Germany – A Complete Introduction to the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany, is one of Europe’s most influential and developed nations. It is a founding member of the European Union (EU) and is renowned for its advanced technology, strong economy, rich culture, and historical significance.
1. A Brief Introduction to Germany
Germany is recognized globally for its engineering excellence, innovation, cultural heritage, and world-class education system. As one of the world’s strongest economies, it plays a major role in European and global affairs.
2. Geographical Location
Basic Details
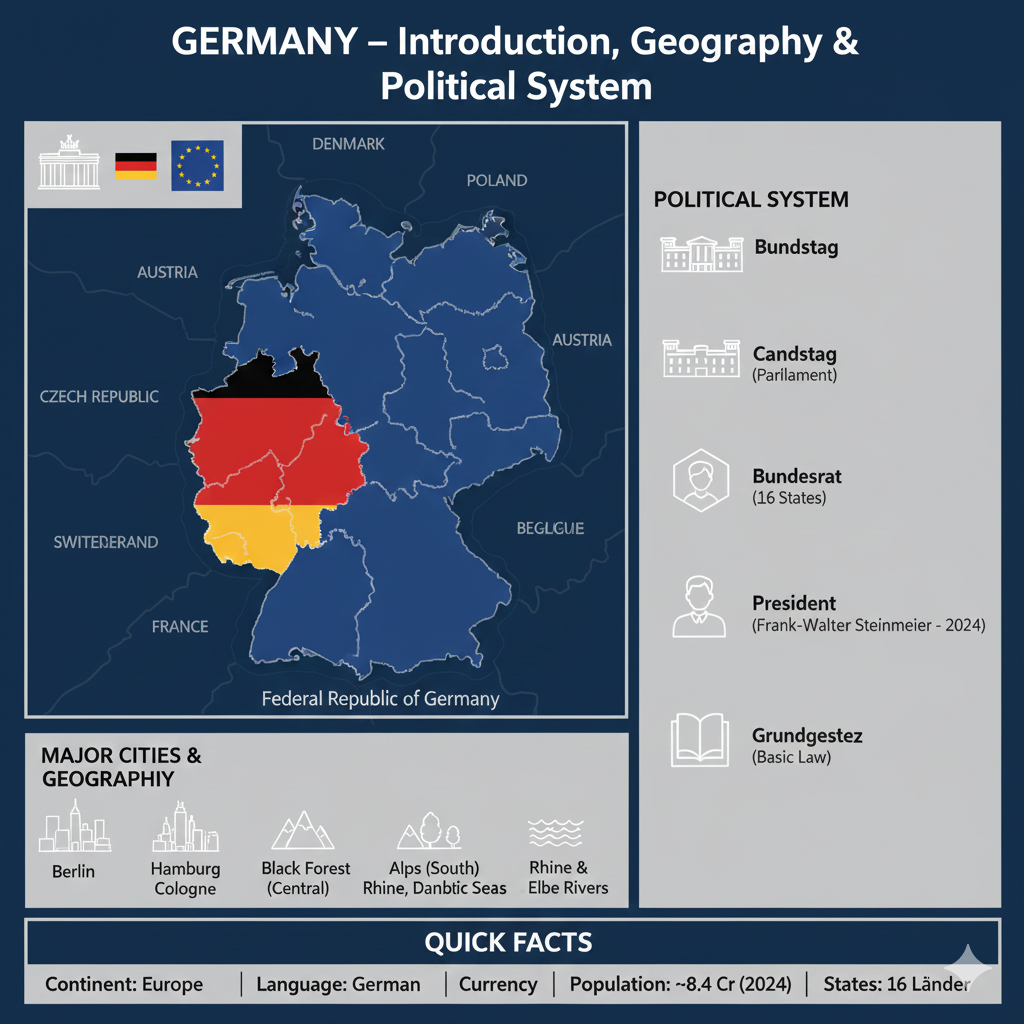
- Continent: Europe
- Capital: Berlin
- Main Cities: Munich, Hamburg, Frankfurt, Cologne
- Language: German
- Currency: Euro (€)
- Population: About 8.4 crore (as of 2024)
- Bordering Countries: Denmark, Poland, Czech Republic, Austria, Switzerland, France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Netherlands
3. Political System
Germany follows a Federal Parliamentary Republic system. Democracy, rule of law, and the constitution called the Basic Law (Grundgesetz) guide its governance.
