Canada
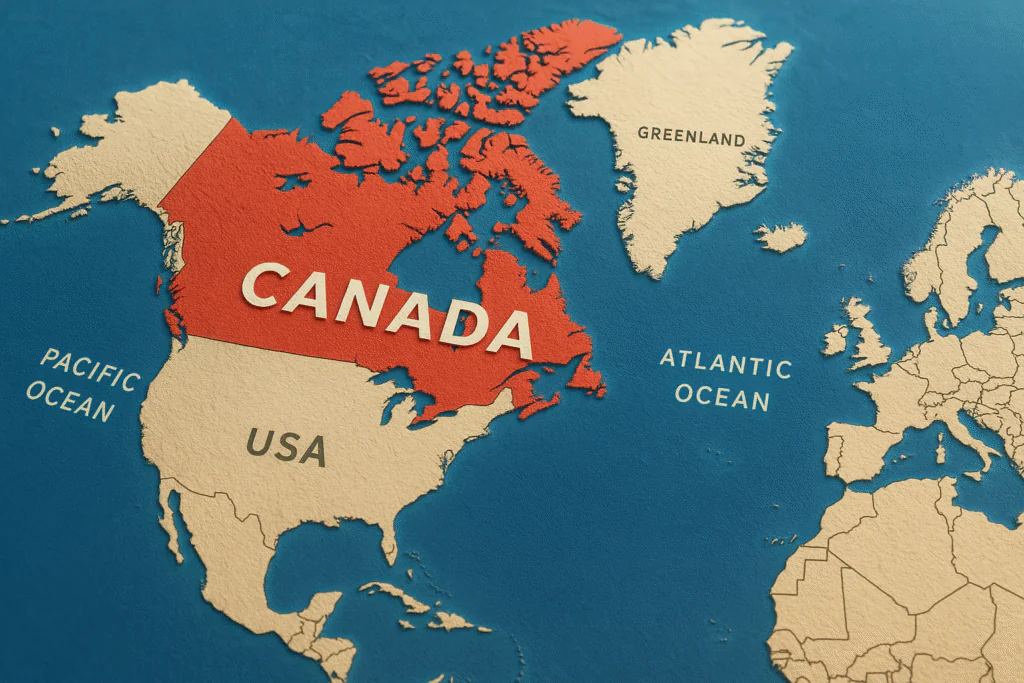
Canada is a huge and developed country located in North America. It is the second largest country in the world and is famous for its natural beauty, multicultural society, high standard of living and economic progress. Canada is considered an ideal nation globally due to peace, education, health and employment opportunities.
Geographical Form of Canada
Location and Border
Canada is located in the North American continent. It has the United States of America (USA) to the south, the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
Major Rivers and Lakes
- St. Lawrence River
- Fraser River
- Great Lakes
Climate
The climate of Canada varies from region to region. Cold Arctic climate is found in the north, while temperate climate is found in the southern parts.
History of Canada
Early History
The original inhabitants of Canada were the “Inuit” and “First Nations” communities.
Colonial Period
The French and later the British established colonies here in the 16th century. Canada received Dominion status in 1867 and gradually developed into an independent nation.
Politics and Administration of Canada
Government System
- Canada is a constitutional monarchy.
- The parliamentary system here is similar to that of Britain.
- King Charles III is the formal head of state of Canada.
Major Political Institutions
- Prime Minister
- Parliament
- Provincial Governments
Economy of Canada
Major Industries
- Natural Resources (Oil, Gas, Minerals)
- Agriculture and Forestry
- IT and Service Sector
- Tourism
Trade and Cooperation
Canada is a member of the G7, G20, and WTO. It trades extensively with the US, China, and the European Union.
Society and Culture of Canada
Multicultural Society
Canada is one of the countries in the world with the highest rate of immigration. Here we can see the integration of different religions, languages and cultures.
Official Languages
- English
- French
Education and Health
Canada’s education system and health system are considered excellent globally.
List of Tourist Destinations
Main Tourist Attractions
- Niagara Falls
- Rocky Mountains
- Banff National Park
- Historical sites of Ottawa and Toronto

Amazon Product
Click below to view full product details and the latest price on Amazon.
