Akkadian Civilization: History , Characteristics and Importance
Akkadian Civilization was the first consolidated imperial civilization of ancient Mesopotamia. This civilization was almost 2334 BC to 2154 BC It flourished till then and was called the king Sargon the Great This civilization succeeded the Sumerian civilization and its culture , language and administrative system had a profound influence on future civilizations.
1. The rise of the Akkadian civilization
( a) Historical background
- Establishment of the Akkadian Empire Sargon the Great has approximately 2334 BC I did it in.
- Sargon the Great conquered the Sumerian city-states and created a unified empire.
- They Akkad He made a city named as his capital , which has not yet been discovered archaeologically.
( b) Geographical location
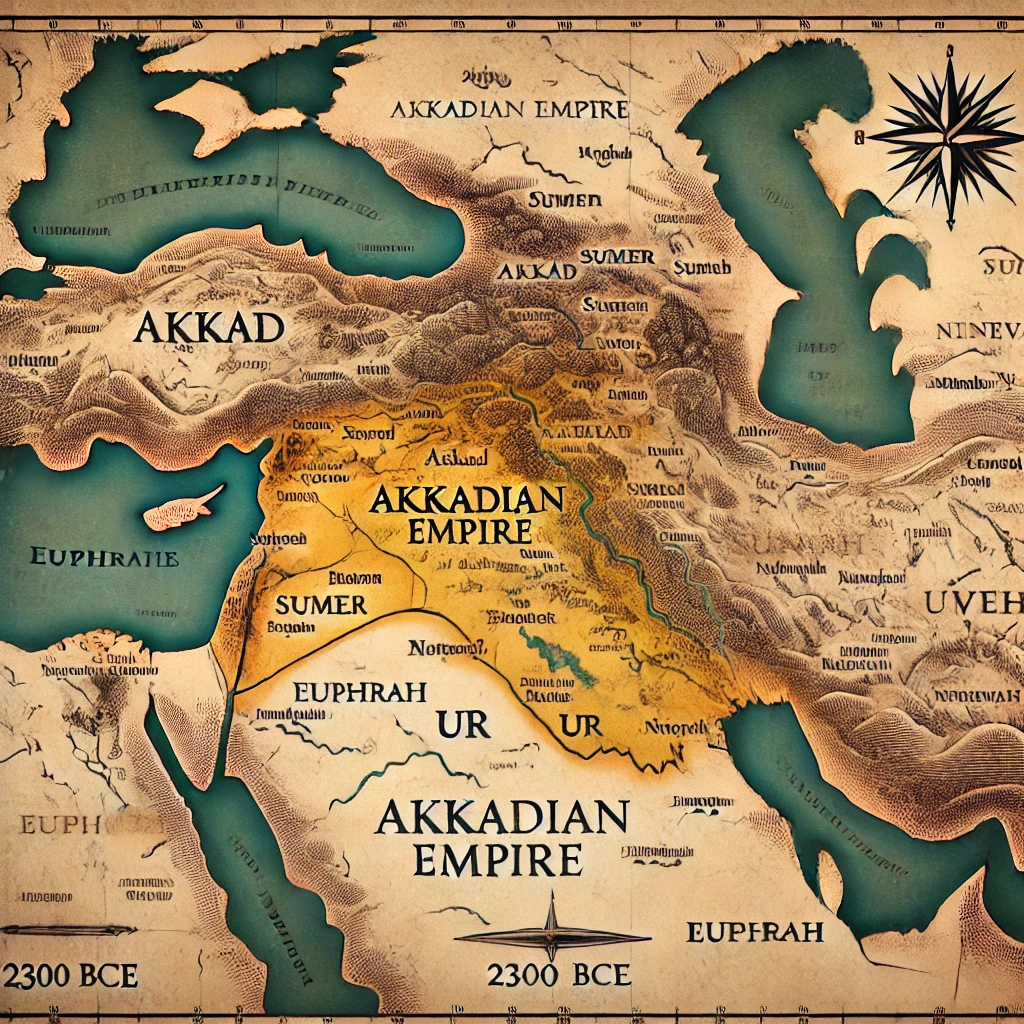
- This civilization Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq) It was settled in , which was situated between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
- The fertile land here was suitable for agriculture and the waterways were important for trade.
2. Main features of Akkadian civilization
( a) System of Governance
- This civilization Monarchical system It was based on.
- The king was considered the representative of God.
- The administrative system was strong and the taxation system was systematic.
- The empire was divided into provinces , which were ruled by local governors.
( b) Language and script
- Main language of Akkadian civilization Akkadian was , which Semitic language family It was related to.
- this language Cuneiform script It was written in , which they adopted from the Sumerians.
- The Akkadian language later became the dominant language in the Babylonian and Assyrian civilisations as well.
( c) Art and Architecture
- In the Akkadian period Sculpture and architecture There was considerable development of.
- ” Victory Stele of Naram-Sin” A famous Akkadian artifact.
- Temples , palaces and other grand structures were built.
( d) Religion and religious beliefs
- In Akkadian civilization Polytheism Was.
- Main deity- Enlil , Inanna , Shamash and Marduk Were.
- The king was worshipped as a representative of God.
( e) Economy and trade
- Agriculture was the main economic activity and barley , wheat , dates, etc. were cultivated.
- Trade was well developed , and Akkadian merchants Iran , India , Egypt and Asia Minor Used to do business till then.
- In business Copper , gold , silver , wood and stone Things like that were important.
3. The decline of the Akkadian civilization
( a) Internal causes
- The empire had become very large , making administrative control difficult.
- Internal rebellions and conflicts began to increase.
( b) External invasion
- On the Akkadian Empire The Gutian tribes invaded , weakening it.
- Ultimately 2154 BC This civilization was ended by the Gutians in 306 BC.
4. The importance of Akkadian civilization
- It is the world’s First Empire , which presented a new model of central administration .
- The Akkadian language later gave rise to the Babylonian and Assyrian languages.
- This civilization influenced many future civilizations in administrative , military and cultural terms.
conclusion The Akkadian civilization was one of the most influential and powerful civilizations of the ancient world. This empire, founded by Sargon the Great, holds an important place not only in Mesopotamia but in the history of the entire world. Its administrative system , language , art , and culture influenced many future civilizations. Although this civilization ended with the invasion of the Gutians , its legacy lived on for centuries.
History of Akkadian Civilization

Akkadian Civilization is the world’s The first imperialist civilization , who established the empire in Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq) 2334 BC to 2154 BC ruled till 1828. Establishment of this civilization Sargon the Great The civilization was founded by , who unified the Sumerian city-states to form a powerful empire. This civilization emerged as a link between the Sumerian and Babylonian civilizations and was famous for its administrative efficiency , military conquests , language and cultural influences.