Key Political Structure
- President: Ceremonial Head
- Chancellor: Head of Government (Current: Olaf Scholz)
- Parliament: Bundestag (Lower House) & Bundesrat (Upper House)
4. Economy of Germany
Germany has the fourth-largest economy in the world. It leads globally in engineering, automotive manufacturing, machinery, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Major Industries
- Automobile
- Engineering
- Chemicals
- Electronics
- Pharmaceuticals
Leading Companies
- BMW
- Mercedes-Benz
- Volkswagen
- Siemens
- Bosch
5. Education and Science
Germany is globally known for offering free or low-cost higher education, making it a preferred destination for international students.
Top Universities
- Heidelberg University
- Technical University of Munich (TUM)
- Humboldt University, Berlin
Germany has also produced many Nobel Prize-winning scientists, including Albert Einstein.
6. Society and Culture
Germany has a rich cultural heritage reflected in its literature, music, art, and philosophy. Its society values punctuality, discipline, and efficiency.
Famous Personalities
- Writers: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
- Composers: Beethoven, Bach
Popular Festivals
- Oktoberfest
- Christmas Market
7. Major Tourist Attractions
- Berlin Wall
- Neuschwanstein Castle
- Black Forest
- Romantic Road
- Cologne Cathedral
Germany welcomes millions of tourists every year with its natural beauty and historic sites.
8. India–Germany Relations
India and Germany share strong economic, educational, technological, and cultural relations.
Key Highlights
- Thousands of Indian students pursue higher education in Germany.
- Both countries cooperate in technology, defence, and green energy.
9. General Information Table
| Subject | Description |
|---|---|
| Capital | Berlin |
| Main Cities | Munich, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Cologne |
| Language | German |
| Currency | Euro (€) |
| Population | Approx. 8.4 Crore (2024) |
| Government System | Federal Parliamentary Republic |
| Current Chancellor | Olaf Scholz (2024) |
| Continent | Europe |
10. Geography and Natural Features
Germany is located in Central Europe and shares borders with nine countries. It is home to rivers, forests, plains, and mountain ranges.
Major Rivers
- Rhine
- Danube
- Elbe
11. Conclusion
Germany is a modern, progressive, and globally influential nation known for its technological development, education system, culture, and disciplined lifestyle. Whether you are a student, entrepreneur, or traveler, Germany offers immense opportunities and experiences.
Germany – Introduction, Geography, and Political System
1. A Brief Introduction to Germany
Germany is a developed and industrialized nation of the European continent, officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany. The country is a global leader in the fields of technology, education, economy, and culture. Its capital is Berlin, and the official language spoken is German. Germany has a population of approximately 8.4 crore and is an important member of the European Union (EU).
Germany is recognized worldwide for its advanced engineering, automobile industry (e.g., BMW, Mercedes-Benz), high-quality education system, and disciplined lifestyle. The nation follows a democratic governance system, and its parliament is called the Bundestag.
Germany has also made significant contributions to science, music, literature, and philosophy. It stands as a global example of peace, innovation, and sustainability.
2. Geographical Location
Germany’s Position in Europe
Germany is a major country located in Central Europe. Its strategic geographical location makes it an economic and political centre of Europe. The nation’s topography, climate, and natural resources have played a crucial role in its development.
Bordering Countries
Germany shares its borders with nine countries, making it a nodal point of Europe:
- North: Denmark
- East: Poland and Czech Republic
- South: Austria and Switzerland
- West: France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands
Sea Coast
Germany also shares coastlines with the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, which play an important role in maritime trade.
Natural Topography
- North: Flat plains
- Central Region: Hills and dense forests
- South: The Alps mountain range, including the highest peak Zugspitze
Major Rivers
- Rhine River: Important for trade and transportation
- Danube: Second-longest river in Europe
- Elbe: Flows through eastern Germany
Climate of Germany
Germany experiences a temperate climate with moderate rainfall throughout the year.
- Summer Temperature: 20°C to 30°C
- Winter Temperature: –5°C to 5°C
Conclusion on Geography
The geographical location of Germany makes it extremely important from an economic, cultural, and strategic point of view in Europe. Its topography and climate support tourism, agriculture, and trade, making life comfortable and prosperous.
3. Political System of Germany
Germany is a Federal Parliamentary Democracy. The governance of the nation functions under its constitution, officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany.