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
Canada is not only geographically vast, but is also a very prosperous nation socially and economically. Its education, health, multicultural society and natural beauty make it one of the best countries in the world. This country will remain a symbol of peace and development in the future as well.
Introduction to Canada
Canada is a huge and developed country in North America. It is the second largest country in the world in terms of area. Canada is famous all over the world for its natural beauty, clean environment, high standard of living, excellent education and health services. The multicultural society, economic progress and employment opportunities here make it an ideal nation. For peace and stability, Canada is counted among the safest and most attractive countries in the world.
Geographical Features of Canada
Canada is a huge country located in North America, whose total area is about 99 lakh square kilometers. It is the second largest country in the world in terms of area. Its geographical structure includes mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, lakes and wide coastal areas, which make it rich in natural terms.
Location and Boundary
- Most of Canada is located in the Northern Hemisphere.
- It is bordered by the United States of America (USA) to the south,
- Arctic Ocean to the north,
- Atlantic Ocean to the east,
- and Pacific Ocean to the west.
- Its coastline is counted among the longest coastlines in the world.
Major Rivers and Lakes
Canada is very rich in terms of water resources. The rivers and lakes here not only enhance the natural beauty but are also helpful in water transport, irrigation and hydroelectric power generation.
- St. Lawrence River – Major route of trade and transportation.
- Fraser River – Famous for fisheries and hydropower.
- Great Lakes – The world’s largest chain of freshwater lakes.
Climate
The climate of Canada is diverse. Cold arctic climate is found in the northern part, while summers are moderate and winters are cold in the central and southern parts. The influence of marine climate is seen in the coastal areas.
👉 The geographical structure of Canada provides the basis for its natural beauty, rich ecology and economic activities (mining, agriculture, tourism, fisheries).
Location and Extent
Canada is located in the North American continent and is a very large country geographically.
- Latitudinal position: The country is spread from approximately 41° North to 83° North latitude and 52° West to 141° West longitude.
- In the south: It shares its longest international land border with the United States of America (USA), called the world’s longest demilitarized border.
- In the north: The Arctic Ocean is located here with many islands and glaciated areas.
- In the east: The Atlantic Ocean connects Canada to Europe.
- In the west: The Pacific Ocean connects it to Asia.
👉 Thus, Canada is surrounded by oceans on all four sides and it shares its land border with America only in the south.
Major Rivers and Lakes of Canada
Canada is one of the richest countries in the world in terms of water resources. There are innumerable rivers and lakes here, which not only enhance the natural beauty but are also important for transportation, irrigation, hydroelectricity production and fisheries.
Major Rivers
St. Lawrence River
St. Lawrence River – This river connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean and is considered the lifeline of Canada’s trade and transportation.
Fraser River
Fraser River – This river flowing in British Columbia is famous for hydroelectricity and fisheries (especially salmon fish).
Mackenzie River
Mackenzie River – It is the longest river in Canada, which flows through the Northwest Territories and falls into the Arctic Ocean.
Yukon River
Yukon River – It flows through Alaska and Yukon province and has been famous since the historic “Gold Rush” period.
Major Lakes
Great Lakes
Great Lakes – This group of lakes (Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie and Ontario) is the chain of the largest freshwater lakes in the world.
Great Bear Lake
Great Bear Lake – This is the largest lake located entirely in Canada.
Great Slave Lake
Great Slave Lake – This lake is located in the Northwest Territories and water transport here is important.
Lake Winnipeg
Lake Winnipeg – This lake is located in the province of Manitoba and is known for fish production.
👉 These rivers and lakes have not only created the geographical identity of Canada but have also influenced its economic development and cultural history.
