed considerably.
Medieval Period :
- Gurjara-Pratihara Empire ( 8th – 10th century) :
- is derived from the “Gurjar” people who were the rulers here.
- This period is known for temple construction and development of Hindu art and culture.
- Solanki Dynasty ( 945-1243) :
- The rule of the Solanki or Chalukya dynasty is considered the golden age of Gujarat.
- At this time Annala Kshatriya culture and temple architecture developed.
- The famous Somnath temple and Rani ki Vav (Patan) are the gifts of this period.
- Delhi Sultanate and Bahmani Rulers ( 13th – 15th Century) :
- Alauddin Khilji and Muhammad bin Tughlaq annexed Gujarat to the Delhi Sultanate.
- 1411 Ahmed Shah founded Ahmedabad , which later became the major city of Gujarat.
Mughal Period ( 16th – 18th century) :
- 1572, Akbar annexed Gujarat to the Mughal Empire.
- During this period, Gujarat became a major centre of trade , especially in the trade of cotton , spices and silk.
- Surat port was a major maritime trade centre of India.
Maratha Rule ( 18th Century) :
- After the fall of the Mughal Empire, Gujarat came under the control of the Maratha Empire.
- During this period, small kings and princely states emerged , who paid taxes to the Maratha Empire.
British period ( 19th – 20th century) :
- Gujarat came under the British Empire in 1818 following the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
- Ahmedabad , Surat , and Bhavnagar became major industrial and trading centres under British administration.
- Gujarat contributed to the independence struggle of 1857 , but the movement failed majorly here.
Contribution in the freedom struggle :
- is the birthplace (Porbandar , 1869) of Mahatma Gandhi , a prominent leader of the Indian independence movement.
- Sabarmati Ashram (Ahmedabad) became the centre of the independence movement.
- Dandi March ( 1930) is famous in history as Salt Satyagraha.
Modern period :
- After 1947 :
- After India’s independence , Gujarat was part of the Bombay Province.
- 1960, Maharashtra and Gujarat were separated and Gujarat was made an independent state.
- Ahmedabad was initially the capital of Gujarat , which was later shifted to Gandhinagar.
- currently :
- Today Gujarat is one of the most developed states of India.
- is known for trade , industry , and cultural heritage.
- Tourist destinations like Rann of Kutch and Gir National Park give it international recognition.
Historical heritage of Gujarat :
- Lothal : Ancient port of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Somnath Temple : Rebuilt seven times , it is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas in India.
- Rani ki Vav (Patan) : UNESCO World Heritage Site , an example of amazing architecture.
- Dwaraka : The mythological city of Lord Krishna.
- Gir National Park : Natural habitat of Asiatic Lions.
The history of Gujarat is diverse and glorious , giving it a special place in the cultural and historical landscape of India.
Indus Valley Civilization (c. 2500–1700 BCE)
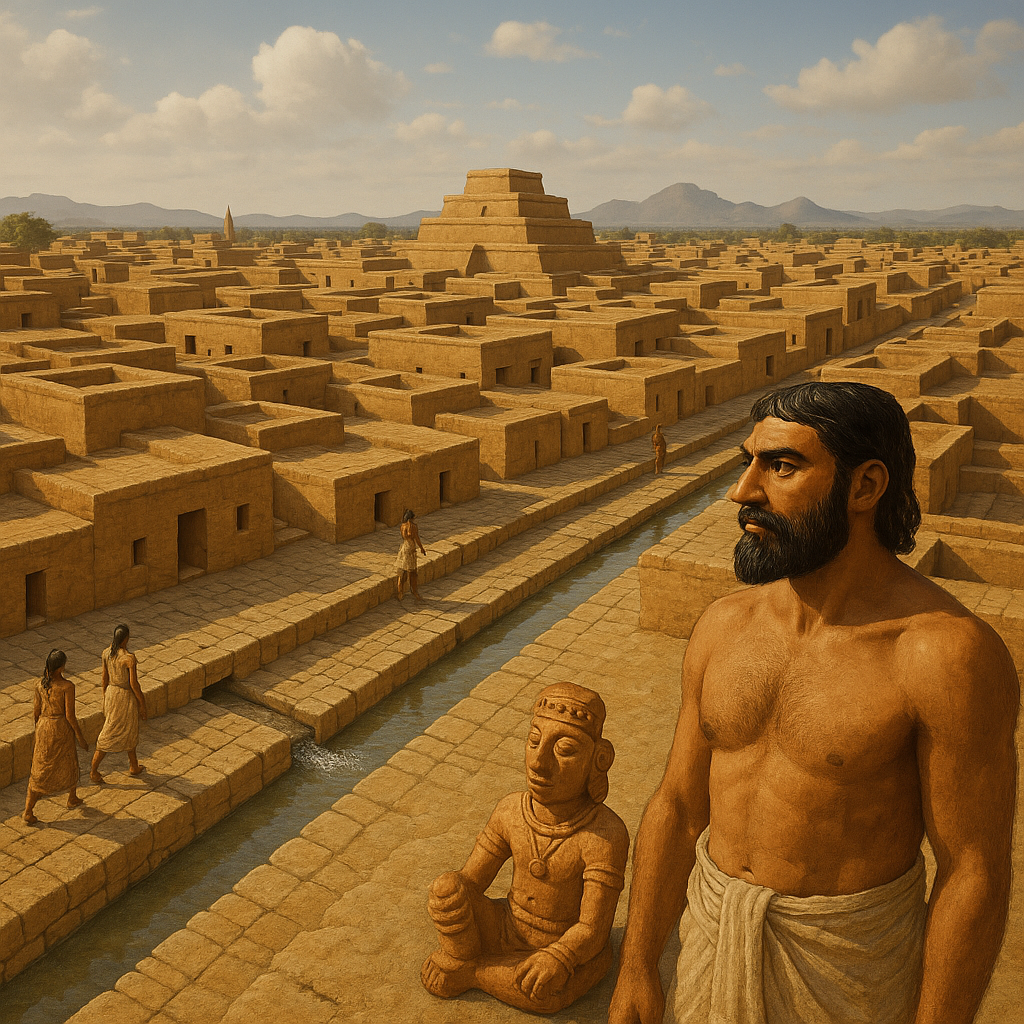

The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the oldest civilizations in the world , which flourished between about 2500 BC and 1700 BC. This civilization was mainly spread across present-day Pakistan , the northwestern part of India and parts of Afghanistan. It is known as the Indus Valley Civilization. Harappan Civilization It is also called Harappa because its first archaeological site was Harappa (in present-day Pakistan).
