Andhra Pradesh
Introduction to Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is a major state located in the southeastern part of India. It is considered one of the states with a rich cultural and historical heritage. The state capital is Amaravati, while the executive capital is Vijayawada, and Visakhapatnam also plays an important role as a major city.
In this article, I share my learnings about Andhra Pradesh—its geography, history, culture, economy, and key facts—so that readers can understand why this state is so significant in India’s development. This experience is also part of a broader learning journey about different Indian states and their unique contributions.
Geographical Location
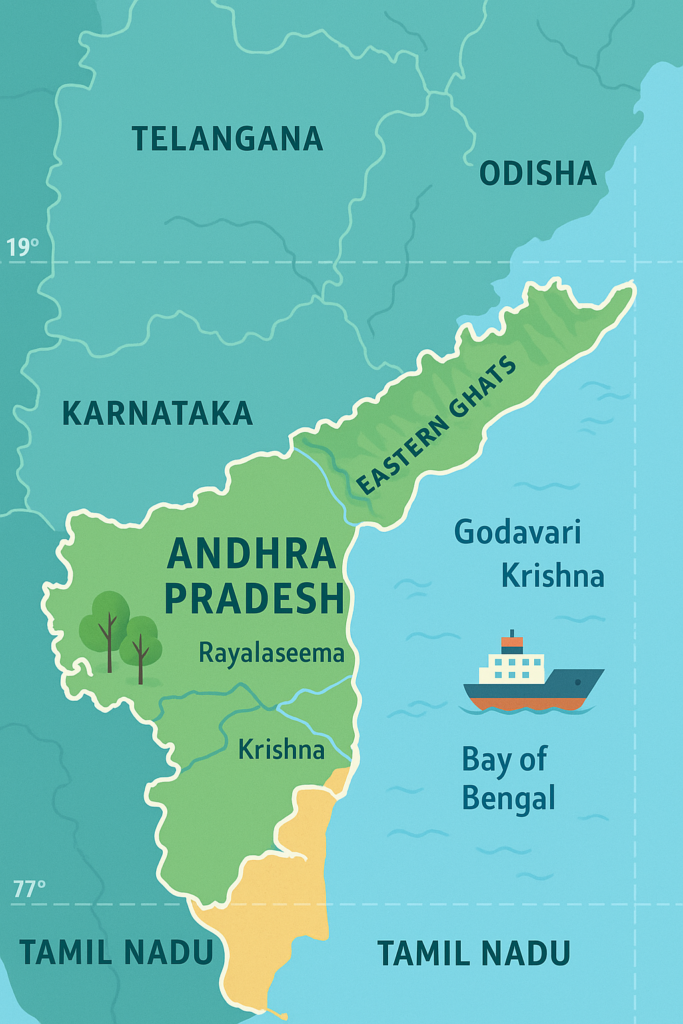
Andhra Pradesh is bordered by Telangana in the north, Karnataka in the west, Tamil Nadu in the south, and the Bay of Bengal in the east. Important rivers like Krishna, Godavari, and Pennar flow through the state. The total area of the state is about 1,62,968 square kilometers.
History of Andhra Pradesh
The history of Andhra Pradesh dates back to the Vedic period, and it is known for the influence of powerful empires like the Satavahanas, Vijayanagara, and the Chalukyas. Andhra Pradesh was formed on a linguistic basis in 1956. In 2014, Telangana was separated and became a new state.
Cultural Heritage of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is famous for its cultural diversity and rich traditions. The state’s identity is strongly reflected in its language, dance, and festivals.
Language
Telugu – The “Italian of the East”
Telugu is the official language of the state. Due to its musical and flowing nature, it is often called the “Italian of the East”.
Dance
Kuchipudi – Classical Dance of Andhra Pradesh
Kuchipudi is the main classical dance form of Andhra Pradesh. It is known for its expressive gestures, graceful movements, and devotional themes, and it holds an important place in Indian classical dance traditions.
Festivals
Major Festivals Celebrated in Andhra Pradesh
Festivals like Ugadi, Makar Sankranti, and Dussehra are celebrated with great enthusiasm and devotion. These festivals reflect the agricultural lifestyle, religious faith, and cultural unity of the people.
Natural Beauty and Tourism in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is full of natural and historical tourist places that attract visitors from across India and abroad.
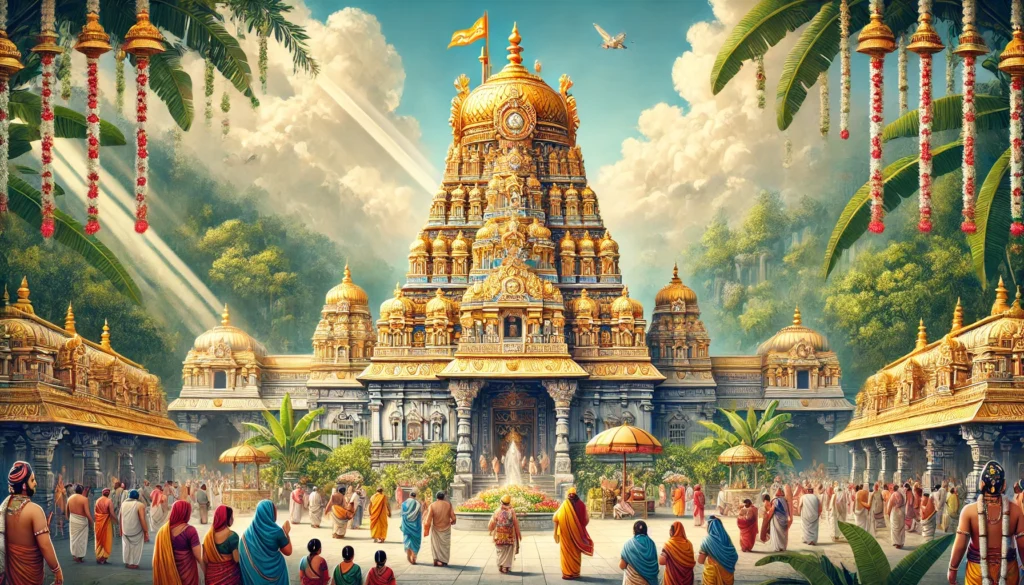
Tirupati Balaji Temple
World-Famous Pilgrimage Centre
Tirupati Balaji Temple is one of the most famous religious places in the world. It is a major pilgrimage centre and a symbol of deep faith for millions of devotees.
