Introduction: Changing Global Politics and India–Russia Relations
India Russia Relations 2025 reflect a major shift in global geopolitics, energy partnerships and India’s strategic positioning in a multipolar world.
The year 2025 marks a significant phase in global geopolitics. The ongoing Russia–Ukraine conflict, shifting power balances, and India’s growing role on the world stage have collectively reshaped India–Russia relations. Once defined by a stable strategic partnership, these ties are now evolving toward a more pragmatic and balanced diplomatic approach.
This transformation is crucial for understanding India’s foreign policy priorities, especially in the context of strategic autonomy, energy security, and multipolar global politics. For students of international relations and aspirants of competitive examinations, the changing dynamics of India–Russia relations offer important analytical insights.
India Russia Relations 2025: Historical Background
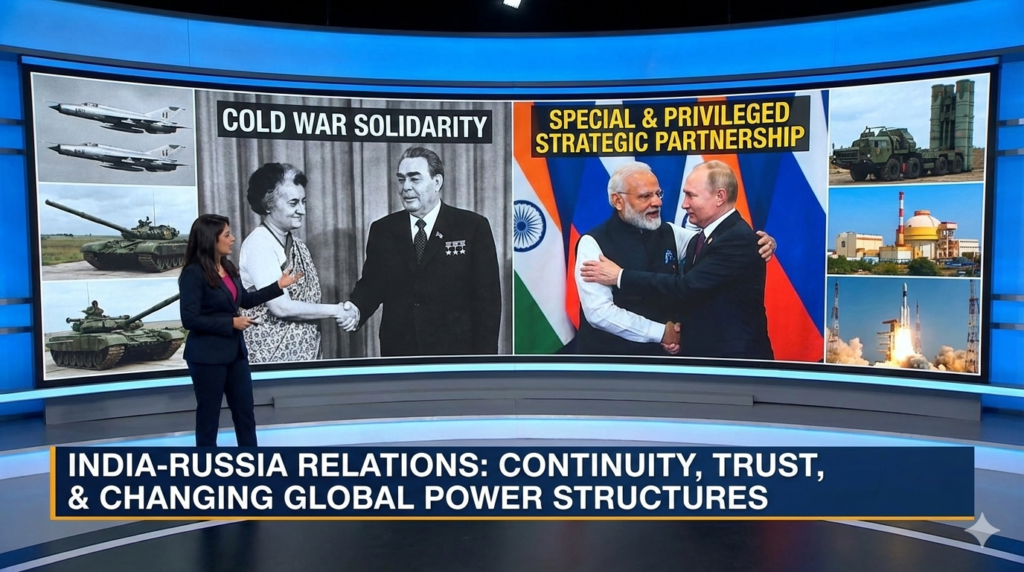
The Cold War Era: India and the Soviet Union
During the Cold War, relations between India and the Soviet Union were built on mutual trust and strategic cooperation. At a time when the world was divided into two rival blocs, the Soviet Union consistently supported India on key international issues, including at the United Nations.
Soviet assistance in defence, heavy industries, science, and space technology played a crucial role in strengthening India’s economic and strategic foundations.
The 1971 Treaty and Strategic Trust
The Indo–Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation signed in 1971 formalised the close relationship between the two countries. This treaty was particularly significant for India, as it provided diplomatic and strategic reassurance during a critical phase in South Asian geopolitics.
Relations After the Disintegration of the Soviet Union
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to major changes in the global power structure. However, bilateral ties did not disappear with this transition.
As the successor state, Russia continued defence cooperation and diplomatic engagement with India. During this period, India also adopted economic liberalisation, which influenced the nature and scope of bilateral relations.
Strategic Partnership in the New Millennium
In the early 2000s, India and Russia elevated their ties to a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership.” Defence cooperation, energy collaboration, and regular high-level political dialogue became the core pillars of this partnership.
This historical trajectory provides the foundation for understanding the evolution of India Russia Relations 2025 and the strategic recalibration visible today.
Russia–Ukraine War and India’s Stand
Outbreak of the War and Global Reactions
The outbreak of the Russia–Ukraine war in February 2022 fundamentally disrupted the global order. Large-scale military conflict in Europe, humanitarian crises, and severe disruptions in energy supply transformed the war from a regional confrontation into a global geopolitical crisis.
The United States and European countries imposed wide-ranging economic, financial, and technological sanctions on Russia, leading to renewed global polarisation.
India’s Neutral Position at the United Nations
During various United Nations resolutions related to the Russia–Ukraine conflict, India refrained from taking a clear side either in favour of or against Russia. By abstaining from voting, India consistently emphasised dialogue, diplomacy, and peaceful resolution of the conflict.
This approach reflected India’s policy of Strategic Autonomy, which seeks to safeguard national interests without aligning with any major power bloc.

Western Pressure and India’s Response
The United States and the European Union expected India to criticise Russia and participate in sanctions. However, India clarified that its priorities lay in protecting its citizens, securing energy supplies, and preserving long-term national interests.
India also underlined that complex international conflicts cannot be resolved through military means alone, and that sustained dialogue remains the only viable path to peace.
Energy Security and a Pragmatic Approach
In the aftermath of the war, the availability of discounted Russian crude oil emerged as a significant economic opportunity for India. Taking energy security into account, India adopted a pragmatic and interest-based approach.
Thus, India’s stance during the Russia–Ukraine war was neither unconditional support nor outright opposition, but a balanced, independent, and realistic reflection of its evolving foreign policy.