Constitution
The constitution of Germany is called the Grundgesetz (Basic Law), implemented on 23 May 1949. It protects the fundamental rights of citizens, democratic values, and the federal structure.
Structure of Government
The German government is divided into three major organs:
1. Executive
- Federal President: Ceremonial head of state with limited powers. (Current: Frank-Walter Steinmeier, 2024)
- Chancellor: Head of Government, responsible for policymaking and administration. Elected from the majority party in the parliament. (Current: Olaf Scholz, 2024)
2. Legislature
Germany has a bicameral parliament:
- Bundestag (Lower House): Members are directly elected by the people; holds major law-making powers.
- Bundesrat (Upper House): Represents the 16 states (Länder); provides advice and approval on federal laws.
3. Judiciary
The Federal Constitutional Court is the highest judicial authority. It interprets the constitution and protects the fundamental rights of citizens.
Federal Structure
Germany is divided into 16 states (Länder), each with its own government. These states hold powers related to education, policing, and cultural policies.
Electoral System
- Bundestag elections are held every five years.
- The country follows a mixed electoral system (proportional representation + majority system).
Conclusion on Political System
The political system of Germany is a strong example of sustainability, transparency, and democracy. Its federal and parliamentary model ensures efficient governance and effective decision-making for public welfare.

4. Economy of Germany
Germany has one of the most powerful and stable economies in the world. It is the largest economy in Europe and the fourth-largest economy globally (based on GDP). Its economic strength is built on industrial development, export-led production, technological innovation, and a highly skilled workforce.
Main Economic Characteristics
| Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Total GDP (2024) | Approximately $4.5 Trillion (USD) |
| World Rank (GDP) | 4th (After USA, China, Japan) |
| Currency | Euro (€) |
| Unemployment Rate | Approximately 5% (Stable) |
| Economic System | Social Market Economy |
Key Industries
Automobile
- Home to world-famous brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, Audi.
- Germany is often called “The World’s Car Factory.”
Engineering and Machinery
- Production of high-quality industrial machines and equipment.
Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
- Major companies such as BASF and Bayer.
- Leading exporter of chemicals and medical pharmaceuticals.
Electronics and Technology
- Key companies include Siemens and Bosch.
- Rapid innovation in automation, AI, and robotics.
Green Energy and Environment
- Global leader in solar and wind energy.
- Transitioning away from nuclear energy under the policy Energiewende.
Exports and Trade
- Major Exports: Vehicles, machinery, electronic goods, chemicals, medical equipment.
- Major Trading Partners: China, USA, France, Netherlands, UK.
- Germany is the third-largest exporter in the world.
Banking & Finance
- Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank are major pillars of Germany’s finance sector.
- Frankfurt is Europe’s financial capital and home to the European Central Bank (ECB).
Education and Workforce
- Highly educated and technically skilled workforce.
- Strong focus on dual training (practical training + academics).
Conclusion
The German economy is built on industry, innovation, exports, and sustainability. Its workforce, economic policies, and global partnerships make Germany a major economic power. India maintains strong ties with Germany in trade and technological collaboration.
5. Education and Science in Germany
Germany is counted among the world’s leading nations in education and scientific research. The system emphasizes quality, research, and technical training. Most higher education programs are free or low-cost, especially in public universities, attracting thousands of international students.
From School to University: The German Education System
1. School Level (Primary to Secondary)
- Begins with Grundschule (Grades 1–4).
- After Grade 4, students choose different schools based on ability:
- Hauptschule: Focus on vocational training.
- Realschule: General education.
- Gymnasium: Prepares for higher education (ends with Abitur).
2. Higher Education
- Universities (Universitäten): Academic and research-based education.
- Universities of Applied Sciences (Fachhochschulen): Practical and technical learning.
- Most public universities offer tuition-free education.
Admission Process
- 12th standard or equivalent qualification is required.
- Foreign students must clear DSH or TestDaF (German language proficiency test).
- Direct admission after Grade 12 from India is generally not possible—students must complete Studienkolleg.