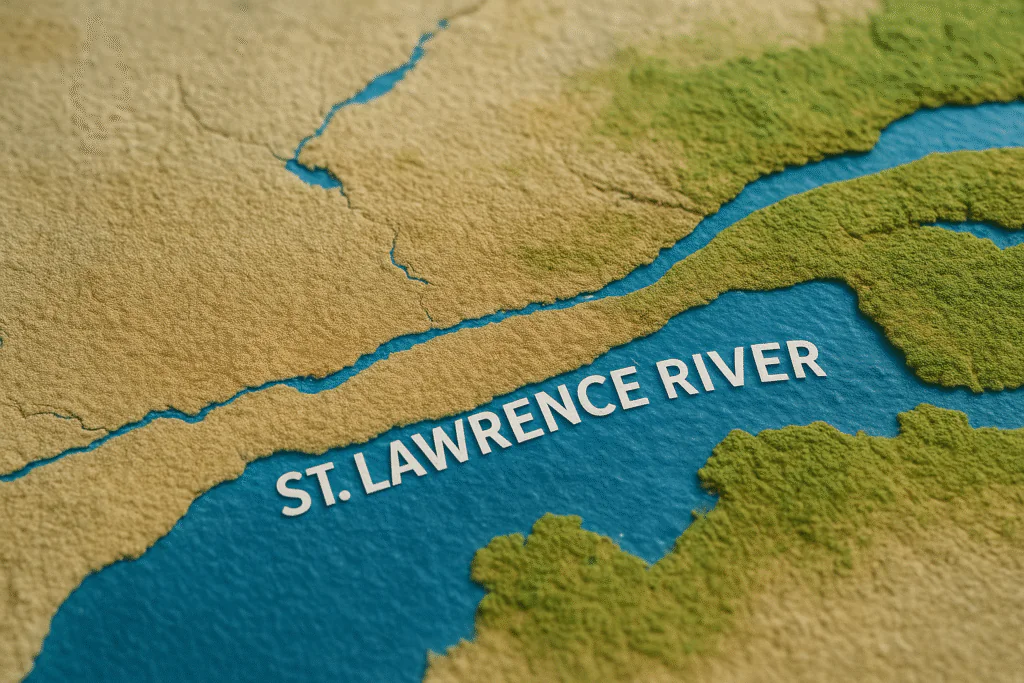
St. Lawrence River
ST. LAWRENCE RIVER
The St. Lawrence River is one of the most important and famous rivers of Canada. It is called the lifeline of Canada because it is not only naturally beautiful but is also extremely important from an economic, commercial and cultural point of view.
Geographical Location
- This river originates from the Great Lakes and travels a distance of about 1,197 kilometers.
- Ultimately it meets the Atlantic Ocean.
- This river flows mainly through the province of Quebec and also forms part of the border between Canada and America.
Key Features
- This river provides international trade routes to Canada.
- Due to the St. Lawrence Seaway, large ships can travel directly from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes.
- Cities like Montreal and Quebec City located on its banks are important economically and culturally.
Economic and Cultural Importance
- Trade and transportation: This river is the backbone of Canada’s import-export.
- Hydroelectricity generation: Several major hydropower projects operate here.
- Tourism: Its natural beauty and historical sites attract millions of tourists.
👉 Thus, the St. Lawrence River is not only a natural heritage but also the mainstay of Canada’s economic strength and international identity.
Fraser River
Fraser River is the longest and most important river in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is world famous for its natural beauty, hydroelectric potential and fisheries (especially salmon fish).
Geographical Location
- The length of Fraser River is about 1,375 kilometers.
- It originates from the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia.
- This river flows southwest and finally meets the Pacific Ocean.
Key Features
- Vancouver is located on the banks of this river and is a major business and tourism center.
- The Fraser River Valley is extremely fertile.
- The salmon fish of this river are world famous.
Economic and Cultural Importance
- Fisheries: Largest source of salmon fish in Canada.
- Hydroelectricity: Several major hydropower projects run on this river.
- Agriculture: The fertile valley supports extensive farming.
- Tourism: The river's scenic beauty attracts thousands of tourists.

Amazon Product
Click below to view full product details and the latest price on Amazon.
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
👉 The Fraser River is considered the economic heartbeat and natural heritage of British Columbia.
Great Lakes (Great Lakes)
The Great Lakes are a group of five large freshwater lakes located in North America. They form the world's largest chain of freshwater lakes shared between Canada and the United States.
List of Great Lakes
- Lake Superior – Largest freshwater lake in the world.
- Lake Michigan – Located entirely in the US.
- Lake Huron – Known for long coastlines and islands.
- Lake Erie – Shallow lake with high fish production.