1. The rise of the Akkadian civilization
( a) Sargon the Great and the founding of the empire
- Sargon the Great around 2334 BCE Established the Akkadian Empire in 300 BC.
- He first Kish He began his career in a minor position in the court of King Ur-Jabba.
- He later established himself as a powerful military leader and began conquering Sumerian cities.
- They Ur , Uruk , Lagash and Nippur Like took control of major cities.
- Eventually they captured the Sumerian king Lugal- Zagezi Defeated and took control of the whole area.
( b) Capital – Akkad
- Sargon the Great Akkad made it his capital , located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
- This city was a very prosperous and advanced trading center.
- However , till date the exact remains of this city have not been found.
( c) Expansion of the Empire
- Sargon the Great founded the Akkadian Empire the Mediterranean Sea to the west , Asia Minor (present-day Turkey) to the north , and Elam (present-day Iran) to the east Spread it.
- He created a strong army , composed of professional soldiers and trained cavalry.
- He campaigned throughout the empire Roads , reservoirs , and trade routes Developed , which boosted commerce and communication.
2. The Golden Age of the Akkadian Empire
( a) Administrative set up
- The Akkadian Empire centralized governance system Developed it.
- The empire was divided into various provinces , which Governor were appointed.
- A well-organised administrative system was created to organise tax collection , army management and trade.
( b) Military power and conquests
- Sargon the Great was succeeded by his sons Rimush and then Manishtushu Ruled by.
- Later , Naram-Sin (2254-2218 BC) took power and established himself ” King of the Four Quarters “ It was declared.
- Naram-Sin expanded the Akkadian Empire to Elam , Syria, and Anatolia.
- He declared himself a god , a first in ancient Mesopotamian history.
( c) Economic and cultural prosperity
- Agriculture , trade and craft industries were highly developed.
- Akkadian merchants for trade India (Indus Valley Civilization) , Egypt , Iran , and Asia Minor drove up.
- Great works of art and architecture were accomplished , especially ” Victory Stele of Naram-Sin” It is famous.
- The Akkadian language became the official language throughout Mesopotamia.
3. The fall of the Akkadian Empire
( a) Internal conflicts and administrative weakness
- Naram-Sin was succeeded by his son Shar-Kali -Sharri (2217-2193 BC) Failed to rule.
- The administration became weak and rebellions began to occur in the provinces.
( b) Gutian Invasion
- About 2154 BC , Gutians attack Akkad .
- These Gutians came from the Zagros Mountains and were extremely aggressive .
- He defeated the Akkadian army and destroyed the capital, Akkad.
( c) Climate change and famine
- Scientific research has shown that at this time Severe drought and climate change This happened , which brought agriculture to a standstill.
- Water sources dried up and people started dying of starvation.
- This weakened the empire and made it an easy prey for external invaders.
4. The legacy of the Akkadian civilization
( a) Language and script
- Akkadian Language the first state language of Mesopotamia Bunny.
- this language later Babylonian and Assyrian civilisations Adopted by.
- The Akkadian language was written in the cuneiform script .
( b) Administrative and military traditions
- Later civilisations , such as The Babylonian and Assyrian empires , adopted the Akkadian administrative system and military strategies.
- The concept of centralized government and provincial division was later seen in the Roman and Persian empires.
( c) Art and culture
- Great works were produced in sculpture and architecture , which continued in the Assyrian and Babylonian civilizations.
- Artifacts such as Naram-Sin’s victory stela remain a subject of study to this day.
conclusion The Akkadian civilization of the world The first imperialist civilization This civilization not only achieved a high level of military and administrative efficiency but also made significant contributions to language, art and culture. The leadership of Sargon the Great, the military prowess of Naram-Sin and the richness of the Akkadian language were the special characteristics of this civilization. Although this civilization was destroyed due to the Gutian invasion and climate change , its legacy continued in the form of the Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations.
The Rise of the Akkadian Civilization

The rise of Akkadian Civilization 2334 BC It happened in , when Sargon the Great He established the first empire in history by uniting the various city-states of Mesopotamia. Prior to this , the region was divided into several independent Sumerian city-states , which were fighting among themselves. Sargon used his military and administrative skills to conquer these states and unite them. Akkad Established a capital called and laid the foundation of a centralized empire.
1. The situation before the Akkadian civilization
( a) Dominance of the Sumerian city-states
- Before the Akkadian Civilization Sumerian Civilization The chiefdom was the , which was divided into several independent city-states.
- in these city-states Ur , Uruk , Kish , Lagash and Nippur He was the chief.
- There was constant conflict between the city-states , which led to no political stability.
( b) The rise of Sargon the Great
- Birth of Sargon the Great Kish It happened in the city.
- Initially he was the king of Kish Ur- Zababa He was a common official in the court of.
- He established himself with his military brilliance and gradually began to take control of the Sumerian kingdoms.
2. Establishment of the Akkadian Empire
( a) Conquest of the Sumerian city-states
- Sargon first Kish Nagar But he took over.
- After this he Ur , Uruk , Lagash and Nippur Such as defeating major city-states in war.
- He finally defeated the Sumerian king Lugal- Zagezi Defeated him and took over the whole of Mesopotamia.
( b) Establishment of the capital city of Akkad
- Sargon established the capital of his new kingdom Akkad Made in the city.
- Akkad became a prosperous trading and cultural center.
- This city was the main center of trade , administration and military activities.
( c) Expansion of the Empire
- Sargon Expands His Empire Asia Minor (present-day Turkey) to the north , the Mediterranean Sea to the west , and Elam (present-day Iran) to the east Did it till then.
- He has a Strong and permanent army , which became the foundation of the stability of his rule.
3. Characteristics of the Akkadian Empire
( a) Centralised administration
- Sargon developed a centralized administrative system , which governed the entire empire Provinces It was divided into.
- leadership of each province Governors appointed by the king I used to do it.
- The tax system and laws were streamlined.
( b) Development of language and script
- Major Language of the Akkadian Empire Akkadian , which later became the official language of the Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations.
- For writing Cuneiform script , which they adopted from the Sumerian civilization.
( c) Economic prosperity
- In the Akkadian Empire Trade and agriculture was highly developed.
- Major trading partners India (Indus Valley Civilization) , Egypt , Iran , and Asia Minor Were.
- In business Copper , gold , silver , wood and stone was imported and exported.
4. Influence of Akkadian civilization
- Sargon the Great introduced the concept of a unified empire , which was later adopted by many other civilizations.