Important sites of the Indus Valley Civilization in Gujarat , such as Lothal , Dholavira , and Remains of Rangpur have been found , which show the prosperity and advanced technical knowledge of this civilization .
Main features of Indus Valley Civilization :
1. Town Planning :
- The cities of this civilization were famous for their wonderful planning.
- The roads had a grid pattern (plan of straight streets) and the drainage system was developed.
- Houses were made of baked bricks and often had wells as well.
2. Main Sites :
- Harappa : first discovered site , famous for agriculture and grain storage.
- Mohenjo-daro : Famous “Great Bath” and prosperous trading centre.
- Lothal ( in Gujarat):
- An ancient port city , where shipbuilding and maritime trade took place.
- dockyard and pearl industry here were famous.
- Dholavira ( in Gujarat):
- Famous for advanced water management system and large reservoir.
- The city was divided into three parts: the citadel , the middle town , and the lower town.
- Kalibangan : Famous for agriculture and irrigation system.
- Rangpur ( in Gujarat): Centre of cotton textile production.
3. Economy :
- This civilization was mainly based on agriculture.
- Major crops: wheat , barley , cotton , and sesame.
- Trade: It was an important centre of local and maritime trade.
- Lothal in Gujarat was a major centre of maritime trade , from where trade took place with Mesopotamia , Persia , and Africa.
4. Script and Writing :
- The script of the Indus Valley Civilization has not been completely read yet.
- It uses pictographs It was used , in which pictures and symbols were inscribed.
5. Religious beliefs :
- People used to worship nature.
- Figures of Shiva or Pashupati , idols of Mother Goddess , and symbols of animals and birds have been found.
- The Peepal tree and the bull were considered sacred.
6. Science and Technology :
- This civilization was advanced in the making of baked bricks , drainage systems , and water management.
- Reservoirs and canals at Lothal and Dholavira bear evidence of this.
7. Social system :
- It was a class-based society.
- People were engaged in farming , trade , craftsmanship , and textile manufacturing.
- The art of jewellery and toy making was also advanced.
8. Reason for the end :
- The reasons for the downfall of this civilization are not clear , but some major reasons could be:
- Drying up of the Saraswati River.
- Climate change.
- External invasion (arrival of Aryans).
- Collapse of agriculture and trade.
Indus Valley Civilization in Gujarat :
Sites in Gujarat , such as Lothal and Dholavira , were the most advanced and prosperous centres of this civilization.
- Lothal : It is considered to be the oldest dockyard in the world. The people here were adept at marine trade.
- Dholavira : Large reservoirs were built in this city to conserve water. This place is an excellent example of architecture and urbanism.
Importance :
- The Indus Valley Civilization laid the foundation for India’s ancient culture , city planning , and trading practices.
- Its remains help in understanding the cultural and historical heritage of the Indian subcontinent.
Evidence of this civilization in Gujarat still makes it an important part of Indian history.
Maurya Empire ( 321–185 BCE)
The Maurya Empire (321–185 BCE) was the first pan-Indian empire of India , which unified large parts of the Indian subcontinent. This empire Chandragupta Maurya and its expansion was done by the great ruler Ashoka It reached its peak during the reign of Emperor Xuanzang. This empire is famous for its efficient administration , military power , economic prosperity , and the spread of Buddhism.
Gujarat was also a part of the Maurya Empire and flourished economically and culturally during this time. Let us understand the history of the Maurya Empire in detail:
Establishment of the Maurya Empire :
- Establishment of the Maurya Empire Chandragupta Maurya in 321 BC .
- Chandragupta defeated Dhanananda, the last ruler of the Nanda dynasty, and made Pataliputra (present-day Patna) his capital.
- His Prime Minister helped to consolidate his power Chanakya (Kautilya) The major contribution was made by ” Economics” Wrote a book named.
Major rulers of the Maurya Empire :
1. Chandragupta Maurya ( 321-297 BC) :
- Chandragupta defeated Alexander’s generals and took over northwestern India and Punjab.
- He added western India including Gujarat to his empire.
- The Greek historian Megasthenes has mentioned the court of Chandragupta.
- Chandragupta adopted Jainism in the last days of his life and ended his life through meditation at Shravanabelagola (Karnataka).
2. Bindusara ( 297-273 BC) :
- Bindusara maintained Chandragupta Maurya’s empire and expanded it to South India.
- The administration of the region of Gujarat was strong during his reign.
3. Ashoka the Great ( 273-232 BC) :
- Ashoka is considered the greatest ruler of the Maurya Empire. His reign was the golden age of the empire.
- Ashoka adopted Buddhism after the Kalinga War ( 261 BCE) and preached non-violence.
- They Dharma Mahamatras He appointed ‘Dahi Shish’ (religious priests) who used to propagate religion and moral values among the people.
- Ashoka spread religion in Gujarat and established peace and prosperity.
- His inscriptions (state orders) have been found in Junagadh, Gujarat , which bear testimony to his rule and the spread of Buddhism.
Maurya Empire in Gujarat :
- Gujarat It was an important region of the Maurya Empire , especially its western coastal areas.
- Chandragupta Maurya added Saurashtra and Kathiawar region of Gujarat to his empire.
- Ashoka’s inscriptions in Junagadh reflect the influence of Mauryan administration and religion in the region.
- Areas such as Lothal and Saurashtra in Gujarat were major centres for trade. These sites became part of international trade during the Maurya Empire , from where trade was conducted with western countries.
administrative law :
- The Maurya Empire had a centralized administrative system.
- The empire was divided into provinces , which Kumar ( Prince) or Mahamaatra It was governed by.
- Gujarat was part of the western province of the Maurya Empire.
- In the Empire Road Construction And Trade routes Developed , which boosted trade and agriculture in Gujarat.
Economic and Social Development :
- The Maurya Empire promoted agriculture and trade in Gujarat.
- Areas like Lothal and Bharuch played an important role in maritime trade.
- Tax was levied on agriculture , which was the main source of state income.
- The society was based on the caste system , but merchants and craftsmen were also respected.
Religion and culture :
- Buddhism spread widely in Gujarat during the reign of Ashoka.
- Buddhist stupas and viharas were built in the Saurashtra region.
- Ashoka preached the message of non-violence and morality , which is visible in his inscriptions.
Decline of the Maurya Empire :
- 185 B.C. Brihadratha assassination of his commander Pushyamitra Shunga Which led to the fall of the Maurya Empire .