Araku Valley
Green Hills and Scenic Beauty
Araku Valley is famous for its greenery, coffee plantations, and beautiful hills. It is a popular destination for nature lovers and tourists seeking peace and fresh air.
Visakhapatnam
Beaches and Industrial Hub
Visakhapatnam, often called “Vizag”, is known for its beaches and industries. It is an important port city and a key industrial and commercial centre in the state.
Amaravati
Buddhist Heritage and Historical Significance
Amaravati is famous as a historical centre of Buddhism. It holds archaeological importance and reflects the ancient spiritual and cultural history of the region.
Economy of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is an important centre for agriculture, industrial production, and IT services. The state plays a vital role in the economic development of India.
Agriculture
“Rice Bowl of India”
Agriculture is a major part of the state’s economy. Rice is the main crop here, and because of its high rice production, Andhra Pradesh is often called the “Rice Bowl of India”.
Industry and Ports
Ports, Shipping, and Industrial Growth
The state is important for ports and the shipping industry. Coastal access to the Bay of Bengal helps Andhra Pradesh develop trade, transport, and industrial growth, supporting both national and international commerce.
Key Facts About Andhra Pradesh
- Formed: 1 November 1956
- Population: About 5 crore (2021 estimate)
- State Tree: Neem
- State Bird: Indian Roller (commonly known as “Neelkanth”)
Conclusion
Andhra Pradesh is known for its rich traditions, pilgrimage sites, ancient monuments, and modern progress. From historical empires to contemporary IT and industrial development, the state has evolved while preserving its cultural roots.
Learning about Andhra Pradesh shows how culture, geography, and economy can work together to build a strong and progressive region. This state contributes significantly to the cultural and economic development of India and offers valuable inspiration for anyone interested in understanding India’s diversity and growth.
FAQ about Andhra Pradesh
Q1. Where is Andhra Pradesh located in India?
Andhra Pradesh is located in the southeastern part of India. It is bordered by Telangana in the north, Karnataka in the west, Tamil Nadu in the south, and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
Q2. What is the capital of Andhra Pradesh?
The legislative capital of Andhra Pradesh is Amaravati. Vijayawada serves as the executive capital, and Visakhapatnam is also an important major city in the state.
Q3. Why is Andhra Pradesh called the “Rice Bowl of India”?
Andhra Pradesh is called the “Rice Bowl of India” because rice is the main crop grown in the state, and it produces a large quantity of rice that helps feed many parts of the country.

Top Quality Amazon Product
Reliable performance, great durability and excellent value — ideal choice for everyday use.
Buy on AmazonQ4. Which classical dance form is famous in Andhra Pradesh?
Kuchipudi is the famous classical dance form of Andhra Pradesh. It is known for its graceful movements, expressive storytelling, and devotional themes.
Q5. What are some popular tourist places in Andhra Pradesh?
Some popular tourist places in Andhra Pradesh include Tirupati Balaji Temple, Araku Valley, Visakhapatnam (Vizag), and Amaravati. These destinations offer a blend of spirituality, natural beauty, and historical significance.
Geographical Location and History of Andhra Pradesh
Geographical Location of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is located in the south-eastern part of India and holds great geographical importance. Its location, climate, topography, and natural resources together make it one of the major states of India.
Status and Boundaries
Andhra Pradesh extends from 12°41′ to 19°07′ North Latitude and 77°00′ to 84°40′ East Longitude. The state is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, which provides it with a long coastline and strategic maritime importance.
- North: Telangana and Odisha
- South: Tamil Nadu
- West: Karnataka
- East: Bay of Bengal
Area and Coastline
The total area of Andhra Pradesh is approximately 1,62,968 square kilometres, making it the seventh-largest state in India.
The state has a coastline of about 972 kilometres, one of the longest in the country. Major ports such as Visakhapatnam and Krishnapatnam located along the Bay of Bengal play a vital role in trade, industry, and tourism.
Topography (Physical Structure)
The topography of Andhra Pradesh is diverse and attractive. It can be broadly divided into three main geographical regions.
1. Coastal Plains (Coastal Andhra)
This region stretches along the Bay of Bengal and is known as Coastal Andhra. It is highly fertile and well-suited for agriculture. The delta regions of the Godavari and Krishna rivers are particularly productive.
2. Rayalaseema Region
Located in the western part of the state, the Rayalaseema region is generally dry and rocky. The land here is relatively less fertile, and hills and plateaus dominate the landscape.
3. Eastern Ghats Mountain Range
The Eastern Ghats run through the interior parts of the state. These hills contribute to the natural beauty and mineral wealth of Andhra Pradesh. Famous locations such as Araku Valley and Borra Caves are situated in this region.