Famous Universities
| University | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Heidelberg University | Germany’s oldest university (Founded 1386) |
| Technical University of Munich (TUM) | Leader in engineering & technology |
| Humboldt University of Berlin | Renowned for humanities and research |
| RWTH Aachen University | Famous for science and industrial innovation |
Science and Research Contributions
Key Areas of Contribution
- Physics, Chemistry, Engineering, Space Science
- Innovations in automobiles and robotics
- Leadership in green technology and environmental engineering
Famous Scientists
- Albert Einstein: Theory of Relativity
- Robert Koch: Father of Bacteriology
- Max Planck: Founder of Quantum Physics
- Otto Hahn: Pioneer of Nuclear Chemistry
Major Research Institutes
- Max Planck Society: World-class research organization
- Fraunhofer Society: Leading applied science institute
- Leibniz Association: Research in social & natural sciences
Special Features for International Students
- Thousands of students from India and other countries study in Germany.
- DAAD offers scholarships for international students.
- Part-time work allowed during studies.
- 18-month job-search visa available after graduation.
Conclusion
Germany’s education system is robust, research-driven, and globally respected. With high academic standards, strong scientific output, and supportive policies, Germany stands as a global hub for innovation, knowledge, and nation-building.
6. German Society and Culture
German society is a beautiful blend of tradition and modernity. The country is renowned for its cultural heritage, art, music, philosophy, and disciplined lifestyle. Values like punctuality, hard work, honesty, and quality form the foundation of German social life.
Characteristics of German Society
| Subject | Description |
|---|---|
| Population | Approximately 84 million (2024 estimate) |
| Ethnicity | Mostly German; minorities include Turkish, Polish, Syrian, etc. |
| Religion | Christianity (Protestant & Catholic), Islam, Atheism |
| Languages | Mainly German; English, Turkish, Arabic also spoken |
| Family Structure | Nuclear family system is common |
Social Life and Values
- Punctuality and discipline are core values.
- Honesty, independence, and respect for privacy are important.
- Gender equality holds great social and political significance.
Cultural Heritage
Literature and Philosophy
- Goethe: Author of "Faust"
- Schopenhauer and Nietzsche: World-renowned philosophers
- Immanuel Kant: Contributor to moral philosophy
Music
- Birthplace of classical music masters such as Beethoven, Bach, Brahms, Weber.
- Important contributor to modern techno and electronic music.
Art and Architecture
- Prominent cities: Berlin, Munich, Dresden
- Popular styles: Gothic, Baroque, Modern architecture
Famous Festivals and Traditions
Oktoberfest
- World’s largest beer festival held in Munich.
- Folk music, traditional costumes, dance, and food.
Christmas Markets
- Held in December with decorations, gifts, and festive food.
Karneval
- Celebrated in February with colorful costumes and parades.
Clothing and Food
Traditional Clothing
- Men: Lederhosen
- Women: Dirndl
Food & Drink
- Main dishes include Bratwurst, Schnitzel, Sauerkraut, Pretzel, and various breads.
- Beer and bread are iconic elements of German cuisine.
Conclusion
The culture of Germany is rooted in a deep historical legacy while embracing modern values. The blend of discipline, creativity, freedom, and collective responsibility makes Germany a strong, balanced, and culturally rich nation.

7. Major Tourist Destinations of Germany
Germany is a wonderful country filled with natural beauty, historic forts, modern cities, and rich cultural heritage. Whether you are a history lover, an art enthusiast, or a nature explorer, Germany offers something unique for every type of traveler.
1. Neuschwanstein Castle – Bavaria
- This fairy-tale castle was built by King Ludwig II.
- It inspired the iconic Disney Cinderella Castle.
- Located amidst the Alps, it is the most famous castle in Germany.
2. Berlin Wall & Brandenburg Gate – Berlin
- The Berlin Wall stands as a historic symbol of the Cold War, now preserved as a memorial.
- The nearby Brandenburg Gate represents German unity and peace.
3. Cologne Cathedral – Cologne
- One of Europe’s most magnificent Gothic cathedrals.
- A designated UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Its height (approx. 157 meters) makes it one of Germany’s most visited landmarks.
4. Black Forest – South-West Germany
- Known for dense forests, mountain villages, lakes, and waterfalls.
- Home of the famous Cuckoo Clock.
- Ideal for trekking, hiking, and experiencing natural tranquility.
5. Romantic Road
- A 350-km scenic route passing through historic towns, castles, and wine regions.
- Includes picturesque towns like Rothenburg, Dinkelsbühl, and Füssen.
6. Munich
- Capital of the state of Bavaria.