- After the fall of the Maurya Empire, several small kingdoms emerged in Gujarat , and later it became part of the Shaka and Kushan empires.
Importance of Maurya Empire for Gujarat :
- The Maurya Empire gave Gujarat an important place in the commercial and cultural landscape of India.
- This provided Gujarat with a strong administrative system and trade contacts.
- Ashoka’s inscriptions and Buddhist remains show the historical importance of this period.
The Maurya Empire not only unified India politically , but also gave a new direction to art , culture , religion and administrative system. Gujarat was an important part of this empire , which was the center of economic and cultural activities of that time.
Medieval period
The Medieval period ( Madhya Yuga) was an important phase of Indian history , extending from approximately the 8th to the 18th centuries. This period was a time of political , cultural , and religious change in India. The medieval history of Gujarat was influenced by the rule of Rajput rulers , the Delhi Sultanate , the Bahmani rulers, and the Mughal Empire. During this period, Gujarat became a centre of trade , cultural prosperity , and religious tolerance.
Medieval History of Gujarat :
1. Rajput dynasties and Chalukya/Solanki rulers ( 945-1243):
- The Chalukya dynasty ( Solanki dynasty) is considered the golden age of the medieval history of Gujarat.
- This dynasty was founded in the 10th century Moolraj Solanki It was done by.
- Prominent Rulers:
- Bhimadev I : It was during his time that Mahmud Ghazni attacked the Somnath temple ( 1025 AD).
- Karnadev Solanki : He made Anahilwara (Patan) his capital and made it prosperous.
- Siddharaj Jaisingh (1094-1143): He is considered the greatest ruler of the Solanki dynasty. During his reign, there was unprecedented development of art , literature , and architecture in Gujarat. The “Rudramhalaya Temple” is a major construction of his period.
- Kumarpal : He patronized Jainism and promoted religious tolerance in the kingdom.
Characteristics of Solanki period :
- Cultural Development : Jainism and architecture flourished during this period.
- Famous Temples :
- Somnath Temple (Gir-Saurashtra)
- Rani ki Vav (Patan) – This is a unique example of architecture.
- Sun Temple of Modhera.
2. Mahmud Ghazni and Invasion of Somnath Temple ( 1025 AD) :
- The Turk ruler Mahmud Ghazni attacked and plundered the Somnath temple in Gujarat.
- This invasion challenged the security and religious heritage of Gujarat.
- Despite this , the Somnath temple was subsequently rebuilt several times.
3. Rule of Delhi Sultanate ( 13th – 15th century) :
- Alauddin Khilji (1298): This ruler of the Delhi Sultanate invaded Gujarat and annexed it to his empire.
- Muslim rule in Gujarat began from this time.
- Muhammad bin Tughlaq Also established his authority over Gujarat.
4. Gujarat Sultanate ( 1407-1573):
- in 1407 Zafar Khan Muzaffar became independent from the Delhi Sultanate Gujarat Sultanate was established.
- Prominent Rulers:
- Ahmed Shah ( 1411-1443) : He founded Ahmedabad and made it the capital. Ahmedabad became the center of trade and cultural activities at this time.
- Mahmud Begada (1458-1511):
- He was one of the most powerful sultans of Gujarat.
- conquered areas such as Junagadh , Champaner , and Diu.
- Trading ports (Surat and Bharuch) developed during his reign.
- Bahadur Shah : During his reign the Mughals invaded Gujarat in 1535 .
Characteristics of the Sultanate period :
- Cultural Development : The famous Jama Masjid and Sidi Sayed’s Jali in Ahmedabad were constructed in this period.
- Trade : Gujarat became a major centre of maritime trade with Arab , African , and European countries.
5. Mughal Empire ( 1573-1707):
- In 1573 , Akbar ended the Gujarat Sultanate and incorporated it into the Mughal Empire.
- During the Mughal period , Surat and Ahmedabad became major trading cities of India.
- became a major centre for European traders (Portuguese , Dutch , British).
- Gujarat experienced economic prosperity under the rule of the Mughals.
Contributions of Mughal Rulers :
- Akbar : He organised the administration of Gujarat and brought stability here.
- Jahangir and Shah Jahan : Promoted trade in Surat and Ahmedabad.
6. Maratha Period ( 18th Century) :
- After the fall of the Mughal Empire, the influence of Marathas increased over Gujarat.
- Gujarat was fragmented into several small principalities and under the control of Maratha chieftains.
- Trade and agriculture systems weakened during the Maratha rule.
Characteristics of Medieval Gujarat :
- religious tolerance :
- In this period, harmony of Hindu , Jain and Muslim cultures is visible.
- Jainism was patronised by both Rajput and Muslim rulers.
- Architecture and art :
- Rajput Architecture : Modhera Sun Temple , Rani Ki Vav.
- Muslim architecture : Jama Masjid of Ahmedabad , Jali of Sidi Saiyed , Rani Roopmati’s Mosque.
- Buddhist and Jain Art : Construction of Jain temples was prominent.
- Business and Economy :
- Gujarat was a major trading centre of medieval India. Trading ports were established in Surat , Bharuch , and Kathiawar.
- , silk , and cotton textiles were exported from India to Europe and Arab countries.
- Culture and Literature :
- , Arabic and Gujarati languages developed in medieval Gujarat .
- Jain literature and texts were compiled during this period.
Medieval Period of Gujarat: In Brief :
The medieval period of Gujarat was a rich cultural and economic era. From Rajput rulers to the Delhi Sultanate , Gujarat Sultanate and the Mughal Empire , this period saw Gujarat making its mark in the fields of trade , art and religion. Cities like Ahmedabad , Surat , and Junagadh became cultural and economic centres of this period.
Modern period
Modern Period is that phase of Indian history which extends from the middle of the 18th century to the middle of the 20th century . This period is the period of modern Indian history in India. British colonialism , social reform movements , and eventually Independence struggle Gujarat is known for this period. Gujarat was a major center of the Indian independence movement during this period.
Gujarat’s historical , cultural , and economic contributions played an important role in the creation of modern India.
Modern period of Gujarat: Major events
1. Beginning of British rule ( from the end of the 18th century) :
- Arrival of the British :
- 1612 the East India Company established its first factory in Surat.
- Surat was an early centre of British trade , but later Calcutta , Bombay , and Madras became more important ports.
- The Maratha Empire had influence over Gujarat until the end of the 18th century , but in 1818 Third Anglo-Maratha War After that the British established their control over Gujarat.