- Akkadian language and administrative system Babylonian and Assyrian Empires Carried forward by.
- Akkadian civilization established new dimensions in art , literature and architecture.
conclusion
The Rise of the Akkadian Civilization as the first empire of the ancient world The civilization of Sumerian civilization not only unified the Sumerian city-states but also created a strong administrative , military and cultural base. The conquests of Sargon the Great , the establishment of the capital Akkad and commercial prosperity made this civilization historically very important. This civilization later became an inspiration for the Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations.
( a) Historical background
Akkadian Civilization : Ancient Mesopotamia was an important civilization of 2334 BC to 2154 BC This civilization emerged after the fall of the Sumerian city-states and is known for establishing the world’s first empire. Establishment of the Akkadian Empire Sargon the Great who unified the scattered Sumerian city-states and laid the foundation of an organized and powerful empire .
1. Geographical location of Mesopotamia
- Mesopotamia Current Iraq , Syria and Turkey It was located in parts of.
- this area The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers It was situated between the two rivers , hence called “the land between two rivers”.
- The fertile land and water sources of this region gave many ancient civilizations the opportunity to develop here.
2. Sumerian civilization and the city-state system
- Before the Akkadian Civilization Sumerian Civilization It was the most prominent here.
- Sumerian People Kish , Ur , Uruk , Nippur , and Lagash Like they were divided into independent city-states.
- Each city-state had its own ruler and they used to fight among themselves.
- There was political instability in the region , which Akkadian rulers used to their advantage.
3. The Rise of Sargon the Great
- Sargon the Great First Ur-Zababa, King of Kish He was a general officer in the court of.
- Later they militarily attacked the Sumerian city-states and took control of them.
- He eventually succeeded to the throne of the Sumerian king Lugal- Zagezi He defeated him and established his authority over the whole region.
- Thus , Sargon the Great Laid the foundation of the Akkadian Empire in 2334 B.C. And established a capital named Akkad .
4. Influence of Akkadian language and culture
- Akkadian Language was different from the Sumerian language And it belonged to the Semitic language group.
- The Akkadian language later Babylonian and Assyrian Civilizations It gained prominence as the official language of.
- in this period Cuneiform script was used , which was adopted from the Sumerian civilization.
5. Expanse and influence of the Akkadian Empire
- Sargon the Great Expands His Empire From Mesopotamia to Syria , Asia Minor (Turkey) , and Persia (Iran) Did it.
- They Organised administration , tax system and military system Started the , which strengthened the empire.
- his successors , especially Naram-Sin ( Naram-Sin), He further strengthened the empire.
conclusion
The historical background of the Akkadian civilization is mainly The instability of the Mesopotamian city-states and the military and administrative capabilities of Sargon the Great This civilization not only became the world’s first organized empire , but also made significant contributions in the field of language , administration and culture . Its legacy was reflected in the later Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations. It can be seen.
( b) Geographical location
Akkadian Civilization : Ancient Mesopotamia , which is today’s Iraq , Syria , and Turkey The centre of this civilization was the region The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers was between , which is called “Mesopotamia”. This fertile region is also called the “birthplace of civilization” , because one of the oldest civilizations of the world developed here.
1. Geographical features
( a) Importance of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers
- Both these rivers were the lifeline of this region and were very important for agriculture and trade.
- The annual floods of the rivers kept the land fertile , which led to progress in agriculture.
- Trade and communication were boosted through water transport.
( b) Regional division of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is usually Two main parts It was divided into:
- Northern Mesopotamia (Akkad) – This region was more arid , but had a good water supply and grasslands , suitable for animal husbandry.
- Southern Mesopotamia (Sumer) – This region was in the river deltas and agriculture was highly developed here due to fertile soil.
( c) Capital of Akkad
- Sargon the Great established the capital of his empire Akkad Established in a city named.
- Although the exact location of this city is still unknown , it is estimated that it was located near modern Around Baghdad (Iraq) Was located.
- Akkad was the main center of trade and administration , from where the entire empire was controlled.
2. Climate and environment
- Climate of Mesopotamia hot and dry The climate here was , with summers being very hot and winters being cold.
- Decreased rainfall necessitated irrigation , which the Akkadians developed efficiently.
- The region had limited natural resources , so resources such as wood , metal, and stone were traded with other regions.
3. Natural resources and trade
- Soil : Due to fertile soil, wheat , barley and dates were cultivated here.
- Water Resources: Irrigation system was developed due to the rivers.
- Mineral Resources: Metals like copper , silver and gold were limited , so they were imported from outside.
- Trade routes: The Akkadian Empire India (Indus Valley) , Egypt , Iran and Asia Minor had established trade relations with.
4. Strategic importance
- The location of Mesopotamia was strategically very important because it Asia , Europe and Africa It was located on a major trade route between.
- Various civilizations and rulers tried to gain control over this region , which led to constant conflicts here.
- The region developed into a permanent administrative center after the establishment of the Akkadian Empire.
conclusion The geographical location of the Akkadian civilization played an important role in its prosperity and advancement. Located along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, this civilization was favorable for agriculture , trade, and military strategy. However , due to the lack of natural resources it had to depend on trade with other regions. The strategic importance of this region made it one of the most important civilizations in history.
Main Features of Akkadian Civilization

Akkadian Civilization : 2334 BC to 2154 BC It flourished till 1000 BC and was the first major empire of ancient Mesopotamia. This civilization was established Sargon the Great , who unified the disparate Sumerian city-states and laid the foundation for a centralized empire. The Akkadian Empire political , social , cultural , military and economic Made many important contributions in these fields.
1. Administrative and political system
( a) The world’s first empire
- The Akkadian Empire was the world’s first centralized empire , ruling over a wide area.
- this empire Asia Minor (Turkey) to the north , the Mediterranean Sea to the west , and Persia (Iran) to the east It spread till.
( b) Centralised governance
- Sargon the Great centralized administrative system developed a system in which the whole empire Provinces were divided into.
- in each province Governors appointed by the king Who was responsible for tax collection , military activities and maintaining law and order .
( c) Military power
- of the Akkadian Empire an organized and standing army , which was prepared by Sargon the Great.
- in this army Professional soldiers Who were always ready to protect and expand the empire .
- The Akkadian army first Shields , bows and arrows , and organized warfare used.
2. Language and script
( a) Akkadian language
- Main language of Akkadian civilization Akkadian , which belonged to the Semitic language family.
- this language is gradually Sumerian Language and later on Babylonian and Assyrian Empires It became the official language of.