Rivers and Water Resources
Water resources are of great importance to Andhra Pradesh, especially for agriculture and irrigation.
- Krishna River: The most important river of the state, supporting irrigation and agricultural activities.
- Godavari River: Also known as “Dakshin Ganga”. Its delta region is highly fertile and forms the agricultural backbone of the state.
- Pennar and Vamsadhara Rivers: These rivers flow through the southern and eastern regions of Andhra Pradesh and support local agriculture.
Climate of Andhra Pradesh
The climate of Andhra Pradesh is predominantly tropical.
- Summer: From March to June, with temperatures rising up to 45°C.
- Monsoon: From June to September, when the south-west monsoon brings rainfall.
- Winter: From November to February, with comparatively mild temperatures.
Mineral Wealth and Natural Resources
Andhra Pradesh is rich in mineral resources such as bauxite, limestone, coal, and mica. Visakhapatnam and its surrounding regions are particularly known for mineral availability and industrial development.

Premium Amazon Product
High quality, reliable performance and excellent durability — ideal choice for everyday use.
Buy on AmazonEnvironment and Biodiversity
The state supports diverse flora and fauna. Protected areas like Kaundinya Wildlife Sanctuary and Papikonda National Park help preserve its biodiversity. Coastal areas are also well-suited for fisheries and marine life.
Overall, the geographical location of Andhra Pradesh makes it naturally rich, agriculturally productive, and suitable for trade and business. Its coastal plains, fertile river deltas, and mountain ranges play a crucial role in the state’s development.
History of Andhra Pradesh
The history of Andhra Pradesh is rich and diverse, spanning from ancient civilizations to the modern era. It includes the Vedic period, Mauryan rule, Satavahanas, Vijayanagara Empire, and the post-independence period. This long historical journey has significantly shaped the political, cultural, and economic development of the region.
Ancient Period
Vedic and Epic Age
Andhra Pradesh finds references in ancient epics such as the Mahabharata and the Ramayana. The “Andhra” people are mentioned in Vedic literature and are believed to be of Dravidian origin. The region was influenced by Vedic civilization and Aryan culture.
Maurya Empire (321–185 BCE)
During the Mauryan Empire, large parts of Andhra Pradesh came under the rule of Emperor Ashoka. Buddhism flourished during this period, and monuments such as the Amaravati Stupa reflect the deep Buddhist influence.
Satavahana Empire (230 BCE – 220 CE)
The Satavahanas were the first major local dynasty of Andhra Pradesh. Their capital was Pratishthanapura. The region became a major centre of trade and culture, with trade links extending to the Roman Empire. Both Buddhism and Brahmanism received royal patronage.
Medieval Period
Ikshvaku Dynasty (3rd–4th Century)
After the decline of the Satavahanas, the Ikshvaku dynasty came to power. They promoted Buddhism and developed important centres such as Nagarjunakonda.
Eastern Chalukyas (7th–12th Centuries)
The Eastern Chalukyas ruled the northern and coastal regions of Andhra Pradesh. Their capital was Vengi, near present-day Vijayawada. Telugu language and literature flourished during this period.
Kakatiya Empire (12th–14th Century)
The Kakatiyas ruled from Warangal. Rulers like Queen Rudramma Devi and Prataprudra Deva brought power and prestige to the dynasty. They constructed forts, temples, and advanced irrigation systems. Warangal Fort is a fine example of Kakatiya architecture.
Vijayanagara Empire (14th–17th Centuries)
Andhra Pradesh witnessed great economic and cultural prosperity under the Vijayanagara Empire. This period is considered a golden age of art, architecture, and literature. Telugu literature reached new heights during the reign of Krishnadevaraya.
Qutb Shahi and Mughal Rule (16th–17th Centuries)
The Qutb Shahi rulers of Golconda controlled parts of the region. Later, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb defeated the Qutb Shahis and annexed the territory into the Mughal Empire.
Modern Period
British Rule (18th Century – 1947)
Andhra Pradesh came under British control and was part of the Madras Presidency. The people of Andhra played a significant role in India’s freedom struggle. Potti Sriramulu sacrificed his life through a hunger strike to demand a separate state for Telugu-speaking people.
Post-Independence Period
On 1 October 1953, Andhra Pradesh became India’s first linguistic state, separated from the Madras Presidency with Kurnool as its capital. On 2 June 2014, Telangana was separated to form a new state. Today, Vijayawada is the executive capital, Amaravati the legislative capital, and Kurnool the judicial capital.
Cultural Heritage and Contribution of Andhra Pradesh
- Language and Literature: Telugu represents the cultural identity of the state.
- Religion: A rich legacy of Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam.
- Art and Architecture: Amaravati Stupa, Warangal Fort, and Vijayanagara temples reflect the state’s architectural brilliance.
The history of Andhra Pradesh reflects a remarkable journey from ancient civilizations to modern development. The state stands as a symbol of historical glory, cultural diversity, and progressive growth in India.
Cultural Heritage of Andhra Pradesh
Introduction
Andhra Pradesh is one of the Indian states where a unique blend of cultural diversity, historical depth, and living traditions can be seen. The cultural heritage of the state is reflected in its dance, music, art, literature, architecture, festivals, and daily life. Ancient traditions continue to thrive alongside modern influences, making Andhra Pradesh culturally vibrant and dynamic.
1. Language and Literature
Language
Telugu is the official language of Andhra Pradesh and holds a prominent place among Indian languages. Due to its melodious and rhythmic nature, Telugu is often called the “Italian of the East”.