2. Economic Development and Exploitation of Gujarat :
- textile industry :
- the 19th century because of the establishment of textile mills here.
- Gujarat’s textile industry grew rapidly during British rule , but it also suffered from excessive taxes and unequal trade policies due to British colonialism.
- Trade and Ports :
- Surat , Bhavnagar , and Kandla became centres of trade.
- The British used Gujarat as a major source for the export of cotton and spices.
3. Social Reform Movement ( 19th Century) :
- Jyotiba Phule and other reformers :
- Social reform movements in Gujarat challenged evil practices such as the caste system , sati , and child marriage.
- Influence of Gandhiji :
- Mahatma Gandhi ( 1869-1948) was born in Porbandar, Gujarat.
- Gandhiji gave new direction to the reform movements and freedom struggle in modern Gujarat.
- their Satyagraha Movement , Swadeshi Movement , and message of non-violence Started from Gujarat.
4. Contribution of Gujarat in Indian freedom struggle :
Gujarat played a central role in the Indian freedom struggle. Key events and personalities:
Mahatma Gandhi and Satyagraha :
- After returning from South Africa in 1915, Gandhiji visited Ahmedabad Sabarmati Ashram was established.
- Champaran Satyagraha ( 1917) And Kheda Satyagraha ( 1918) :
- The Kheda Satyagraha took place in the Kheda district of Gujarat , where Gandhiji led the farmers. It was a successful movement against the British tax system.
- Non-cooperation Movement ( 1920) And Salt Satyagraha ( 1930) :
- March 12 , 1930, Mahatma Gandhi Dandi March He started the Salt March , in which he protested against the Salt Law. This movement culminated in Dandi (Gujarat) and became a major symbol of the freedom struggle.
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel :
- Sardar Patel ( 1875–1950), known as the “Iron Man” , was from Kheda district of Gujarat.
- They Led the Bardoli Satyagraha (1928) , a successful movement for tax remission for farmers.
- unified India by integrating more than 500 princely states into independent India .
Other prominent leaders :
- Mohanlal Pandya : With Gandhiji in Kheda Satyagraha.
- Ravishankar Maharaj : Social and political reformer.
- Narhari Parikh and Mahadev Desai : Close associates of Gandhiji.
5. Educational and social development :
- Many educational institutions were established in Gujarat , including those in Ahmedabad Gujarat Vidyapeeth ( established by Gandhiji) is the prominent one.
- Social reformers worked for women’s education , eradication of untouchability , and Dalit upliftment.
6. Partition and Independence of India ( 1947):
- At the time of independence , major cities of Gujarat such as Ahmedabad , Surat and Vadodara contributed significantly to the economic reconstruction of the country.
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel played a leading role in maintaining the unity and integrity of India.
7. Reorganisation of Gujarat ( 1960):
- In 1960 , Maharashtra and Gujarat were divided into two separate states.
- Ahmedabad became the first capital of Gujarat , which was later Gandhinagar was transferred to.
Modern Era of Gujarat: Characteristics :
- economic prosperity :
- Gujarat became an economic centre of modern India due to its textile industry , spices , and salt production.
- After independence , cities like Ahmedabad , Surat , and Vadodara became the main centres of industrial development.
- Contribution in the freedom struggle :
- Movements like the Dandi March and the Kheda Satyagraha became the inspiration for India’s independence.
- Great leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Sardar Patel gave Gujarat a leading place in the political map of India.
- Cultural Development :
- Gujarati literature and art also developed unprecedentedly in the modern period.
- Narsinh Mehta The contribution of Shaikh and other poets enriched Gujarati culture.
- Religion and tolerance :
- There was an atmosphere of religious and social tolerance in Gujarat. Mahatma Gandhi’s principles further strengthened it.
conclusion :
, economic , and cultural center of India . Gujarat made a significant contribution in the freedom struggle and after independence it emerged as an industrially and economically progressive state. The leadership of great leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Sardar Patel made the role of Gujarat historic in the creation of modern India.
Geographical

Gujarat is an important state located in the western part of India , known for its geographical and cultural diversity. The region presents a unique blend of geographical elements such as sea , plains , mountains and deserts. Let us understand the geographical location of Gujarat in detail:
Geographical location and boundaries of Gujarat :
- Latitude and Longitude :
- Expansion of Gujarat 20°1′ North latitude from to 24°7′ North Latitude Up to and 68°4′ East Longitude From 74°4′ East Longitude Till then.
- This region is located in the Northern Hemisphere.
- boundaries :
- In the answer : Rajasthan.
- In the south : Maharashtra.
- In the east : Madhya Pradesh.
- To the west : Arabian Sea.
- In the northwest : Sindh province of Pakistan.
Area and Population :
- The total area of Gujarat is approximately 1,96,024 sq.km , making it the sixth largest state in India.
- 2021 India census , it is one of the most densely populated states in India.
Geographical Area :
Gujarat can be divided geographically into four main regions:
1. Rann of Kutch :
- The region is located in the northwest of Gujarat and is part of the desert and semi-desert terrain.
- The Rann of Kutch is divided into two parts:
- Great Rann : An area with abundant salt.
- Chhota Rann : Famous for wildlife , especially Indian wild ass It is found here.
- The land here gets filled with water during monsoon and remains dry the rest of the time.
- Famous Kutch Festivals It is held here.
2. Peninsula of Saurashtra :
- Saurashtra is the central part of Gujarat , also known as “Kathiawar”.
- The region is surrounded by the sea and has several rivers flowing through it , like the Bhadrakali and Shetrunji.
- The terrain of Saurashtra is hilly and plateau.
- The region is famous for the Gir Forest , where Asiatic Lion Are found.
3. South Gujarat :
- is blessed with rivers like Narmada , Tapi , and Damanganga.
- The soil here is fertile and suitable for cultivation of sugarcane , cotton , and rice.
- The region is industrially developed , especially Appearance And Valsad There are major industrial centers here.
4. North Gujarat :
- The area is semi-arid and dependent on agriculture.
- Banaskantha , Patan , and Mahesana districts are located here.
- There is a problem of water shortage and barren land here.
Natural Resources :
Gujarat is a state rich in natural resources:
- Mineral Resources :
- Oil and Natural Gas: Kutch and Ankleshwar areas.
- Salt: Rann of Kutch is the major source of salt production in India.
- Limestone , bauxite , and fluorineite are also found here.
- Forests and Wildlife :
- The Gir forests of Gujarat are famous for Asiatic lions.