- A beautiful blend of tradition and modernity.
- Famous for Oktoberfest, museums, art galleries, and Bavarian culture.
7. Hamburg
- One of Europe’s major port cities.
- Known for its canals, lakes, and historic warehouse district (Speicherstadt – UNESCO Site).
- Perfect destination for lovers of modern architecture and music.
8. Heidelberg
- A charming old university town.
- Known for its river views, hilltop castle, and medieval architecture.
- Popular for its literary and cultural environment.
9. Zugspitze – Highest Peak in Germany
- Located in the Alps mountain range.
- Ideal for skiing, snowboarding, and scenic cable-car rides.
- Height: 2,962 meters above sea level.
10. Dresden
- A cultural and historical city located on the banks of the Elbe River.
- Attractions include Frauenkirche, Zwinger Palace, and Semper Opera House.
- A remarkable example of reconstruction after World War II.
Conclusion
Germany offers a diverse tourism experience—combining history, culture, nature, adventure, and modern lifestyle. Whether you want to explore castles, enjoy scenic mountain views, or relax in peaceful German villages, the country offers unforgettable experiences for every traveler.

8. Relations Between India and Germany
Relations between India and Germany are strong, deep, and multidimensional. Both nations share common values such as democracy, human rights, environmental protection, and global peace. Over time, these relations have become increasingly robust and diverse across political, economic, educational, cultural, and scientific areas.
Political Relations
- India and Germany are Strategic Partners.
- Since 2001, the two countries have held India–Germany Intergovernmental Consultations (IGC) — a mechanism India shares with very few nations.
- Regular high-level meetings take place between Indian Prime Ministers and German Chancellors.
- Germany is India’s largest trading partner within the European Union.
Economic and Trade Relations
| Area | Statistics / Facts |
|---|---|
| Bilateral Trade | USD $30+ Billion (2023–24 estimate) |
| Major Exports (India → Germany) | Gems & Jewellery, Pharmaceuticals, Textiles, IT Services |
| Major Imports (Germany → India) | Machinery, Automobiles, Chemicals, High-tech Equipment |
| German Companies in India | 1800+ (including Siemens, Bosch, BMW, etc.) |
- Germany has shown strong interest in India’s Make in India initiative.
- India is emerging as a major technology and startup hub for German businesses.
Education and Academic Collaboration
- Thousands of Indian students pursue higher education in German universities, especially in STEM fields.
- DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service) provides scholarships to Indian students.
- The Goethe-Institut (Max Mueller Bhavan) promotes German language studies in India.
- There are several academic MoUs and joint research programs between IITs, IISc, and leading German universities.
Science and Technology Cooperation
- Both countries collaborate in biotechnology, environment, AI, space research, and energy.
- The Indo-German Science & Technology Center (IGSTC) supports joint research projects.
Renewable Energy and Environmental Cooperation
- Strong partnership in solar energy and green hydrogen development.
- Germany has supported India’s National Solar Mission (NSM) with technical and financial assistance.
- The Indo-German Green and Sustainable Development Partnership focuses on climate-friendly solutions.
Cultural and People-to-People Contact
- Max Mueller Bhavan (Goethe-Institut) plays a key role in connecting Indians with German culture and language.
- German film festivals, art exhibitions, concerts, and academic conferences are held across India.
- Indian Yoga, Ayurveda, and Bollywood are highly popular in Germany.
Conclusion
India–Germany relations are built on trust, cooperation, and shared interests. The two nations are working closely to address global challenges such as climate change, technological innovation, education, and world peace. This partnership is expected to grow even stronger and more diverse in the years ahead.
Conclusion
Germany is not only a leading European nation but also a global symbol of science, technology, education, innovation, environmental protection, and cultural values. Along with its historic castles and modern cities, Germany’s social structure, democratic governance, and economic progress make it a respected nation worldwide.
The relationship between India and Germany shows how two countries with different cultural backgrounds can build a strong and successful partnership based on shared values, mutual respect, and cooperation.
References
- Federal Foreign Office of Germany (Auswärtiges Amt)
- Germany – Country Profile, Federal Ministry of the Interior
- Statistisches Bundesamt (Federal Statistical Office of Germany)
- German Missions in India – Indo-German Relations
- CIA World Factbook – Germany
- Encyclopaedia Britannica – Germany
- Study in Germany – DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service)