Literature
Telugu literature has a long and rich history that began during the Satavahana period. The golden age of Telugu literature flourished under the Vijayanagara Empire. Poets Nannayya, Tikkanna, and Errapragada are collectively known as the “Telugu Trinity” for their monumental contribution to Telugu literature. In the modern era, writers and poets like Gurajada Apparao and Shri Shri gave new direction and depth to literary expression.
2. Art and Architecture
Temple Architecture
Andhra Pradesh is renowned for its temples built in the Vijayanagara and Chalukya styles, showcasing artistic excellence and spiritual devotion.
Major Temples
- Tirupati Balaji Temple: Dedicated to Lord Venkateshwara.
- Srikalahasti Temple: A major Shiva temple.
- Lepakshi Temple: Famous for its magnificent architecture and giant Nandi statue.
Buddhist Art
Amaravati and Nagarjunakonda are important centres of Buddhist art and architecture. The Amaravati Stupa, along with Buddhist chaityas and viharas, represents the rich Buddhist heritage of Andhra Pradesh.
Forts and Palaces
Historical forts such as Warangal Fort and Golconda Fort, along with Kondapalli Fort, highlight the military and architectural achievements of past rulers. Kondapalli Fort is now a popular tourist destination.
3. Dance and Music
Kuchipudi Dance
Kuchipudi is the classical dance form of Andhra Pradesh and is renowned worldwide. This dance form combines storytelling, drama, expressive gestures, and rhythmic movements, often portraying mythological and devotional themes.
Music
Carnatic music forms an integral part of the musical heritage of Andhra Pradesh. Great composers such as Thyagaraja, Muthuswami Dikshitar, and Syama Shastri share a deep cultural connection with the region.
4. Handicrafts and Crafts
- Kondapalli Toys: Handmade wooden toys that reflect exceptional craftsmanship.
- Kalamkari Art: Hand-painted textiles depicting mythological and religious stories.
- Metal Art and Sculpture: Unique metal craftsmanship from regions like Penugonda and Dharmavaram.
- Ikat Sarees and Mangalgiri Fabrics: Traditional woven sarees and textiles famous for their quality and design.
5. Festivals and Celebrations
- Ugadi: Telugu New Year festival symbolizing new beginnings.
- Makar Sankranti: A major harvest festival celebrated over three days.
- Ram Navami and Dussehra: Important religious and cultural festivals.
- Tirupati Brahmotsavam: A grand nine-day festival at the Tirupati Balaji Temple.
- Visakha Festival: Cultural celebrations held in Visakhapatnam.

Premium Amazon Product
High quality, reliable performance and excellent durability — ideal choice for everyday use.
Buy on Amazon6. Religion and Traditions
Andhra Pradesh has been a centre of multiple religions throughout history. Hinduism, Buddhism, and Islam have all contributed to its cultural fabric. Major religious sites include Tirupati, Srisailam, and Kanaka Durga temples for Hinduism, and Nagarjunakonda and Amaravati for Buddhism. Islamic traditions are also significant, especially in regions like Kadapa.
Social customs such as marriages, festivals, and community rituals reflect unity, harmony, and shared cultural values.
7. Food Culture of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh cuisine is known for its spicy and flavorful taste.
- Hyderabadi Biryani
- Gutti Vankaya (Stuffed Eggplant)
- Pulihara (Tamarind Rice)
- Payasam and Ariselu (Traditional sweets)
Seafood is also widely consumed in the coastal regions of the state.
8. Cultural Events and Fairs
- Kuchipudi Festival: Celebrates classical dance art.
- Tirupati and Amaravati Festivals: Religious and cultural gatherings.
- Punnami Festival: Known for cultural and spiritual performances.
9. Films and Theatre
The Telugu film industry, popularly known as Telugu cinema, is one of the largest film industries in India. Alongside cinema, traditional theatre and folk performances continue to play an important role in preserving cultural expression.
Conclusion
The cultural heritage of Andhra Pradesh is the soul of the state. Its language, art, traditions, festivals, cuisine, and architecture not only enrich Indian culture but also give it global recognition. Andhra Pradesh stands as a powerful example of how the richness of the past can coexist harmoniously with modern life.