( b) cuneiform script
- The Akkadian people Sumerian Cuneiform Script and modified it to suit their language.
- use this script State orders , business records , and religious texts It was used to write down.
3. Economic and trade system
( a) Development of agriculture
- The region was extremely fertile because of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers , allowing agriculture to develop.
- Main Crops Wheat , barley , dates and pulses Were.
- Advanced irrigation system was developed , in which canals and reservoirs were constructed.
( b) Trade relations
- Trade was the backbone of the Akkadian economy , and they imported and exported goods from distant regions.
- The major trading partners were:
- , textiles , and precious stones from the Indus Valley Civilization (India-Pakistan) .
- Wood and precious metals from Egypt.
- Copper and silver from Iran and Asia Minor.
4. Religious and cultural characteristics
( a ) Polytheism
- Akkadian People They were polytheistic , that is they worshipped many gods and goddesses.
- The major deities were:
- Anu – God of the sky .
- Enlil – God of wind and storms.
- Inanna or Ishtar – Goddess of love and war .
- Shamash – Sun god and guardian of justice.
( b) Construction of temples and ziggurats
- In Akkadian civilization Ziggurat Huge temples named were constructed.
- Ziggurats were multi-storey structures , made of bricks, and were regarded as the abode of the gods.
5. Art and Architecture
( a) Sculpture and Architecture
- In Akkadian art Realism In which realistic expressions were given in sculptures and paintings.
- Famous Akkadian Artworks:
- Bronze statue of Sargon the Great.
- of Naram-Sin .
- Akkadian Seals ( Cylindrical Seals), Which were used to authenticate administrative and business documents.
6. Fall of the Akkadian Empire
( a) Internal rebellion and administrative problems
- After the death of Sargon the Great, instability in the empire increased.
- Due to weak rulers and administrative chaos, rebellions started occurring in various provinces.
( b) External invasion
- The hill tribe called Gutians has approximately 2154 BC attacked and destroyed the Akkadian Empire in 300 BC.
- After this , the Akkadian Empire declined and it gradually This changed as the Neo -Sumerian Renaissance began.
conclusion
The Akkadian civilization has contributed to world history the establishment of the first empire , organised administration , military efficiency , and Extensive business network Their language , script , art and religious traditions were seen in the later Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations. However , due to internal conflicts and external invasions, the Babylonians and Assyrians continued to exist. Due to this the empire could not last for long , but its influence remained for a long time.
( a) System of Governance
Akkadian Civilization : The world’s first centralized empire was , which Sargon the Great In this empire Efficient administrative system , organized military force , and effective tax system Akkadian system of governance was developed autocratic rule of the king It was based on the Constitution of India , but various administrative reforms were made to run it smoothly.
1. Absolute Monarchy
- Akkadian Empire Monarchical system of government It was based on the rule of the king , in which the king had absolute power.
- to the king Representative of the gods It was believed that due to this his power had a religious basis also.
- The king was not only the military and administrative head , but he was also the chief justice and the supreme authority of religious rituals.
Administrative Policies of Sargon the Great
- Sargon the Great City-State System put an end to a Unified Empire was established.
- He divided the whole empire into two groups to make the rule effective. Administrative Provinces divided into.
- In these provinces Governors ( governors or ensi) and local administrators appointed by the king Who were employed in collecting taxes and maintaining law and order.
2. Administrative organisation
( a) Partition of the empire
- The Akkadian Empire was divided into small Administrative regions ( Provinces) It was divided into.
- administration of each province Governors appointed by the king I used to see which Ensi ( Ensi) or Ishaku ( Ishakku) It was said.
( b) Role of Governors
The governors were entrusted with the following functions:
- Tax Collection : A tax system was implemented to raise resources necessary for the empire.
- Military Control : Military units were deployed in every province to maintain security.
- Law and Order: The Governor intervened in judicial matters and enforced local laws.
- Irrigation & Public Works : Canals and reservoirs were managed for water supply and agricultural purposes.
3. Military System
( a) Organised and standing army
- Akkadian rulers first Permanent and organized army ( Standing Army) Was constructed.
- this army was under the direct control of the king And apart from protecting the empire, it also helped in its expansion.
- The soldiers were provided with regular salaries and facilities.
( b) Military strategy and weapons
- The Akkadian army Shields , bows and arrows , spears and chariots used.
- in battle strategy Phalanx system was used , in which the soldiers formed an organised line and attacked the enemy.
- Reign of Sargon the Great The Akkadian army Sumerian city-states , Syria , Asia Minor and Persia Expanded his empire till.
4. Taxation & Economy
( a) Tax system
- The tax system was streamlined under Akkadian rule.
- Taxes were collected in the following ways:
- Agricultural Taxes: Farmers had to give a certain portion of their produce to the government.
- Trade Tax: Merchants had to pay a part of their income as tax.
- Labor Tax: In some cases, labour service ( Corvée Labor) had to be given in the form of tax , like digging of canals or military service.
( b) Business and resource management
- The Akkadian rulers protection of trade routes Paid special attention to.
- Business Partners:
- Indus Valley Civilization (India-Pakistan) from gold , precious stones and spices.
- Egypt From wood and metals.
- Iran and Asia Minor From copper and silver.
5. Judicial System
( a) Law and justice system
- Under Akkadian rule unwritten laws was followed.
- mainstay of the justice system Royal Decrees And Religious Codes Were.
- power to make legal decisions Kings , governors, and chief judges of the city-state had have.
( b) Penal system
- The criminals were given severe punishments , which included Fine , Exile , Imprisonment and Corporal Punishment Were included.
- In matters relating to property and business Trade Contracts and Loan Documents was of special importance.
6. Religious Administration
( a) Relation between king and religion
- In the Akkadian system of government the king Representative of the gods was considered.
- The responsibility of performing religious rituals and pleasing the gods was of the king and the high priests .
( b) Management of temples and ziggurats
- Management of temples Religious officials and priests It was done by.
- The temples received large amounts of donations and grain taxes , which made them financially prosperous as well.
7. Characteristics of the Akkadian system of government
| Speciality | Description |
| Type of governance | Centralized Monarchy |
| Administrative divisions | The empire was divided into provinces |
| Army | Standing and organized army , new weapons and tactics |
| tax system | Agricultural , trade and labor taxes imposed |
| Justice System | Written laws , harsh punishments , contract system |
| Religious administration | The king was considered the representative of the gods |
conclusion Akkadian system of governance Monarchy , military power , taxation system , judicial administration and religious rule Sargon the Great created a balanced mix of military and administrative skills. Sargon the Great created a strong empire on the strength of his administrative skills and military strategies. organized empire which laid the foundation for the coming Babylonian and Assyrian Empires Paved the way for.