- Lake Ontario – Smallest lake, connected to the Atlantic Ocean via St. Lawrence River.
Key Features
- The lakes provide about 20% of the world's total surface freshwater.
- The Great Lakes system covers 2,44,000 square kilometers.
- Linked rivers and canals form the St. Lawrence Seaway, a major international trade route.
Economic and Cultural Importance
- Trade and transportation: Heavy shipping between Canada and the US.
- Fisheries: Major source of fish production.
- Agriculture and water supply: Lakes supply irrigation and drinking water.
- Tourism: Beaches, islands, and water sports attract tourists.
👉 The Great Lakes are not only part of Canada's geographical identity but also vital to its economy and culture.
Climate of Canada
The geographical area of Canada is very vast, so the climate varies greatly by region. The northern part is extremely cold, while the southern part has a pleasant and temperate climate.
Arctic Climate (Northern Part)
- Located in the Arctic Circle.
- Snow remains frozen most of the year.
- Temperatures stay far below zero.
- Sparse population and challenging living conditions.
Prairie Climate (Central Part)
- Vast plains known as Prairies.
- Warm summers and long cold winters.
- Best agricultural region, called the “Granary of Canada”.
Temperate Climate (Southern Region)
- Found in Ontario and Quebec.
- Moderate summers and very cold winters.
- Highest population density.
Maritime Climate (Western Coastal Region)
- Found in British Columbia and Vancouver.
- Mild weather throughout the year.
- High rainfall and milder winters.
👉 Thus, the climate of Canada is extremely diverse due to its geographical expanse and proximity to three oceans.

History of Canada
The history of Canada is extremely rich and diverse. This country shows a long journey from the civilization of ancient natives to colonial rule and finally becoming an independent and developed nation.
Early History
- The first inhabitants of Canada were the Inuit, First Nations and Métis communities.
- These people depended on hunting, fishing and gathering.
- They had their own distinct culture, languages and traditions.
European Arrival and Exploration (15th–16th Century)
- In 1497, John Cabot discovered the Newfoundland region.
- In 1534, Jacques Cartier explored the area of the St. Lawrence River.
- After this, European traders started the fur trade here.
Colonial Period
- In the 17th century, the French established a colony called “New France”.
- After the Treaty of Paris (1763), Britain took over a large part of Canada from France.
- During British rule, the influence of the English language and parliamentary traditions increased.
Confederation of Canada (1867)
- On 1 July 1867, Canada received the status of “Dominion of Canada”.
- Initially, it included four provinces: Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
- Gradually, other provinces and territories joined to form today’s 10 provinces and 3 territories.
Journey Towards Independence
- The Statute of Westminster (1931) gave legislative independence to Canada.
- In 1982, the Constitution Act provided full constitutional independence and Canada adopted its own constitution.
Modern Canada
- Today Canada is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.
- It is world famous for peace, human rights, multicultural society and economic development.
👉 The history of Canada shows how this country passed through Indigenous traditions, French and British colonial rule, and independence movements to become a strong and developed nation.
Early History of Canada
The early history of Canada is linked to its Indigenous Peoples. Long before the European arrival, diverse communities lived here with rich traditions and culture.
Indigenous Communities
- Inuit – Lived in the Arctic regions of northern Canada.
- First Nations – Spread across various regions depending on hunting, agriculture and fishing.
- Métis – Communities formed by the mixing of Indigenous people and European settlers.
Lifestyle and Culture
- These people lived closely with nature.
- Main livelihood came from hunting (deer, bear, bison), fishing and gathering wild plants.
- They had distinct languages, art, religion and social systems.
- Many Canadian folklore, dances and traditions originated from these communities.
Before European Arrival
- Indigenous people had established trade routes across Canada.
- Natural resources like fur, copper and stones were exchanged.
👉 Early history tells us that Canada is built on the civilization and culture of Indigenous communities, whose heritage remains a vital part of Canada’s identity.
Colonial Period of Canada
Canada’s colonial period began in the 16th century with the arrival of European explorers and settlers, deeply shaping Canada's political, cultural and economic framework.
French Colonies (New France)
- In 1534, Jacques Cartier explored the St. Lawrence River and claimed land for France.