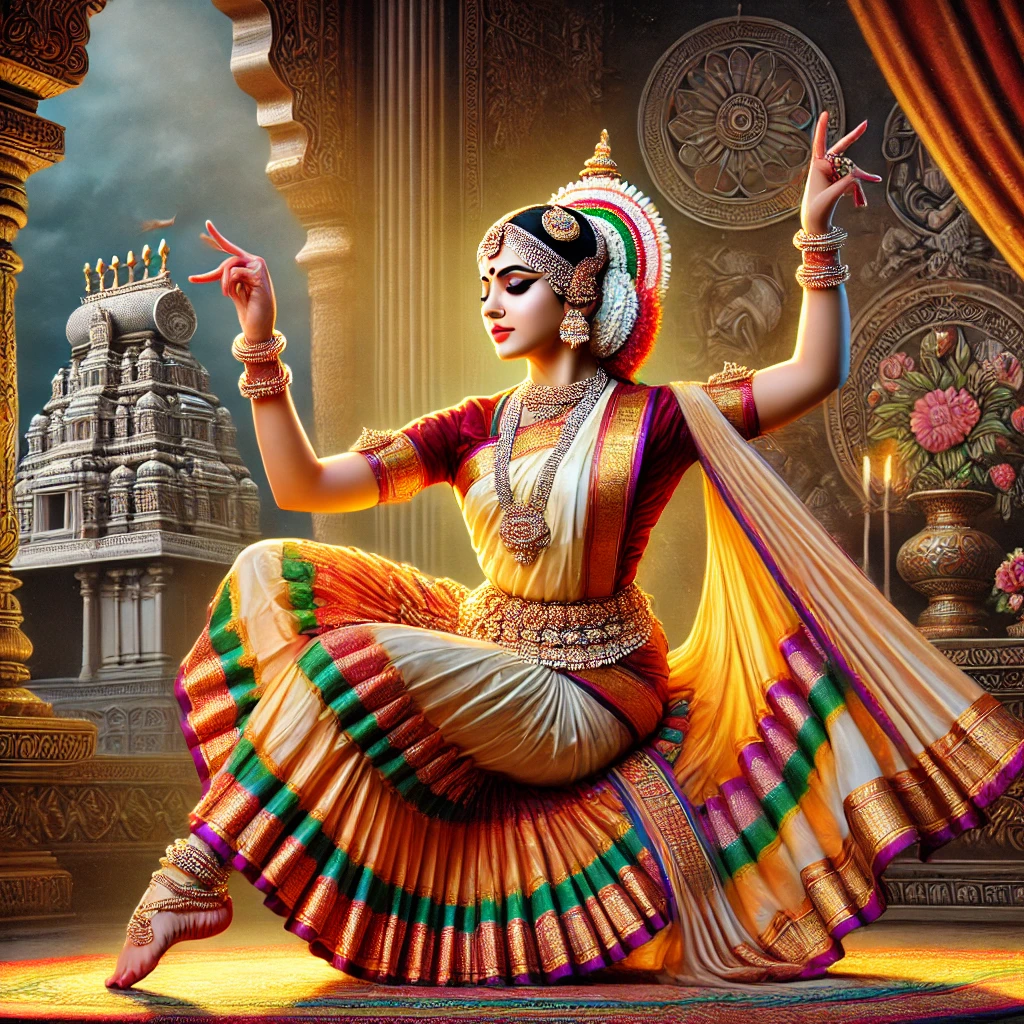
Kuchipudi: Classical Dance of Andhra Pradesh
Introduction
Kuchipudi is one of the classical dances of India and a proud symbol of the cultural identity of Andhra Pradesh. It originated in Kuchipudi village of the Krishna district, from which the dance derives its name. More than just a form of entertainment, Kuchipudi is deeply rooted in religious devotion and cultural traditions, blending storytelling, music, and expressive movement into a powerful artistic form.
History and Emergence of Kuchipudi
The history of Kuchipudi can be traced back to ancient times when it was performed in temples as a form of worship. The dance is based on the principles of the Natya Shastra, written by Maharishi Bharata, which lays the foundation of Indian classical dance and drama.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, Siddhendra Yogi gave Kuchipudi a systematic structure and transformed it into a medium for presenting religious stories and mythological characters. During this early phase, Kuchipudi was performed exclusively by male dancers, who also enacted female roles.
By the 20th century, Kuchipudi moved beyond temple spaces and evolved into a stage-based performing art, gaining recognition across India and the world.
Key Features of Kuchipudi Dance
1. Acting (Abhinayam)
Kuchipudi is rich in dramatic expression. It beautifully combines bhava (emotion), raga (melody), and tala (rhythm). Through detailed facial expressions, eye movements, and graceful postures, dancers bring stories vividly to life.
2. Storytelling and Themes
The dance mainly portrays stories from Hindu mythology. Episodes from the Ramayana, Mahabharata, and Bhagavata Purana are commonly performed. Characters such as Lord Krishna, Lord Rama, and Goddess Parvati hold a central place in Kuchipudi narratives.
3. Dance and Music
Kuchipudi presents a harmonious blend of Natyam (dance) and Sangitam (music). It is performed to the accompaniment of Carnatic music and is known for rhythmic footwork, swift movements, and complex body postures that require precision and balance.
4. Costumes and Ornaments
Bright and colourful costumes are a distinctive feature of Kuchipudi. Dancers wear specially designed traditional sarees or dhotis that allow flexibility of movement. Ornaments such as headgear, necklaces, garlands, and anklets enhance the visual grandeur of the performance.
5. Unique Presentation Style
Unlike many other classical dances, Kuchipudi includes not only pure dance (nritta) and expressive acting (abhinaya), but also spoken dialogues. Another unique aspect is the performance on brass plates, where dancers display exceptional balance and control while executing rhythmic steps.
Major Dance Dramas of Kuchipudi
- Bhama Kalapam: A famous dance drama based on the love story of Rukmini and Lord Krishna.
- Gopala Katha: Depicts the childhood stories and divine exploits of Lord Krishna.
- Sri Krishna Leela Tarangini: Composed by Narayana Tirtha, this work portrays important events from the life of Sri Krishna.

Premium Amazon Product
Reliable performance, excellent quality and everyday usability — a trusted choice for users.
Buy on AmazonKey Artists and Their Contributions
Several renowned artists played a crucial role in bringing Kuchipudi to national and international platforms.
- Vempati Chinna Satyam: His contribution in shaping Kuchipudi as a refined stage art and popularising it worldwide is invaluable.
- Yamini Krishnamurthy: A legendary dancer who took Kuchipudi to new artistic heights.
- Raja and Radha Reddy: Modern ambassadors of Kuchipudi who presented the dance form on global stages.