( b) Language and script
The language and script of the Akkadian civilization have great historical importance. Akkadian language One of the world’s oldest Semitic languages , which later became the basis of the Babylonian and Assyrian languages. To write this language Sumerian Cuneiform Script were used , which the Akkadians developed to suit their own needs.
1. Akkadian Language
( a) Origin and development of language
- Akkadian Language Semitic language family which was related to today’s Arabic and Hebrew language It was connected to.
- The oldest evidence of this language 2400 BC It is available around.
- With the expansion of the Akkadian Empire, this language replaced the Sumerian language and became the primary means of communication throughout Mesopotamia.
( b) Major forms of the Akkadian language
Two major forms of the Akkadian language developed:
- Old Akkadian – 2500–2000 BCE
- this language Reign of Sargon the Great It was used in.
- Babylonian and Assyrian forms – after 2000 BCE
- later from the Akkadian language Babylonian and Assyrian languages were developed.
2. Script: Cuneiform Script
( a) Sumerian influence and use of cuneiform
- initially used to write the Akkadian language Sumerian Cuneiform Script was adopted.
- this script It was made up of a combination of vertical and diagonal lines , which Clay Tablets But it was written with the help of pointed wood or reed.
- Gradually, Akkadian scholars modified this script according to their language and added new words to it. Phonetic symbols Added to.
( B) Features of the script
- In cuneiform script Pictographic and Phonetic Symbols It was a mixture of.
- this script Right to Left It was written.
- In this Over 600 symbols was used.
- to write it down Pointed Stylus A pencil was used to make marks on wet clay tablets.
3. Use of language and script
( a) Administrative and government documents
- The Akkadian rulers Orders related to governance , tax collection , and military campaigns used this language and script to keep records of.
- Example:
- Tablets of the Orders of Sargon the Great .
- Naram-Sin’s victory proclamations .
( b) Religious texts and literature
- in the Akkadian language Religious texts , hymns , and ritual texts Were written.
- The most famous texts:
- Epic of Gilgamesh – This is one of the oldest epics in the world.
- Enuma Elish – This is a text telling the Creation Myth .
( c) Trade and diplomacy
- Trade contracts and treaties were also written in the Akkadian language.
- of the Akkadian Empire Trade documents and treaties It was used to establish contact with many countries.
4. Influence of language and script
( a) Use as an international language
- Akkadian Language Southern Mesopotamia , Northern Syria , Asia Minor , and Persia It extended up to.
- It is at that time Diplomatic Language , which was used for communication between different states.
( b) Emergence of Babylonian and Assyrian languages
- Beyond the Akkadian Language Babylonian and Assyrian languages It developed.
- during the Babylonian and Assyrian empires The cuneiform script continued to be used .
5. Decline of the Akkadian language and script
( a) Influence of Aramaic language
- About 1000 BC After that , Aramaic language Its influence began to increase.
- Gradually the use of the Akkadian language began to decline, and it Moved towards decline .
( b) End of the cuneiform script
- The use of cuneiform script declined with the advent of the Aramaic and Phoenician scripts .
- About By 500 BC this script became completely extinct .
6. Conclusion
Contribution of the Akkadian language and the cuneiform script It was very important in the administration , literature , and religious rituals of ancient civilizations . This language was the most popular language of its time. first international language bunny and to write it down One of the world’s first scripts , cuneiform , was used. Although it later declined due to the influence of the Aramaic language , it had a profound influence on the Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations.
( c) Art and Architecture
Akkadian Civilization was extremely rich in the field of art and architecture. During this period Realistic sculpture , detailed engravings , and impressive architecture Akkadian artists war , political power , and religious matters prominently featured in his art.
1. Characteristics of Akkadian art
- In art Realism and Detailing was included.
- to the rulers Great and like gods It was shown.
- related to war and conquest Relief Sculptures They were made.
- Metal Statues , Cylinder Seals , and Inscriptions was constructed.
2. Major artistic achievements
( a) Sculpture
Sculptures of the Akkadian period display extreme detail and realism.
1. Victory Stele of Naram-Sin
- It is the most famous example of Akkadian art.
- In this inscription King Naram-Sin To like a god is shown.
- The king is shown climbing a mountain and crushing his enemies.
- In this inscription three stars which are symbols of Akkadian gods .
2. Bronze Head of Sargon the Great
- It is a masterpiece of Akkadian art , which Nineveh It was found in.
- This head Bronze It is made of bronze and depicts a powerful and regal image of Sargon.
- This statue is a work of Akkadian artists Skill in metalwork Displays the .
3. Cylinder Seals
- These were small cylindrical seals with finely engraved pictures and writings on them.
- These were used in trade and administration.
- in cylinder seals Images of kings , gods and religious rituals They were engraved.
- In the famous Akkadian cylinder seal ” Royal Hunting Scenes” ( Royal Hunting Scenes) Are prominent.
3. Architecture
The architecture of the Akkadian civilization was inspired by the Sumerian tradition , but it Strength , elegance , and new construction techniques was added.
( a) Temples & Ziggurats
- In Akkadian architecture Religious buildings was given prominence.
- Like the Sumerians , Akkadian rulers also Ziggurat Built multi-storey temples named.
- this ziggurat were made of bricks And these had stairs leading upwards.
- Ziggurats were considered the abode of the gods and priests performed rituals here.
- Example: Ziggurat of Akkad
( b) Palaces & Fortresses
- The Akkadian kings Strong castles and fortresses , which were centers of administration and military security.
- The walls of these buildings were thick and high , so that they remained safe from attacks.
- In the palaces Wall Paintings And Carved Doorways was used.
4. Materials used in art and architecture
- Brick and clay – mainly used in building construction Mud Bricks was used.
- Bronze and Copper – Metals were widely used in sculpture and weapons making.
- Stone – Limestone and sandstone were used for sculptures and inscriptions .
5. Influence of Akkadian art
The art and architecture of the Akkadian period Babylonian and Assyrian Civilizations was deeply influenced by.
- The later rulers Naram-Sin’s Victory Column Adopted the style of relief sculptures like.
- Tradition of ziggurat construction Babylonian and Assyrian architecture It continued in also.
- In sculptures and inscriptions Realism and depth The style was further developed.
6. Conclusion Akkadian art and architecture Political power , religious faith , and military victory expressed it effectively. Their Sculpture , inscriptions , ziggurats , and cylinder seals of that time Creative excellence and technical prowess Later civilisations , such as Babylon , Assyria and Persia But this art and architecture also had a deep impact.