- Blackbuck , Indian wild ass , and many bird species are found here.
- Main forest areas: Gir , Kutch , and South Gujarat.
- National Parks: Gir National Park , Velavadar National Park , Rann of Kutch.
- Water Resources :
- Narmada , Sabarmati , Tapi , Mahi , and Damanganga are the major rivers of Gujarat.
- built on the narmada river Sardar Sarovar Dam Important for irrigation and hydroelectricity.
climate :
The climate of Gujarat can be divided into three main types:
- Tropical climate : Hot and dry.
- Monsoon climate : Rainfall occurs mainly between June and September.
- Winter climate : It is cold from November to February.
Rain:
- Kutch and North Gujarat receive less rainfall.
- Saurashtra and South Gujarat receive moderate to heavy rainfall.
Land and Agriculture :
- The land of Gujarat is mainly of four types:
- Alluvial soil : In the plains of Narmada and Tapi.
- Black Soil : Suitable for cotton cultivation in Saurashtra.
- Sandy soil : In the Rann of Kutch.
- Saline soil : In coastal areas.
- Main Crops :
- Food grains: Wheat , millet , sorghum.
- Cash crops: Cotton , sugarcane , tobacco.
- Others : Peanuts , Oilseeds.
Coastal Areas and Ports :
- The coastline of Gujarat is approximately 1,600 kilometres long , which is the longest in India.
- Major Ports:
- Kandla: Major commercial port.
- Porbandar: Birthplace of Mahatma Gandhi.
- Dahej and Hazira: Industrial and shipping centres.
Geographical features of Gujarat :
- Rann Utsav : Rann of Kutch is famous for its natural beauty and cultural significance.
- Gir Forest : The last natural habitat of the Asiatic Lion.
- Contribution of Rivers : Narmada and Sabarmati are important for agriculture and drinking water.
- Industrial development : Industrial areas like Dahej and Surat.
- Maritime Trade : Gujarat is the maritime trade gateway of India.
conclusion :
Gujarat’s geographical location makes it a special state of India. Its diversity – desert , coastal areas , fertile plains , and forests – not only makes it rich in natural resources , but also makes it important from an economic , cultural , and environmental point of view.

Culture
culture of Gujarat is famous for its rich traditions , colorful festivals , unique arts , and unity in diversity. This state is not only the economic and industrial hub of India but is also known for its cultural heritage and glorious traditions. Let us understand the culture of Gujarat in detail:
1. Language and Literature :
- Gujarati language :
- Main language of Gujarat Gujarati It is one of the 22 recognized languages of India .
- It is an Indo-Aryan language and Mahatma Gandhi It has been the mother tongue of many great literary figures including.
- Other languages: Hindi , English , Sindhi , and Kutchi.
- Gujarati Literature :
- Gujarat has a long history of literature. Narsinh Mehta , Dayanand Saraswati , Premchand , and Umashankar Joshi Like there have been great poets and writers.
- Saint Literature : Influence of the thoughts of Narayandas and Kabirdas during the Bhakti movement.
- Gujarati novels , dramas , and poems are also popular in modern literature.
2. Religion and Spirituality :
Gujarat is a confluence of various religions , with Hinduism , Jainism , Islam , Buddhism , and Zoroastrianism present.
- Hinduism :
- Lord Krishna’s residence in Dwarka (Saurashtra).
- Major temples: Dwarkadhish Temple , Somnath Temple , and Ambaji Temple .
- Jainism :
- Gujarat is a major centre of Jainism.
- Famous Jain Temples: Palitana , Girnar , and Shyamala Tirtha .
- Islam :
- Gujarat also has influence of Islamic architecture. The Lattice of Sidi Sayed And Jama Masjid This is an example of this.
- Zoroastrianism :
- There is a large population of Parsis in Surat and Navsari.
3. Arts and Crafts :
Gujarat is famous for its traditional arts and crafts.
i. Textiles and Handicrafts :
- Patola of Patan :
- This is an ancient weaving technique in which double single weave is done.
- Bandhani (Bandhej) :
- This dyeing style of fabric is famous for colorful sarees and dupattas.
- Zari and Zardosi :
- Surat is famous for zari embroidery.
ii. Clay and metal crafts :
- Terracotta Art : Famous in rural areas of Kutch and Saurashtra.
- Metal Crafts : Brass and Bronze Sculptures.
iii. Wood and stone carving :
- Exquisite carvings of wood and stone can be seen on temples , mansions , and houses.
iv. drawing :
- Warli and Pithora Art : Traditional paintings done in tribal areas.
- Rangoli : Made outside houses on festivals.
4. Dance and music :
The cultural identity of Gujarat is reflected in its traditional dance and music.
Dance :
- Garba :
- The most famous dance of Gujarat , performed during the worship of Goddess Durga.
- This Navratri It is celebrated on a large scale during.
- Dandiya Raas :
- This dance is performed with dandiya (wooden sticks) and is dedicated to the love of Lord Krishna and Radha.
- Tipani Dance :
- Women traditionally do this during agricultural work.
Music :
- Traditional Gujarati music is based on devotional and folk songs.
- Light music : devotional compositions , couplets of saints and compositions of Narsinh Mehta.
- Folk Music : Charan Geet , Raas Geet , and Garbi songs .
5. Food :
Gujarat’s cuisine is famous for its vegetarian dishes. Its taste is a balance of sweet , sour , and spicy.
i. Main dishes :
- Dhokla : A light and tasty dish made from rice and gram flour.
- Khandvi : Thin layered roll made from gram flour and curd.
- Thepla : Traditional flatbread made with fenugreek and spices.
- Undhiyu : A mixed vegetable dish made in winter.
- Fafda and Jalebi : A popular snack.
ii. Sweets :
- Ghevar , Mohanthal , and Ghaari of Surat .
Drinks :
- buttermilk And Lemonade .
6. Festival :
The cultural life of Gujarat is enriched by its colourful festivals.
- Navratri : 9 days of worship of Goddess Durga and Garba dance.
- Makar Sankranti (Uttarayan) :
- Kite flying festival.
- In Ahmedabad Kite Festival is organised.
- Rath Yatra : The journey of Lord Jagannath is celebrated with great pomp in Ahmedabad.
- Diwali : Celebrated with enthusiasm throughout Gujarat.
- Rann Utsav : A cultural and tourist festival held in Kutch.
- Janmashtami : Grand celebration of the birth anniversary of Lord Krishna in Dwarka.