Kuchipudi in the Modern Era
In contemporary times, Kuchipudi is no longer limited to religious performances. It has emerged as a respected stage art, showcased at cultural festivals and international events. Institutions such as the Kuchipudi Kala Academy continue to work towards preserving, teaching, and promoting this classical dance form.
Conclusion
Kuchipudi is not only the cultural identity of Andhra Pradesh but also a priceless heritage of Indian classical dance. Its dramatic expression, musical richness, and rhythmic elegance make it unique among classical dance forms. By maintaining its traditional roots while embracing modern presentation, Kuchipudi continues to remain relevant and inspiring for future generations.
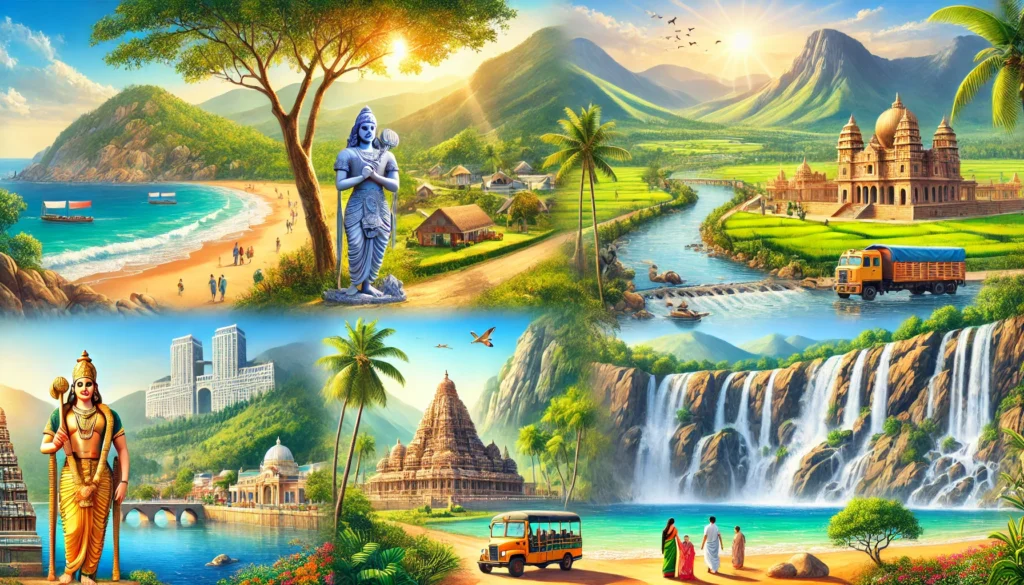
Natural Beauty and Tourism of Andhra Pradesh
Introduction
Andhra Pradesh is a rich amalgamation of natural beauty, historical landmarks, and cultural heritage. The state is blessed with long coastlines, scenic beaches, lush hill stations, waterfalls, caves, wildlife sanctuaries, ancient temples, and historic forts. Due to its geographical diversity and natural charm, Andhra Pradesh has emerged as one of India’s popular tourist destinations.
Natural Beauty of Andhra Pradesh
1. Beach Tourism
The vast coastal belt of Andhra Pradesh along the Bay of Bengal is home to several peaceful and scenic beaches that attract tourists throughout the year.
Ramakrishna Beach (Visakhapatnam)
Ramakrishna Beach is known for its calm atmosphere and scenic beauty. Major attractions here include the INS Kursura Submarine Museum and beautiful coastal views.
Rushikonda Beach (Visakhapatnam)
Surrounded by green hills and golden sands, Rushikonda Beach is popular for water sports and adventure activities.
Manginapudi Beach (Machilipatnam)
Manginapudi Beach holds both historical and religious significance and offers a peaceful seaside experience.
Bheemunipatnam (Bhimili) Beach
This beach offers tourists a serene environment and a glimpse of historical colonial heritage along with natural beauty.
2. Waterfalls
Andhra Pradesh is home to several waterfalls that enhance the natural charm of the state.
Ethipothala Falls (Guntur)
Situated on the Chandravanka River, Ethipothala Falls is surrounded by lush greenery and wildlife, making it a scenic picnic destination.
Kandhakattu Waterfalls (Visakhapatnam)
This waterfall is surrounded by dense forests and is popular among trekkers and nature lovers.
Talakona Falls (Chittoor)
Talakona Falls is the highest waterfall in Andhra Pradesh and is located inside the Sri Venkateswara National Park. The water here is believed to have medicinal properties.
3. Hill Stations
Araku Valley (Visakhapatnam)
Araku Valley is famous for its green landscapes, coffee plantations, and cool climate. Major attractions include Borra Caves and Padmapuram Gardens.
Lambasingi (Visakhapatnam)
Known as the “Kashmir of Andhra Pradesh”, Lambasingi is famous for its cool weather, mist-covered valleys, and occasional snowfall-like conditions.

Top Quality Amazon Product
Durable build and reliable performance — ideal for everyday use with trusted quality.
Buy on Amazon4. Caves
Borra Caves (Araku Valley)
Borra Caves are limestone caves known for their stunning natural formations and mystical lighting. Many of the structures inside are associated with mythological beliefs.
Belum Caves (Kurnool)
Belum Caves are among the longest cave systems in India and are famous for their unique limestone formations and underground pathways.
5. Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks
Sri Venkateswara National Park (Tirupati)
This national park is rich in biodiversity and is home to tigers, leopards, deer, and a wide variety of flora and fauna.
Konda Reddy Wildlife Sanctuary
Known for its dense forests, this sanctuary shelters rare wildlife species and offers eco-tourism opportunities.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (Kakinada)
Coringa is famous for its mangrove forests and migratory birds, making it a paradise for bird watchers and nature enthusiasts.