- In 1608, Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec City.
- French colonies were mainly based on the fur trade.
- Missionaries spread Christianity and built cultural ties with Indigenous communities.
British Colonies
- By the late 17th century, British explorers and settlers began arriving.
- After the Treaty of Paris (1763), Britain took control of Canada from France.
- British rule strengthened the influence of English language, British law and parliamentary system.

Amazon Product
Click below to view full product details and the latest price on Amazon.
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Conflict and Cultural Tension
- Frequent conflicts occurred between French and British colonies.
- Tensions existed between French Catholics and British Protestants.
- Despite conflict, French culture remained strong especially in Quebec.
From Colony to Dominion
- Canada gradually gained administrative autonomy during British rule.
- In 1867, the “Dominion of Canada” was established under the British North America Act.
👉 The colonial era laid the foundation of Canada’s bilingual (English–French) culture and political system.
Politics and Administration of Canada
Canada is a Constitutional Monarchy and Federal Parliamentary Democracy. Its political and administrative structure reflects British traditions while maintaining Canadian identity.
Constitutional System
- The British monarch (currently King Charles III) is the formal head of state.
- The monarch is represented by the Governor General in Canada.
- The real power lies with the elected Parliament and the Prime Minister.
Parliamentary System
The Parliament of Canada consists of two houses:
House of Commons
- Lower house; members are elected by the people.
- The leader of the majority party becomes the Prime Minister.
Senate
- Upper house; members are appointed by the Governor General on the Prime Minister’s advice.
- Main role is to review and refine laws.
Executive
- The Prime Minister is the head of the government.
- He appoints cabinet ministers and sets national policies.
- The Governor General formally passes bills.
Federal Structure
- Canada has 10 provinces and 3 territories.
- Provinces handle education, health and natural resources.
- The central government handles defence, foreign policy and currency.
Judiciary
- The Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court.
- The judiciary protects the Constitution and resolves federal–provincial disputes.
Political Parties
- Liberal Party
- Conservative Party
- New Democratic Party (NDP)
- Bloc Québécois
- Green Party
👉 Thus, Canadian politics is a blend of British parliamentary tradition and Canadian federalism, built on democracy, bilingualism and multiculturalism.
Canada’s System of Government
Canada’s system of governance is known as Constitutional Monarchy and Parliamentary Democracy. It is inspired by Britain but structured according to Canadian federal needs.
Constitutional Monarchy
- King Charles III is the formal head of state.
- Represented by the Governor General.
- Real power lies with the elected government.
Parliamentary Democracy
- People elect representatives to the House of Commons.
- The leader of the majority party becomes the Prime Minister.
- Senators are appointed and review legislative bills.
Federal Structure
- Canada has 10 provinces and 3 territories.
- Central Government handles defence, foreign affairs, currency.
- Provinces handle education, health, natural resources.
👉 In simple words: King = Formal Head, Prime Minister = Real Head, Parliament = Legislative Power, Provinces = Regional Governments.
Major Political Institutions of Canada
Prime Minister
- The real head of the Canadian government.
- Leader of the majority party in House of Commons.
- Appoints cabinet and leads national policies.
Parliament of Canada
House of Commons
- Lower house with elected representatives.
- Prime Minister and cabinet come from here.
Senate
- Upper house; appointed members.
- Reviews and amends laws.
Governor General
- Represents the British monarch in Canada.
- Approves laws and appoints Prime Minister.
Provincial Governments
- 10 provinces and 3 territories.
- Each has its own assembly and Premier.
- Handles education, health, transport, and local administration.
Judiciary
- Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court.
- Protects Constitution and legal rights.
👉 Canada’s political institutions work together to maintain a stable, democratic and multicultural governance system.

Amazon Product
Click below to view full product details and the latest price on Amazon.
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Economy of Canada
Canada is one of the most developed and stable economies in the world. The country is based on natural resources, modern technology, and highly skilled human resources. High standard of living, social security, and global trade partnerships make its economy strong.
Major Industries
- Natural Resources – Oil, gas, gold, uranium, and minerals.
- Agriculture and Forestry – Production of wheat, barley, canola oil, and timber.
- IT and Services Sector – Information technology, banking, and communication services.