7. Costumes :
The people of Gujarat are known for their traditional dress:
- Male :
- Kurta-pyjama , dhoti , and Turban .
- Women :
- Chaniya-choli , which is decorated with traditional jewellery.
8. Folktales and Traditions :
- Krishna Leela :
- The stories and festivals related to the life of Lord Krishna are an important part of the culture here.
- Saint poet Narsinh Mehta Stories of : Inspiration for love and devotion.
- Stories from the battlefield :
- Stories of bravery and sacrifice are found in the folk songs of Kutch and Saurashtra region.
9. Architecture and Sculpture :
The architecture of Gujarat reflects its cultural heritage:
- Temple Architecture : Somnath Temple , Dwarkadhish Temple.
- Islamic architecture : Sidi Sayed Mosque , Jama Masjid.
- Ancient City : Ahmedabad , declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
10. Tribal culture :
The tribal communities of Gujarat are known for their unique traditions and customs:
- Major tribes: Bhil , Rathwa , Garasia , and Koli.
- Their art , music , and handicrafts are an integral part of Gujarat’s culture.
conclusion :
The culture of Gujarat is a confluence of its traditions , festivals , food , and art. The state cherishes its diversity and is a symbol of unity and tolerance. The culture of Gujarat influences not only the Indian but also the global culture.
Economic
Gujarat is one of the economically strongest and fastest growing states of India. Its economy is based on agriculture , industry , trade , and service sector. Gujarat’s economic model is famous for promoting balanced development and entrepreneurship. Let us understand the economic development of Gujarat in detail:
1. Historical background and foundation of economic development :
- Contribution to History :
- The economic development of Gujarat has been significant since ancient times.
- Indus Valley Civilization At that time, it was a major center of trade and commerce.
- In the medieval period , ports like Surat and Bhavnagar in Gujarat were centres of international trade.
- During the British period , Gujarat became a major centre of textile industry and maritime trade.
- Modern foundations :
- After independence , Gujarat gave priority to industrialisation , agriculture , and port development.
- 1960 , Gujarat became an independent state by separating from Mumbai , after which emphasis was laid on industrial policies and infrastructure here.
2. Nature of economy :
Gujarat’s economy is multi-faceted , with agriculture , industry , the service sector , and international trade contributing significantly.
i.Gross State Domestic Product ( GSDP):
- Gujarat’s GSDP in 2022-23 is approximately Rs 16 lakh crore , making it one of the wealthiest states in India .
- of Gujarat Per capita income Higher than the Indian average.
- Industrial growth rate: over 10% .
ii. Sectoral contribution to the economy :
- Agriculture : 18-20%
- Industry : 45-50%
- Service sector : 30-35%
3. Agriculture sector :
Gujarat is one of the leading states in India in terms of agricultural production.
i. Major Crops :
- Cash Crops:
- Cotton : Gujarat is known as the “Cotton Heartland”.
- Peanut : The largest share of peanut production in India comes from Gujarat.
- Oilseeds : Cultivation of soybean and sesame.
- Food grains:
- Millet , wheat , sorghum.
- Paddy (mainly in South Gujarat).
ii. Irrigation and water management :
- Narmada Project :
- Supply of irrigation and drinking water through the Sardar Sarovar Dam.
- Use of drip irrigation and water management techniques in agriculture.
iii. Milk production :
- Gujarat is a leader in milk production.
- AMUL ( Gujarat Co-operative Milk Marketing Federation) is a global brand.
4. Industrial area :
Gujarat is called the “Growth Engine of India” because its industrial sector is highly developed.
i. Major Industries :
- textile industry :
- Ahmedabad is called the “Manchester of India”.
- Surat and Vadodara also have a major contribution in textile production.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industry :
- 62% of India’s total petrochemical production takes place in Gujarat.
- Reliance Industries And ONGC Companies such as are located here.
- Automobiles and Engineering :
- Companies like Tata , Ford , and Maruti Suzuki have set up large plants in Gujarat.
- Pharmaceutical :
- Gujarat is a leader in pharmaceutical production. Ahmedabad and Vadodara are its major centres.
ii. Industrial areas and hubs :
- Vadodara-Ankoleshwar Industrial Corridor .
- Dahej and Hazira : Heavy industry and petrochemical hubs.
- Kandla and Mundra : Port based industrial development.
5. Trade and Commerce :
Gujarat’s trade and commerce sector contributes significantly to India’s economy.
i. Ports and Maritime Trade :
- Gujarat’s 1,600 kilometre-long coastline is the basis of its trading power.
- Major Ports:
- Kandla Port : India’s busiest port.
- Mundra Port : Operated by the Adani Group , it is a private port.
- Gujarat accounts for almost all of India’s maritime trade 40% He handles it.
ii. Business Centres :
- Surat: Diamond and textile industries.
- Ahmedabad: Textile , industrial and commercial centre.
- Rajkot: Machinery and cutlery production.
iii. International trade :
- contributes more than 25% of India’s total exports .
- Main export products: Chemicals , petrochemicals , textiles , diamonds , and agricultural products.
6. Service sector :
Gujarat’s service sector is growing rapidly and IT , banking , tourism , and education are major contributors to it.
i. IT and Digital India :
- In Gujarat GIFT City (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) is India’s first international financial services centre.
- The state is promoting digital technology and startups.
ii. Banking and Finance :
- There are major banking hubs in Gujarat.
- Ahmedabad is a major centre for corporate finance and investment.
Tourism :
- Cultural and Religious Tourism : Somnath , Dwarka , and Statue of Unity.
- Rann Utsav : Rann of Kutch attracts tourists.
- Wildlife Tourism : Gir National Park and Blackbuck Sanctuary.
7. Energy and Infrastructure :
Gujarat is a leader in energy production and infrastructure development.
i. Energy sector :
- Most in India Solar and wind power generation .
- Mokha And Raw Major centers of wind energy.
- Kankaria Solar Power Park : Asia’s largest solar power park.
ii. Infrastructure :
- Smart City Initiatives : Ahmedabad , Surat , Vadodara , and Rajkot.
- Expressways and Industrial Corridors:
- the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor ( DMIC) is in Gujarat.
8. Policy and Governance :
The progressive policies of the Gujarat government have made it an economic powerhouse.
- Business-friendly policies : land acquisition , tax relief , and industrial subsidies.
- ” Vibrant Gujarat” Conference :
- This is an investor conference held every two years to attract international investments .
- Make in India : Gujarat is a major partner.
9. Challenges and Opportunities :
Challenges :
- Environmental Problems: Industrial Pollution.