( d) Religion and religious beliefs
Akkadian Civilization mainly It was polytheistic , worshipping many different gods. Akkadian religion was influenced by Sumerian religious traditions , but had some differences . New Gods And political elements The Akkadian rulers themselves Representative of the gods They believed in this and attributed their victory and rule to be the result of divine mercy.
1. Main religious features
- Polytheism – The Akkadians worshiped many gods .
- Deification of Kings – Some Akkadian kings were worshiped as gods.
- Construction of Temples and Ziggurats – Grand temples and ziggurats were built to worship the gods.
- Tradition of rituals and sacrifices – Animal sacrifices and other offerings were offered in religious rituals.
- Afterlife Beliefs – There was a belief that the soul goes to a dark world after death.
2. Akkadian gods and their characteristics
Akkadian religion worshiped many gods associated with various natural and divine forces. Some of the major gods are as follows:
| God | Role and characteristics |
| Anu ( Anu) | God of Heaven and Major Gods |
| Enlil | God of air and earth , controller of fate |
| Enki | Water , Wisdom , and Magic |
| Inanna/ Ishtar | love , war , and fertility |
| Shamash | God of the Sun and Justice |
| Sin | god of the moon |
| Marduk | Later became the supreme god in Babylon |
| Ninurta | god of war and agriculture |
| Dumuz ( Dumuzid/Tammuz) | God associated with fertility and animal husbandry |
( a) Inanna/Ishtar – Goddess of love and war
- Ishtar in the Akkadian civilization one of the most prominent goddesses Was.
- He love , fertility , war , and power It represented the .
- Ishtar is often lions and stars It was shown to be connected to.
- Its most famous temple Temple of Ishtar Was.
( b) Shamash – God of the Sun and Justice
- To Shamash god of the sun was considered.
- He Justice , Truth and Prophecy It was a symbol of.
- Akkadian kings and priests sought Shamash’s blessing for their decisions.
( c) Enlil – powerful god
- To Enlil Controller of storms , winds , and fate was considered.
- its main temple Nippur city It was located in.
- Kings worshiped Enlil before their conquests.
3. Religious places and temples
The Akkadians worshiped their gods in a grand manner Temples and Ziggurats I used to do it.
( a) Ziggurat – religious tower
- In Akkadian architecture Ziggurat shrines Were.
- These were huge , stepped structures , intended to place the deities at a higher elevation.
- Among the famous ziggurats ” Ziggurat of Akkad” Was the chief.
( b) Temples
- Huge temples were built for each major deity.
- Among these Priests performed rituals and offered sacrifices to the gods.
- of gods in temples Statues and offering altars ( Altars) They used to be.
4. Religious rituals and traditions
( a) Sacrifices
- Sacrifices played an important role in Akkadian religion.
- Animals , crops and other materials were offered to the gods.
( b) Festivals and religious celebrations
- In honor of various gods in Akkadian civilization Organizing special festivals It was done.
- The most prominent among these ” Akitu Festival “ Which was the New Year festival.
- This festival Marduk It was celebrated to worship the deity.
( c) Divination and Astrology
- Akkadian People Divination and Astrology But they believed in it.
- cosmic events , animal sacrifices , and dreams By interpreting these, kings and priests tried to gain knowledge about the future.
5. Afterlife Beliefs
- In Akkadian civilization concept of after death was influenced by Sumerian ideas.
- He believed that the soul after death Netherworld I go away.
- to this folk ” Irkalla “ It was said to be a place where the souls of the dead resided without any happiness.
6. Relationship between religion and politics
- The Akkadian kings Representative of the gods was considered.
- King Guardians of the temples and they ruled over their Divine Grace They used to say that it was received from.
- Naram -Sin was the first Akkadian king to declare himself a “god” .
7. Conclusions Akkadian Religion based on polytheism It was a religion in which worship of gods , religious rituals and concepts of the afterlife were given special importance. This religion developed from Sumerian influence but it had many differences. The tradition of considering the king as God religious traditions of the Akkadian civilization later Babylonian and Assyrian religion became the basis of.
( e) Economy and trade
the Akkadian Civilization was based on agriculture , trade , animal husbandry and cottage industries. This civilization One of the first imperialist powers to organize trade and economy Akkadian rulers secured trade routes and established a centralized economic system , which led to the expansion of commerce throughout Mesopotamia.
1. Agriculture and production
The backbone of the Akkadian economy Agriculture Was.
- Major Crops: Barley , wheat , dates , vegetables and sesame
- irrigation system: Construction of Canals and Reservoirs
- For agriculture Use of agricultural tools , ploughs and animals It was done.
- The government has asked the farmers Tax levied on products and developed the grain storage system.
( a) Irrigation system
- for water management in the Akkadian period Construction of artificial reservoirs and canals to be done.
- Flood control and drainage systems were created , which increased agricultural production.
- To maintain fertility Crop Rotation was followed.
2. Industry and Craftsmanship
Various industries and crafts were an important part of economic activity in Akkadian society.
- Metallurgy : Weapons , jewellery and statues were made from copper , bronze and gold .
- Pottery : Pottery and decorative items were made.
- Knitting and Clothing Manufacturing ( Textile Industry): Clothes were made from wool and linen.
- Construction Industry : Craftsmen played a major role in the construction of temples , palaces and public buildings.
3. Trade and commerce
The Akkadian Empire Extensive business network Developed , which strengthened economic ties with remote areas.
( a) Major trade routes
- The Akkadian Empire Trade from Mesopotamia to Arabia , India , Egypt, and Asia Minor Did.
- land and water routes Trade was conducted through.
- Important Trading Centres: Akkad , Ur , and Nippur .
( b) Imports and Exports
Akkadian merchants imported and exported a variety of goods.
| Items to be imported | Items to be exported |
| Copper | Grains |
| Tin | Clothing and Textiles |
| Silver and Gold | Pottery |
| Precious Stones | Weapons & Tools |
| Wood | Statues and decorative items |
( c) Trading partners and major trading centres
- Dilomu ( Dilmun – modern Bahrain and Kuwait) – copper and wood
- Magan ( modern -day Oman and United Arab Emirates) – copper and shipbuilding materials
- Meluhha ( Indus Valley Civilization) – Precious stones and pearls
- Elam ( modern Iran) – metals and textiles
4. Currency and exchange system
The Akkadian economy had a limited concept of currency , but there were many uses for trade. Barter System was used.
( a) Major medium of exchange
- Silver : It was used for commercial exchange.
- Measurement units: The ” shekel ” was the standard weight of silver.
- Accounting and Records: Business transactions were recorded on clay tablets .