- Tourism – Boosted by Niagara Falls, the Rocky Mountains, and national parks.
Trade and Partnerships
- Member of G7, G20, WTO, and NAFTA (now USMCA).
- Largest trading partners: United States, China, and the European Union.
- Main exports: Oil, minerals, timber, automobiles, and agricultural products.
Financial System
- Canada’s banking system is extremely safe and reliable.
- The Bank of Canada is the central bank responsible for monetary policy.
- The Canadian Dollar (CAD) is the official currency.
Employment & Living Standard
- Diverse job opportunities in health, education, IT, and mining.
- High salaries, social security, and quality of life attract global immigrants.
👉 In conclusion, Canada’s economy is based on natural resources, modern technology, and international trade. It is stable, developed, and globally influential.
Major Industries of Canada
Canada’s economy is based on many diverse industries. Its vast land, abundance of natural resources, and modern technology make it one of the developed nations of the world.
Natural Resources Industry
- Production of oil, natural gas, coal, gold, uranium, and diamonds.
- Canada is one of the world’s largest oil and gas exporters.
- Mineral and energy resources form the backbone of the economy.
Agriculture & Forestry
- Canada is known as the “Granary of the World”.
- Major production of wheat, barley, canola, and pulses.
- Forestry supports the wood and paper industry.
Industry & Manufacturing
- Automobile manufacturing is strong, especially in Ontario.
- Aerospace, machinery, and metal industries are major contributors.
- Food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing are also crucial.
Information Technology and Services Sector
- Toronto, Vancouver and Montreal are major IT and startup hubs.
- Banking, financial services and telecommunications strengthen this sector.
Tourism
- Natural beauty and famous destinations such as Niagara Falls, Rocky Mountains and Banff National Park attract millions.
- Tourism generates huge revenue every year.
👉 Thus, Canada’s natural resources, agriculture, manufacturing, IT, and tourism industries are the strongest pillars of its economy.
Trade and Cooperation of Canada
Canada’s economy is largely based on international trade and global cooperation. Due to vast natural resources, modern industries and strategic geographical position, Canada plays an important role in world trade.
Major Trade Partners
United States of America (USA)
- Canada’s largest trading partner.
- Over 70% of exports go to the US.
- Main exports: Automobiles, oil, gas, agricultural products.
China
- Second largest trade partner.
- Exports include agricultural goods, minerals and energy products.
European Union (EU)
- Trade includes technical goods, pharmaceuticals and machinery.
Trade Organizations & Memberships
- G7 & G20 – Group of the world’s largest economies.
- WTO – Promotes free and fair trade.
- USMCA – Largest free trade agreement in North America.
Exports & Imports
Exports
- Oil and gas
- Minerals and metals
- Agricultural products (wheat, canola, pulses)
- Automobiles and machinery
Imports
- Electronics and machinery
- Industrial equipment
- Pharmaceuticals and consumer goods
- Vehicles and technology products
Global Cooperation
- Active member of the United Nations (UN).
- Participates in international peacekeeping missions.
- Supports climate change action, human rights and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
👉 In summary, Canada’s trade and global cooperation are the main pillars of its economy. The US, China and the EU are key partners, and its memberships in G7, G20 & WTO strengthen its global influence.

Society and Culture of Canada
Canada is famous all over the world for its multicultural identity, social harmony and rich cultural diversity. Here one can see a confluence of different religions, languages and traditions.
Multicultural Society
- Canada is often called the “Immigrants’ Nation” because people from almost every country of the world have settled here.
- Indian, Chinese, French, British, African and Middle-Eastern communities live here in large numbers.
- Despite cultural differences, everyone enjoys equal rights and opportunities.
Official Languages
- English and French are the two official languages of Canada.
- French is spoken more in Quebec, while English dominates other provinces.
Religion and Belief
- Christianity is the major religion of Canada.
- Followers of Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Buddhism and Judaism are also present in large numbers.
- Religious freedom is a core part of Canada’s social identity.
Education & Healthcare
Education
- Canada’s education system is considered world-class.
- Universities like the University of Toronto, McGill University and the University of British Columbia are globally renowned.