- Water Crisis: Water shortage in some areas of Kutch and Saurashtra.
- Poverty and regional inequality.
Possibilities :
- Development of green energy.
- Expansion of infrastructure in rural areas.
- Favourable environment for more investments.
conclusion :
Gujarat’s economic growth is the result of its visionary policies , entrepreneurship , and effective use of natural resources. With balanced growth in agriculture , industry , trade , and service sectors , Gujarat is not only the economic engine of India but is also making its mark globally.

Tourist
Tourism in Gujarat is a symbol of its rich cultural , historical , religious , and natural heritage. The state is one of the major tourist destinations in India and attracts millions of tourists every year. The diversity of Gujarat is reflected in its culture , wildlife , temples , historical buildings and festivals. Let us understand the major tourist destinations of Gujarat in detail:
1. Historical and cultural sites
is linked to ancient civilisations , rulers , and the colonial period , which is reflected in its historical sites.
i. Ahmedabad ( UNESCO World Heritage City) :
- Sabarmati Ashram :
- Founded by Mahatma Gandhi , it was the centre of the Indian independence struggle.
- The Forge of Sidi Sayed :
- A masterpiece of Islamic architecture.
- Jama Masjid :
- Built in the 15th century.
- Kalupur Swaminarayan Temple :
- This temple is famous for its unique architecture and beauty.
ii. Patan (Rani ki Vav) :
- Rani ki Vav :
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is considered to be the most beautiful stepwell in Gujarat.
- Patola of Patan :
- It is a centre of ancient cloth weaving techniques.
iii. Saurashtra region :
- Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park :
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and has Hindu and Jain temples.
- Junagadh :
- Girnar Hills and Nawabi Palace.
2. Religious places
Gujarat is also famous for religious tourism. The temples , mosques and other religious places here give a feeling of spirituality.
i. Dwarka (one of the four Dhams) :
- Dwarkadhish Temple :
- It is a temple of Lord Krishna and one of the Char Dham pilgrimages.
- Rukmini Temple :
- Temple dedicated to Goddess Rukmini.
ii. Somnath (Jyotirling) :
- Somnath Temple :
- is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and has historical and religious significance.
iii. Ambaji Temple :
- Ambaji :
- It is one of the Shakti Peethas and is located in the Banaskantha district of Gujarat.
iv. Shatrunjaya (Palitana) :
- It is one of the holiest pilgrimage sites of Jainism and has over 900 temples.
v. Modhera (Sun Temple) :
- This temple is dedicated to the Sun God and is famous for its architecture and craftsmanship.
3. Wildlife and nature tourism
Gujarat is also known for its unique wildlife sanctuaries and natural spots.
i. Gir National Park :
- It is the only natural habitat of the Asiatic lions.
- , leopard , jackal and many bird species are found here .
ii. Rann of Kutch :
- Rann Utsav :
- Desert of Kutch is a wonderful sight , where “Rann Utsav” is organized every year.
- Dholavira :
- A major site of the Indus Valley Civilization.
iii.Blackbuck National Park (Velavadar) :
- It is famous for the rare Blackbuck deer.
iv. Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary :
- This bird sanctuary becomes home to migratory birds in winter.
v. Marine National Park (Jamnagar) :
- It is India’s first marine national park and one can see rare marine life and coral reefs here.
4. Beach and Harbour Sites
The long coastline of Gujarat is an important tourist attraction.
i. Mandvi Beach :
- Located in Kutch, this serene beach is famous for its white sands and historical havelis.
ii.Daman and Diu :
- is known for its beaches , churches , and Portuguese culture.
iii. Bet Dwarka :
- It is an island connected to Lord Krishna’s city Dwarka.
5. Modern sites and monuments
Amazing examples of modern architecture can also be seen in Gujarat.
i. Statue of Unity :
- It is the world’s tallest statue of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel ( 182 metres height).
- It is built in Kevadia on the banks of river Narmada.
- eco-tourism , jungle safaris , and museums around it.
ii. GIFT CITY :
- Located in Gandhinagar, it is India’s first international financial services centre.
6. Folk culture and festivals
The festivals and fairs of Gujarat reflect the culture and traditions of the state.
i. Navratri and Garba :
- It is a festival of dance and worship celebrated for 9 days.
- Garba and Dandiya of Gujarat are world famous.
ii. Uttarayan (Kite Festival) :
- This festival organised on the occasion of Makar Sankranti is the biggest kite flying event.
iii. Rann Utsav :
- It is a cultural and tourist festival held in the Rann of Kutch.
iv. Shatrunjay Fair (Palitana) :
- This is the main fair of Jainism.
7. Other important sites
- Sardar Sarovar Dam :
- This dam built on the Narmada River is a centre of attraction for tourists.
- Girnar Hills :
- This is a religious and natural place.
- Dandiya and Rathwa Folk Art :
- Tribal art and dance of these areas also promote tourism.
conclusion :
Gujarat has something for every type of tourist , be it a religious pilgrim , wildlife lover , historian , or a lover of art and culture. The tourist places here reflect the diversity and glorious heritage of the state. Tourism in Gujarat is not just a sightseeing tour , but it is a cultural experience that enriches everyone.