5. Taxation System
The Akkadian Empire had an organized tax system.
- from farmers and traders Taxes were collected in the form of grains , animals , and craft products .
- Use of taxes It was used in military campaigns , temple construction , and administrative work .
- Special officers were appointed for tax collection.
6. Transport and trade routes
The transportation system was developed to enable the trade to function smoothly.
( a) Water Transport
- For Akkadian trade Use of rivers (Tigris and Euphrates) It was done.
- Boats & Ships They were important in the transportation of commercial goods.
- for sea trade Use of the Persian Gulf It was done.
( b) Land Transport
- Use of Carts & Donkeys It was used for transportation of goods.
- to protect the trade routes Military posts were established .
7. Collapse of the economy
The economy of the Akkadian Empire weakened for several reasons.
- constant wars and invasions This affected trade and agriculture.
- Drought and climate change Due to this, agricultural production declined.
- due to administrative weakness Weak tax collection and economic stability It’s done.
8. Conclusion Economy of the Akkadian Civilization agriculture , trade , and crafts The expansion of trade routes and an organized tax system strengthened it , but later Political instability and environmental challenges The Akkadian trade system Babylonian and Assyrian Civilizations It also had a profound effect on the economy of
3. The decline of the Akkadian civilization
Akkadian Civilization happened gradually due to many factors. This civilization approximately 2334 BCE to 2154 BCE flourished until , but eventually Internal rebellion , external aggression , climate change and administrative weaknesses It was destroyed because of.
1. Political instability and administrative weakness
- Akkadian Empire The first centralized empire It was a powerful state , but it was difficult to run its administration smoothly.
- The empire had expanded greatly , making it difficult to control.
- in various city-states Growing discontent and rebellion of local rulers weakened the empire.
- The power of the kings declined , due to which anarchy began to spread in the administration.
( a) Naram-Sin and the rebellion
- Naram-Sin ( 2254–2218 BCE) The most powerful king of Akkad was ” God-King “ It was declared.
- but during his reign Internal rebellions and external attacks increased .
- The Akkadian army was sent in several times to put down rebellions , putting a heavy strain on resources.
2. External aggression and attack of Gutian invaders
- The Akkadian Empire was weakened by several external invaders.
- The deadliest attack Gutian Tribe , which was done by They came from the Zagros Mountains of Iran .
- The Gutians continued to attack the cities of Akkad and gradually they Captured the capital, Akkad .
- During the Gutian reign Trade and agriculture came to a standstill , leading to an economic crisis.
3. Climate change and environmental problems
- Destruction of river embankments and drought Was one of the major causes for the decline of the Akkadian civilization.
- According to scientific research , around 2200 B.C. One Serious climate change happened , which spread throughout Mesopotamia There was a severe drought .
- There was a sharp drop in crop production , which Hunger and famine Such situations arose.
- Irrigation systems were damaged , halting agricultural production.
4. Economic collapse and blockage of trade routes
- The Akkadian economy was badly affected by wars , invasions and environmental problems.
- Trade routes were blocked , preventing Akkadian merchants from importing essential goods from other states.
- due to economic crisis Decline of craftsmen and traders This happened , which increased instability in the society.
5. Social unrest and cultural decline
- Due to external attacks and internal conflicts Social instability spread .
- The people of the city-states became tired of the anarchy and became increasingly hostile towards the empire. insincere Have become.
- Religious and cultural activities were disrupted , due to which despair spread in the society.
6. The final stage and culmination of the decline
- Around 2154 BCE , Gutian invaders The city of Akkad was completely destroyed .
- The Akkadian Empire ended and was replaced by The Sumerian city-states regained independence .
- The influence of the Akkadian civilization ended , but its language and administrative system survived Adopted in the Babylonian and Assyrian civilisations .
7. Conclusions
The fall of the Akkadian civilization Multidimensional process The reasons for this were political , military , economic , and environmental.
- External invasions (Gutian tribes)
- Drought and environmental crisis
- Chaotic administration and internal rebellion
- Economic instability and collapse of business
The Akkadian Empire ended , but its administrative and cultural legacy continued Babylon and Assyria It had a profound impact on civilizations like.
( a) Internal Causes
The fall of Akkadian civilization was not only due to external invasions and natural disasters , but there were many other reasons behind it. Internal causes Within the empire Political instability , administrative weakness , economic crisis and social rebellion There were problems like these which weakened its roots.
1. Administrative weakness and over expansion of the empire
- Akkadian Empire First Centralized Empire but its area had become much larger.
- The rulers were able to maintain control over all the city-states. fail Were happening.
- for smooth running of the administration Regional governors were appointed , but several governors rebelled.
- Excessive bureaucracy and corruption weakened the administration.
2. Succession disputes and weak rulers
- Great ruler Sargon ( Sargon of Akkad) and Naram- Sin After that weak rulers came to power.
- regarding succession Conflict in the royal family We have begun.
- empire due to weak kings Started dividing into various powerful clans .
- The central power began to weaken , leading to increased rebellions in the city-states.
3. Internal rebellion and revolt of the city-states
- Under the Akkadian Empire Sumerian city-states ( Ur, Lagash, Nippur) , which were earlier independent.
- The Sumerian rulers did not accept Akkadian rule , so they There were constant rebellions .
- Huge military force was deployed to suppress the rebellions , which Excessive strain on military resources Fell.
- due to revolts in the empire Political instability increased and the number of soldiers decreased.
4. Economic crisis and failure of the tax system
- to maintain the empire Heavy taxes were levied , which angered the general public.
- because of excessive taxes and wars The condition of farmers and traders worsened .
- increased attacks on trade routes Business activities were affected .
- due to economic crisis It became difficult to pay the soldiers , which weakened the army.
5. Social discontent and anarchy
- because of high taxes and wars The life of the common people became difficult .
- The rise in social inequality The gap between the rich and the poor deepened .
- The Akkadian rulers themselves ” Representative of God ” ( Divine King) They started declaring this , which increased religious and social discontent.
- Farmers and workers People started revolting , which affected agriculture and production.
6. Military weakness and discontent of soldiers
- because of the constant wars and rebellions The soldiers had to fight continuously .
- Due to lack of military resources and soldiers not getting proper salary The army became weak .
- In the troops Lack of loyalty and they often joined forces with rebel groups.
- to fight the Gutians and other external invaders The Akkadian army was not adequately prepared .
7. Religious dissent and neglect of old traditions
- Rulers like Naram-Sin established themselves as He was declared a ” god” , which angered religious leaders.
- The neglect of traditional deities has created a public religious dissent Increased.