Major Tourist Attractions of Andhra Pradesh
1. Religious and Pilgrimage Tourism
Tirupati Balaji Temple
One of the most famous and richest temples in the world, this temple dedicated to Lord Venkateshwara holds immense religious and cultural importance.
Amaravati
Amaravati is famous for its ancient Buddhist heritage and its association with Lord Shiva.
Srikalahasti Temple
Known for the Vayu Linga, Srikalahasti is one of the Panchabhuta temples and a major pilgrimage centre.
2. Historical and Cultural Sites
Charminar (Hyderabad)
Charminar is a historic monument known for its architectural excellence and cultural significance.
Golconda Fort
Famous for its advanced acoustics and strong fortification, Golconda Fort represents medieval architectural brilliance.
Kondapalli Fort
Kondapalli Fort is known for its historical importance and for the famous Kondapalli wooden toys.
3. Modern Tourist Destinations
Visakhapatnam (Vizag)
Visakhapatnam is known for its beaches, green hills, and industrial growth. Popular attractions include Kailasagiri and Subhash Chandra Bose Park.
Amaravati Capital Region
Amaravati, the planned capital city of Andhra Pradesh, is emerging as a modern urban and cultural centre.
4. Adventure Tourism
Papanasam Dam
This location is popular for trekking, nature exploration, and adventure sports.
Araku Valley
Activities such as trekking, ziplining, and camping make Araku Valley a favourite destination for adventure seekers.
Tourism Development Efforts
The Government of Andhra Pradesh has undertaken several initiatives to promote tourism. Beaches, hill stations, and pilgrimage centres are being developed as world-class destinations. Special tourism packages, improved infrastructure, and better facilities are also being introduced to attract international tourists.
Conclusion
The natural beauty and tourism of Andhra Pradesh offer something unique for every type of traveller. Its scenic beaches, hill stations, waterfalls, wildlife sanctuaries, historical monuments, and sacred pilgrimage sites make the state truly special. Travelling through Andhra Pradesh not only refreshes the mind but also provides a deep connection with its rich natural and cultural heritage.
Tirupati Balaji Temple
Introduction
Tirupati Balaji Temple, also known as Sri Venkateswara Swamy Temple or Tirumala Temple, is located in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. Dedicated to Lord Venkateshwara, an incarnation of Lord Vishnu, this temple is one of the most sacred, richest, and most visited pilgrimage centres in India. Beyond religion, Tirupati represents faith, devotion, and spiritual discipline for millions of devotees.
Historical Importance of the Temple
Tirupati Balaji Temple has a history that goes back over 1,200 years. References to the temple can be found in ancient Tamil Sangam literature. Over centuries, dynasties such as the Pallavas, Cholas, Pandyas, and the Vijayanagara Empire patronised and developed the temple.
During the Vijayanagara period, the temple received immense wealth and was richly adorned with gold, silver, and precious gems, transforming it into one of the most prosperous religious institutions in India.
Location and Natural Beauty
The temple is situated on the Tirumala Hills, part of the Saptagiri (Seven Hills), which are believed to symbolise the divine form of Lord Venkateshwara. Located at an altitude of about 3,200 feet above sea level, the temple is surrounded by lush greenery and serene natural landscapes, enhancing its spiritual atmosphere.
Temple Architecture
Tirupati Balaji Temple is a magnificent example of Dravidian architectural style. The grand Gopuram (main gateway) is beautifully decorated and visually striking. Inside the sanctum sanctorum stands a black stone idol of Lord Venkateshwara, about 8 feet tall, richly adorned with ornaments.
The deity is depicted holding the Shankha, Chakra, Gada, and Padma. Various structures within the temple complex, decorated with gold and silver, further enhance its grandeur.
Religious Significance
According to belief, Lord Venkateshwara resides in Tirumala to protect mankind during Kali Yuga. The temple is considered one of the sacred centres of the Vaishnavite tradition and holds immense devotional importance. Devotees believe that visiting Tirupati fulfils wishes and brings spiritual blessings.
Special Rituals and Celebrations
Tirupati Brahmotsavam
The grandest annual festival of the temple, celebrated over nine days. During this festival, the idol of Lord Venkateshwara is taken out in majestic processions on beautifully decorated chariots.
Sarva Darshan
Sarva Darshan allows devotees from all backgrounds to have the darshan of the Lord. Every day, lakhs of devotees stand in long queues with devotion and patience.
Laddu Prasadam
The Tirupati Laddu is world-famous and offered as sacred prasadam. It is a unique identity of the temple and holds religious as well as cultural value.
Hair Donation (Kalyana Katta)
Devotees donate their hair as a symbol of surrender and devotion to the Lord. This tradition is a distinctive feature of Tirupati Balaji Temple.
Centre of Wealth and Prosperity
Tirupati Balaji Temple is believed to be the richest temple in India. Devotees donate gold, silver, precious stones, and cash in large amounts. The annual income of the temple runs into thousands of crores of rupees.
Facilities and Arrangements for Devotees
The temple administration provides online booking facilities for darshan. Free accommodation, food, and medical services are available within the temple premises. Specially designed walking paths allow devotees to reach Tirumala on foot as an act of faith.
Nearby Tourist Attractions
- Srikalahasti Temple: A major Shiva temple near Tirupati.
- Padmavathi Temple (Tiruchanur): Dedicated to Goddess Lakshmi.
- Talakona Falls: A scenic waterfall near Tirupati.