Healthcare
- Canadian health services are public-funded, providing low-cost or free essential care.
Festivals & Traditions
- Canada Day – National Day on July 1.
- Thanksgiving Day – Celebration of harvest and gratitude.
- Christmas and Easter – Major Christian festivals.
- Multicultural festivals like Diwali, Chinese New Year and Eid are celebrated widely.
Arts & Sports
- Canada is known for its contributions to literature, music and film.
- Ice Hockey is considered the national sport.
- Lacrosse holds the status of the official summer sport.

Amazon Product
Click below to view full product details and the latest price on Amazon.
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
👉 In conclusion, Canada’s society and culture are based on diversity, tolerance and harmony. It is culturally rich and globally admired.
Multicultural Society of Canada
Canada is considered one of the world’s largest multicultural societies. People of different races, religions and languages live together while preserving their traditions.
Impact of Immigration
- Canada welcomes millions of immigrants every year.
- Indian, Chinese, African, French, British and Arab communities form major segments.
- Immigration boosts economic growth and cultural diversity.
Equality & Tolerance
- The Canadian government guarantees equal rights for all citizens.
- Discrimination based on race, language, religion or gender is prohibited.
- Social tolerance and mutual respect are key strengths of Canadian society.
Cultural Diversity
- People of many religions and cultures live together.
- Festivals such as Diwali, Eid, Chinese New Year, Hanukkah and Christmas are celebrated collectively.
Linguistic Diversity
- English and French are the official languages.
- Punjabi, Hindi, Chinese, Arabic and Spanish are also spoken widely.
👉 In conclusion, Canada’s multicultural society makes it one of the most tolerant and progressive countries in the world.
Official Languages of Canada
Canada follows a strong bilingual policy, giving official status to two languages.
English
- The most widely spoken language in Canada.
- Used in government, business, education and technology.
- Dominant in provinces like Ontario, Alberta and British Columbia.
French
- The second official language.
- Spoken mainly in Quebec, where French culture is deeply rooted.
- New Brunswick is the only officially bilingual province.
Bilingual Policy
- All government documents and services are provided in both languages.
- Citizens can receive services in either English or French.
Other Languages
- Punjabi, Hindi, Chinese, Arabic, Spanish and Tagalog are widely spoken due to immigration.
👉 In conclusion, the official languages of Canada reflect its bilingual identity but its linguistic diversity makes it a true multicultural nation.
Education & Healthcare in Canada
Canada’s education and health systems are among the best in the world and form the foundation of its high standard of living.
Education System
Public Education
- Primary to secondary education is free and high in quality.
- Each province has its own education department, but high standards are maintained nationwide.
Universities & Higher Education
- Canadian universities rank among the world’s best.
- Top institutions: University of Toronto, McGill University, University of British Columbia, University of Alberta.
- Canada is known for research and technical education.
Immigrants & International Students
- Canada is a popular destination for foreign students.
- Education is available in both English and French.
Healthcare System
Public Healthcare
- Healthcare services are government-funded.
- Citizens and permanent residents receive essential medical services at little or no cost.
Provincial Responsibility
- Each province manages its own health system.
- Hospital and doctor fees are covered by the government.
Quality & Availability
- Canadian healthcare is safe, accessible and high quality.
- Preventive healthcare is given special importance.
Key Highlights
- Equal access to education and healthcare.
- Significant government spending on both sectors.
- High standard of living and strong welfare system.
👉 In conclusion, Canada’s education and health system make it an ideal welfare state where citizens receive quality services throughout their lives.

Tourist Places in Canada
Canada is famous all over the world for its natural beauty, historical heritage and modern cities. Its magnificent lakes, mountains, national parks and multicultural cities attract tourists.
Major Tourist Destinations in Canada
Niagara Falls (Ontario)
- One of the most famous waterfalls in the world.
- Tourists can go near the waterfall by boat (Maid of the Mist).
Banff National Park (Alberta)
- The oldest national park in Canada.
- Famous for lakes, snowy peaks and wildlife.
Toronto (Ontario)
- The largest city in Canada.
- CN Tower and Toronto Islands are major attractions.
Vancouver (British Columbia)
- A beautiful blend of nature and modernity.