- By imposing taxes on temples and religious places The conflict between priests and the public increased .
- Religious instability weakened Akkadian rule and many people began to oppose the rulers.
8. Conclusion
The collapse of the Akkadian Empire was due to a variety of internal causes , including administrative failure , economic crisis , internal rebellion, and social discontent.
- Weak administration and Extreme expansion
- Struggle over the king’s succession
- Revolt of the city-states and internal rebellion
- Excessive taxes and economic instability
- Religious and social discontent
These internal factors have This weakened the empire from within , allowing Gutian invaders to destroy it.
( b) External Invasion
External invasions played an important role in the decline of Akkadian civilization. Especially Gutian Tribe and other outside powers attacked Akkad , weakening and eventually destroying the empire. These invasions proved to be the greatest challenge to the Akkadian military and administration.
1. Gutian Invasion
( a) Who were the Gutians ?
- Gutian A nomadic and hill tribe was , which Zagros Mountains of Iran I used to live in.
- They were divided into small groups and were mainly Looting and raids used to do it.
( b) Gutian Invasion and their strategy
- Gutian first Sumerian City-States But they continued to attack , due to which their power increased.
- They gradually began raiding Akkadian cities and plundering their resources.
- The Akkadian army fought them at first , but Constant war and shortage of soldiers They became weak because of it.
- About 2154 BC , the Gutian tribe attacked the capital of Akkad And destroyed it completely.
- after this The Gutians ruled southern Mesopotamia for many years .
2. Amorites and Elamites invasion
( a) Influence of the Amorite tribe
- Amorites A western nomadic tribe that later settled in Babylon .
- After the fall of the Akkadian Empire , the Amorite people gradually spread into southern Mesopotamia. started increasing his power .
( b) Elamite invasion
- Elamites The people came from eastern Mesopotamia (present-day Iran).
- After the Akkadian Empire weakened , the Elamite people also began to attack the city-states .
- They challenged Akkadian rule at times and supported local rebellions.
3. Effects of invasions
( a) Economic crisis and collapse of business
- due to external attacks Trade routes were disrupted , affecting Akkad’s economy.
- Gutian and other invaders The cities were looted and destroyed , due to which industry and trade came to a standstill.
( b) Administrative disintegration
- Akkadian rule was weakened by the invasions and The city-states began to revolt .
- Due to the decrease in military power, the ruler Unable to control rebellions and invasions Have become.
( c) Cultural and social degradation
- due to external attacks Akkadian art , architecture, and writing system Was impressed.
- Many important Akkadian monuments and temples Destroyed by Gutian invaders .
- In society fear , chaos, and disorder spread , causing people to migrate to other city-states.
4. Conclusion
External invasions played a decisive role in the decline of the Akkadian civilization.
- Gutian Tribe launched the deadliest attack and destroyed the capital, Akkad.
- Amorite and Elamite invasions destroyed the remaining power of Akkad.
- Because of these attacks Political instability , economic decline , social disintegration and cultural decay Happened.
After these external attacks The Sumerian city-states gradually regained their independence , leading to the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in Mesopotamia The emergence of new civilisations Happened.
Importance of Akkadian Civilization
Akkadian Civilization was the first civilization in world history Great imperial civilization It was a civilization which made many important contributions in the field of governance , administration , language , art , military strategy and cultural development. This civilization approximately 2334 BCE to 2154 BCE It flourished till 1000 BC and its influence was felt on the subsequent civilisations also.
1. First Centralized Empire
- Akkadian Empire The first organized and centralized empire in history Was.
- King Sargon the Great ( Sargon of Akkad) unified the separate city-states for the first time Imperialist system of governance Laid the foundation of.
- This system will later Babylonian and Assyrian Empires It was also adopted in.
2. Administrative and legal system
- The Akkadian rulers Administrative centralization and throughout the empire Appointed government officials ( Governors) .
- Tax System and Military Organization was effectively implemented.
- this model later Babylonian , Assyrian, and Persian empires Adopted by.
3. Akkadian language and writing system
- Akkadian Language The first Semitic language , which became the official language throughout Mesopotamia .
- this language The Sumerian language was influenced by And later it became the basis of the Babylonian and Assyrian languages.
- Akkadian Language Cuneiform Script It was written in , which was later adopted by Babylon and Assyria also.
4. Military strategy and the beginning of conquests
- Akkadian Empire It was the first power to establish an organised army and a permanent military force .
- Sargon the Great For the first time, he organised professional army , which helped in expanding his empire.
- To expand his empire, he Tactics of naval operations through rivers Also adopted.
5. Contribution to art , architecture and sculpture
- In Akkadian art Development of realistic sculpture and detailed engraving Happened.
- Victory Stele of Naram – Sin It is an important artifact of the Akkadian period.
- in this period huge palaces , temples and public buildings was constructed.
- Akkadian architecture further developed Had a profound influence on Babylonian and Assyrian architecture .
6. Development of religion and religious traditions
- Akkadian Religion was influenced by Sumerian traditions , but they introduced the worship of many new gods.
- They The king was considered the representative of God , which provided a religious basis to the monarchy.
- In the Akkadian pantheon Inanna , Enlil , and Shamash He was the chief.
- This religious system later Developed in the Babylonian and Assyrian civilisations .
7. Trade and economic growth
- The Akkadian Empire Expanded trade and established economic relations with various regions .
- They Developed trade routes to Iran , India , Syria and Anatolia (Turkey) .
- Akkadian traders Copper , gold , silver , wood and precious stones traded for.
8. Social and cultural influences
- The Akkadian civilization spread throughout Mesopotamia Cultural Integration Promoted to.
- Sumerian and Akkadian culture There was a mixture of these , which later led to the development of the Babylonian and Assyrian civilisations.
- They Began the tradition of preserving literature , religious texts and administrative records .
9. Impact on future civilizations
- The Akkadian administrative and military model Babylonian , Assyrian and Persian Empires influenced by.
- The tradition of the Divine Kingship Started with the Akkadian civilization , which was later adopted by many civilizations.
- Akkadian cuneiform script and language Became the official language of the Babylonian and Assyrian empires .
10. Conclusion
Akkadian Civilization It was the first great imperial power in history to develop new ideas in the fields of administration , language , military strategy , arts and trade. unprecedented contribution Gave.
- of this civilisation Political and administrative system inspired later civilisations.
- Akkadian Language It was in use in Mesopotamia for hundreds of years.
- Art , architecture and religious traditions Became the basis for the development of Babylonian and Assyrian civilizations.
Even after the fall of the Akkadian civilization , its Culture , administration and language on many civilisations to come Lasting impact left it.