Important Persons
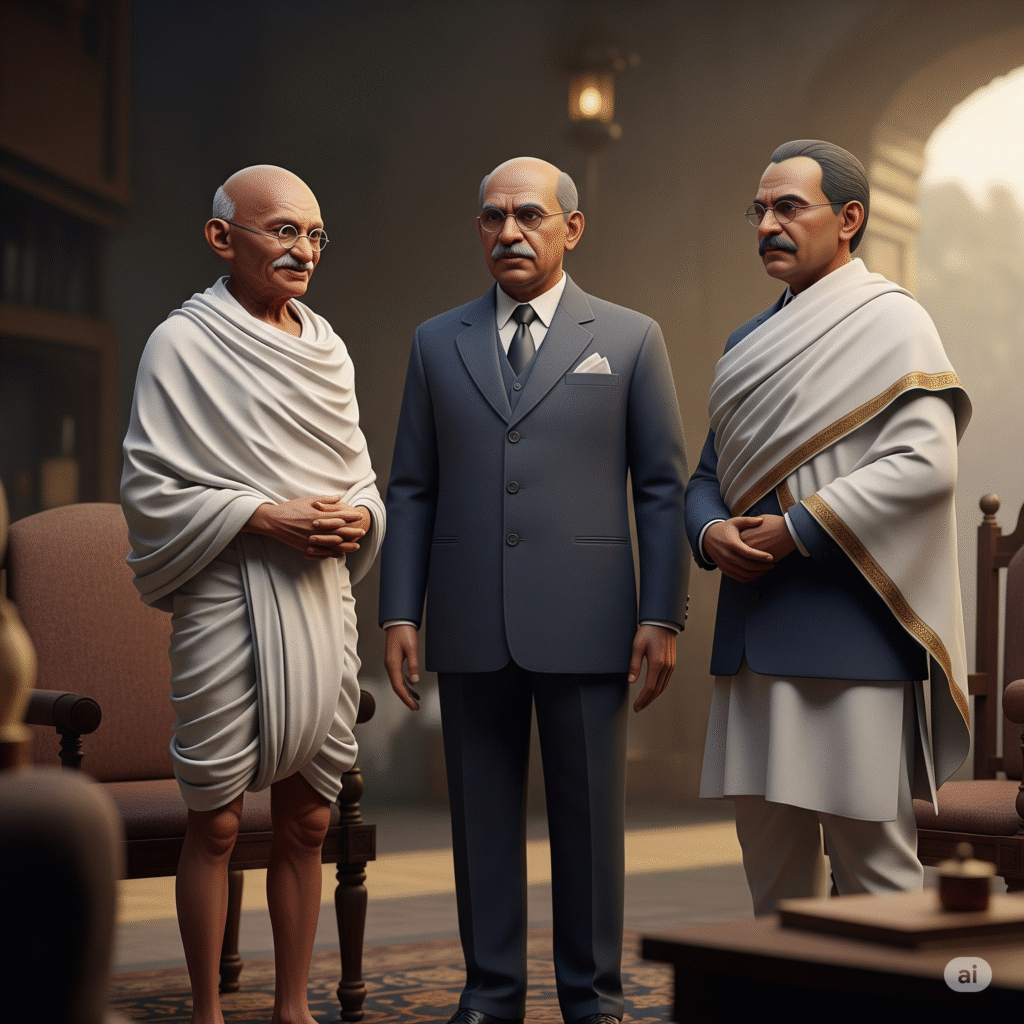
Gujarat has given India many great personalities who have contributed significantly to the country’s social , political , and cultural development. Among these , people like Mahatma Gandhi, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel , and Dinkar Rao Makarand (who is somewhat less famous) are particularly noteworthy. Let us understand them in detail:
1. Mahatma Gandhi ( 1869-1948)
Mahatma Gandhi’s life is an important milestone in the Indian freedom struggle and the global human rights movement. He was revered as the ‘ Father of the Nation ‘ and his philosophy is still relevant throughout the world.
i. Birth and early life :
- Mahatma Gandhi was born on 2 October 1869 in Porbandar , Gujarat. His father’s name was Karamchand Gandhi and mother’s name was Putlibai.
- Gandhiji had deep faith in morality and truth since childhood.
ii. Education and life abroad :
- He received his early education in Porbandar and Rajkot. Later , he went to England , where he studied law and became a barrister.
- While living in England, Gandhiji understood various aspects of Indian culture , religion and life and this later reflected in his thoughts.
iii. Conflict in South Africa :
- In South Africa, Gandhiji fought against apartheid and for the rights of Indians.
- There he Satyagraha And humble resistance Adopted the principles of , which later became influential in the Indian independence struggle.
iv. Contribution in Indian freedom struggle :
- 1915 and joined the Indian National Congress.
- They Swadeshi Movement , Salt Satyagraha ( 1930) , Quit India Movement ( 1942) Led movements such as.
- their Satyagraha And Nonviolence His theory became famous all over the world. His view was that the struggle for freedom can be done without violence.
- His philosophy of life was based on ‘ truth ‘, ‘ non-violence ‘, and ‘ morality ‘ .
v. Attainment of independence and contribution :
- attained independence on 15 August 1947 under the leadership of Gandhiji .
- Although Gandhi’s life was a symbol of personal struggle and sacrifice , he always remained true to his ideals , which had a profound impact on societies in India and the world.
vi. Death :
- Mahatma Gandhi was assassinated by Nathuram Godse on 30 January 1948. His sacrifice was a defining moment in the Indian freedom struggle.
2. Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel ( 1875-1950)
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel was the first Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister of India , known as the “Iron Man” . His contribution was extremely significant in the integration of the Indian Union and strengthening the administrative structure.
i. Birth and early life :
- Sardar Patel was born on 31 October 1875 in Nadiad , Gujarat.
- He belonged to a simple farmer family but excelled in education. He studied law and became a barrister.
ii. Entry into the Indian National Congress :
- Sardar Patel started his political career in 1917 with the Champaran Movement under the leadership of Gandhiji.
- Later he became a close associate of Gandhiji and played an active role in Ahmedabad.
iii. Integration of the Indian Union :
- After attaining independence in 1947 , the integration of 565 princely states of India was a major challenge. Sardar Patel successfully accomplished this task.
- He entered into agreements with the rulers of princely states and exerted strong pressure for their merger with India , thereby maintaining the political and geographical unity of India.
iv. Patel’s contribution and legacy :
- He played an important role in implementing the Indian Constitution.
- Patel’s role first home minister of the government of India was extremely important as.
- His strong leadership and administrative skills helped bring stability to the Indian administration.
v. Statue of Unity :
- World’s tallest statue in memory of Sardar Patel , in India statue of unity It is built , which is 182 meters high and is situated in Kevadia on the banks of river Narmada.
3. Dinkar Rao Makrand
Dinkar Rao Makarand is a relatively less known , but important figure , who contributed to various aspects of society during his time.
i. Life and Work :
- Dinkar Rao Makarand was a renowned social worker , writer , and journalist. His life was based on various issues of the society.
- He worked in the field of reform and education in Indian society.
ii. Contribution and Scope :
- Dinkar Rao Makarand presented his views on topics like social reform , women’s rights , and rural development.
- actively stood against casteism , discrimination and other inequalities in Indian society .
iii. Literary contribution :
- Makarand wrote many articles , poems and books in which he expressed his deep understanding and views on social issues .
- His literary contribution was significant as a social reformer and thoughtful writer.
conclusion :
No Indian can ever forget the contribution of Mahatma Gandhi and Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel. Gandhiji adopted the path of non-violence for the freedom struggle , while Patel played an important role in unifying the Indian Union. Social workers like Dinkar Rao Makarand worked to make the society aware through social reform and literary contribution. The contribution of these great people gave a new direction to Indian society and politics.