- Stanley Park and Capilano Suspension Bridge are famous.
Québec City (Quebec)
- A UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Known for European-style buildings and Château Frontenac.
Ottawa (Ontario)
- Capital of Canada.
- Parliament Hill, Rideau Canal and National Museum are major attractions.
Jasper National Park (Alberta)
- Part of the Rocky Mountains.
- Best for trekking, camping and wildlife viewing.
Prince Edward Island
- Famous for beaches and natural beauty.
- Known as the setting of the novel “Anne of Green Gables”.
Whistler (British Columbia)
- World-famous ski resort.
- Host of the 2010 Winter Olympics.
Churchill (Manitoba)
- Known as the “Polar Bear Capital of the World”.
- Famous for viewing polar bears and Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis).
Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls is a world-famous waterfall located on the border of Canada and the USA. It is situated on the Niagara River flowing between Ontario (Canada) and New York State (USA).
Main Features
- The waterfall has three parts:
- Horseshoe Falls – Canadian side.
- American Falls – US side.
- Bridal Veil Falls – US side.
- Horseshoe Falls is the largest and most attractive.
- About 3,000 tons of water falls every second.
Tourist Attractions
- Maid of the Mist Boat Tour – Takes visitors close to the waterfall.
- Niagara Parks – Beautiful green parks.
- Illumination Show – Waterfalls lit up with colorful lights at night.
- Niagara SkyWheel – Panoramic aerial view.

81-Key Electronic Cash Register / POS System
Ideal for small businesses, shops and retail checkout — supports multiple sales functions, numeric keypad, and clear display. :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}
👉 View on Amazon*As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Best Time to Visit
- May to September – Peak tourist season.
- Winter gives a partially frozen and unique view.
Special Significance
- One of the natural wonders of the world.
- Major contributor to Canada’s tourism economy.
- A popular honeymoon destination.
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also called “The Rockies,” are one of the most magnificent mountain ranges in North America. In Canada, they lie across Alberta and British Columbia.
Key Features
- Length: About 4,800 km.
- Elevation: Peaks rise up to 3,900 meters.
- Geography: Glaciers, lakes, valleys, and snow-capped mountains.
- Wildlife: Bears, deer, wolves, foxes and many birds.
Tourist Attractions
Banff National Park
- The most famous park in the Rockies.
- Known for lakes, glaciers and scenic hiking trails.
Jasper National Park
- Second major national park of the Rockies.
- Ideal for camping, trekking and wildlife spotting.
Lake Louise & Moraine Lake
- Beautiful blue lakes with breathtaking mountain views.
- Canoeing, photography and hiking available.
Winter Sports
- Whistler and Banff are world-famous for skiing and snowboarding.
Best Time to Visit
- Summer (June–September): Best for hiking and lake trips.
- Winter (December–March): Best for skiing and snow activities.
Special Significance
- Important part of Canada's natural heritage.
- Major contributor to adventure tourism and eco-tourism.
Conclusion of the Article on Canada
Canada is not only geographically vast and diverse, but also extremely rich socially, culturally and economically. Its major highlights include:
- Geographical diversity: From Arctic lands to temperate regions with rivers, lakes and wildlife.
- History and politics: A mix of Indigenous heritage, French and British colonial past, now a federal democratic nation.
- Economy: Strong industries in natural resources, agriculture, IT, manufacturing and tourism.
- Society and culture: Multiculturalism, bilingualism and high living standards.
- Education and health: World-class systems offering security and prosperity.
- Tourism: Iconic sites like Niagara Falls, Rockies, Banff and Jasper attract global travelers.
👉 In short, Canada represents peace, natural beauty, diversity and development. Its strong policies and rich culture will keep it an ideal nation globally.
References
- Government of Canada – Official Website
- Statistics Canada – Population, language, employment and economy
- Canada Tourism – Official travel guide
- University of Toronto, McGill University – Research sources
- Canadian Encyclopedia – thecanadianencyclopedia.ca
- World Bank – Canada overview
- UNESCO – World Heritage Sites in Canada
- Lonely Planet – Canada travel guide
- National Geographic – Canada nature and travel
- CIA World Factbook – Canada
- IMF Country Reports – Canada economy