Importance of Tirupati Balaji Temple
Tirupati Balaji Temple is not only a religious destination but also a symbol of faith, devotion, and spiritual peace. The serene environment and divine energy provide mental and spiritual calm to devotees. Every year, millions of pilgrims visit this world-famous shrine.
Conclusion
Tirupati Balaji Temple stands as a unique symbol of Indian religion and culture. It is a sacred confluence of devotion, faith, and tradition. A visit to Tirupati is not merely a pilgrimage, but a deeply spiritual experience that leaves a lasting sense of peace and fulfilment.
Economy of Andhra Pradesh
Overview
The economy of Andhra Pradesh is one of the fastest-growing economies in India. It is driven by agriculture, industry, services, and abundant natural resources. The state’s favourable geography, climate, and long coastline significantly contribute to its economic strength.
Major Economic Sectors
Agriculture and Allied Activities
Andhra Pradesh is known as the “Rice Bowl of India”. Major crops include rice, sugarcane, cotton, chilli, tobacco, maize, and pulses. The state holds a leading position in chilli production.
Horticulture crops such as banana, papaya, lemon, and coconut are widely cultivated. Andhra Pradesh ranks first in fish production in India, supported by the Krishna and Godavari deltas and long coastline. Dairy and poultry industries also contribute significantly.
Industrial Sector
The industrial sector is expanding rapidly. Key industries include:
- Information Technology (IT)
- Textiles and handloom industry
- Chemicals and fertilizers
- Cement and building materials
The Visakhapatnam–Chennai Industrial Corridor (VCIC) is a major initiative aimed at boosting industrial growth.
Service Sector
Tourism, education, healthcare, banking, and financial services form the backbone of the service sector. Destinations like Tirupati, Araku Valley, and Visakhapatnam strengthen tourism-based income.
Natural Resources and Energy
Andhra Pradesh is rich in minerals such as bauxite, limestone, coal, silica sand, and granite. The state produces energy through thermal, hydro, and solar power, with major solar projects in Kadapa and Kurnool.

Premium Amazon Product
Stylish design, excellent build quality and reliable performance — perfect for daily use.
Buy on AmazonRole of Coastal Area
With a coastline of about 974 km, Andhra Pradesh plays a crucial role in fisheries, seafood export, and port-based trade. Visakhapatnam Port is one of the busiest ports in India, along with Krishnapatnam and Kakinada ports.
Government Initiatives
- Rythu Bharosa Scheme: Financial support for farmers.
- Special schemes for fishermen.
- Development of SEZs and industrial parks.
- Employment generation through infrastructure projects.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges include regional imbalance after state bifurcation, climate change, irrigation issues, and infrastructure pressure. However, the state has immense potential in port-based industries, green energy, IT, tourism, and services.
Conclusion
Andhra Pradesh’s economy is built on a balanced mix of agriculture, industry, and services. With abundant resources, supportive policies, and strategic coastal advantages, the state is poised to play a major role in India’s and the global economy.
Andhra Pradesh: Key Facts and Features
Geographical Location
Andhra Pradesh is located on the south-eastern coast of India. It is bordered by Telangana (north), Karnataka (west), Tamil Nadu (south), and the Bay of Bengal (east). The state has a long coastline of about 974 km.
Administrative Structure
- Executive Capital: Visakhapatnam
- Proposed Capital: Amaravati
- Districts: 26
- Official Language: Telugu
- Population: ~5 crore (2021 estimate)
- Chief Minister: Y. S. Jagan Mohan Reddy
- Governor: S. Abdul Nazeer
Culture and Heritage
Telugu literature, Kuchipudi dance, traditional music, and festivals such as Ugadi and Dussehra form the cultural backbone of the state.
Major Tourist Destinations
Key attractions include Tirupati Balaji Temple, Araku Valley, Talakona Falls, Belum Caves, and Golconda Fort.
Conclusion
Andhra Pradesh stands out for its cultural richness, natural beauty, and economic potential. With diverse resources and growing opportunities, the state is well positioned to play a vital role in shaping India’s future.
Conclusion
Andhra Pradesh stands as a remarkable example of how tradition and progress can coexist in harmony. From the spiritual grandeur of the Tirupati Balaji Temple—one of the most sacred and revered pilgrimage sites in the world—to its rapidly growing economy driven by agriculture, industry, services, and coastal advantages, the state reflects both cultural depth and modern aspiration.
Its rich history, vibrant traditions, classical arts like Kuchipudi, fertile river deltas, mineral wealth, and long coastline together form a strong foundation for sustainable development. With continuous government initiatives, expanding infrastructure, and rising investment in sectors such as IT, renewable energy, tourism, and port-based industries, Andhra Pradesh is steadily strengthening its position on the national and global stage.
Overall, Andhra Pradesh is not only a land of faith, heritage, and natural beauty but also a state of immense economic potential and future opportunities. Its journey from ancient civilization to a modern growth-driven state makes it one of the most significant contributors to India’s cultural identity and economic progress.
References

Premium Amazon Product
High-quality build, reliable performance, and excellent value — perfect choice for everyday use.
Buy on Amazon- Government of Andhra Pradesh – Official Portal
- Andhra Pradesh Tourism Development Corporation (APTDC)
- Ministry of Tourism, Government of India – State Tourism Data
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) – Monuments & Culture Reports
- Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD) – Official Information
- India Meteorological Department – Andhra Pradesh Climate Data
- Planning Department, Andhra Pradesh – Economic Survey & Statistics
- National Informatics Centre (NIC) – District & Administrative Details