1barIndia Russia Relations 2025: Impact on India’s Changing Foreign Policy
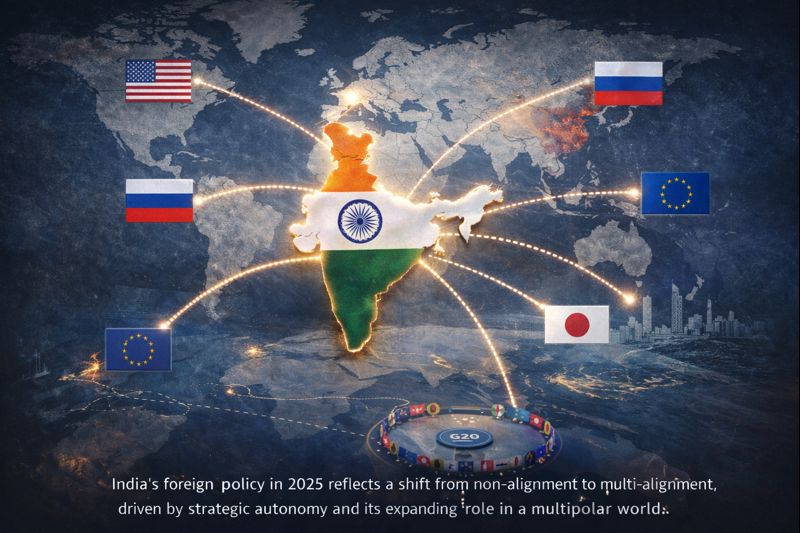
From Non-Alignment to Multi-Alignment
During the Cold War, India’s foreign policy was shaped by the principle of non-alignment. By 2025, however, India has moved toward a policy of multi-alignment, seeking balanced relations with multiple global powers.
Rather than relying on a single bloc, India now simultaneously engages with the United States, Russia, Europe, and Indo-Pacific countries, reflecting a more flexible and pragmatic diplomatic approach.
The Concept of Strategic Autonomy
At the core of India’s foreign policy lies the principle of Strategic Autonomy, which emphasises the ability to take independent decisions based on national interests. India’s response to the Russia–Ukraine war clearly demonstrates this approach, which significantly shapes the direction of India Russia Relations 2025.
India’s Expanding Role on the Global Stage
In 2025, India increasingly views itself not merely as a regional power, but as an emerging global actor. Its active engagement in forums such as the G20, the Global South, and the Indo-Pacific highlights the evolving nature of India’s foreign policy.
A New Phase in Defence Cooperation
India’s Traditional Dependence on Russian Defence Supplies
For several decades, a significant portion of India’s defence capabilities has been based on military equipment supplied by Russia (formerly the Soviet Union). Fighter aircraft, tanks, submarines, and missile systems have formed the backbone of bilateral defence cooperation.
This partnership provided India with strategic stability and reliable military support during challenging geopolitical periods. Defence collaboration remains a crucial pillar of India Russia Relations 2025.
Make in India and Defence Diversification
By 2025, India’s defence policy reflects a clear shift. Under the initiatives of Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat, India is promoting domestic defence manufacturing and reducing long-term dependence on foreign suppliers.
Simultaneously, India has expanded defence cooperation with countries such as France, the United States, and Israel, leading to greater diversification in defence procurement.
Why Russia Still Matters
Despite diversification efforts, Russia continues to play an important role in India’s defence ecosystem. Advanced air defence systems such as the S-400, the BrahMos missile programme, and maintenance of legacy platforms keep defence ties strategically relevant.
Thus, in 2025, defence cooperation between India and Russia is evolving from dependency toward partnership, co-production, and technological collaboration.
Energy, Oil, and Economic Diplomacy
Energy Security and National Interests
For a rapidly growing economy like India, energy security remains a critical national priority. India’s heavy dependence on imported oil and gas makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy markets.
In this context, relations with an energy-rich country like Russia play a significant role in India’s long-term energy strategy. Energy cooperation has therefore become a defining pillar of India Russia Relations 2025.
Import of Discounted Russian Crude Oil
Following the Russia–Ukraine war and the imposition of Western sanctions, Russia began offering its crude oil at discounted prices. India capitalised on this opportunity by importing large volumes of Russian crude oil.
This decision not only reduced import costs but also helped India manage inflationary pressures and maintain economic stability.
Local Currency Trade and Payment Mechanisms
To reduce dependence on the US dollar, India and Russia explored trade settlement mechanisms based on local currencies such as the rupee and the rouble. This initiative aimed to facilitate bilateral trade while strengthening financial sovereignty.
The Broader Scope of Economic Diplomacy
Energy cooperation goes beyond mere trade and forms a key component of India’s broader economic diplomacy. Energy ties with Russia provide India with strategic flexibility and greater autonomy in decision-making at the global level.
China Factor and India’s Strategy
Growing Russia–China Strategic Proximity
In recent years, strategic, military, and economic cooperation between Russia and China has increased significantly. Western sanctions have further pushed Russia towards greater dependence on China, reshaping power dynamics in Asia.
This growing proximity raises concerns for India, particularly in the context of unresolved border disputes and ongoing strategic rivalry with China.
India’s Security Concerns
For India, the primary concern is that Russia–China relations should not evolve in a manner detrimental to India’s strategic interests. An excessive Russian tilt towards China could adversely affect India’s security calculations.
Therefore, maintaining engagement with Russia remains strategically important for India.
Policy of Balance and Dialogue
India’s approach is neither to distance itself from Russia nor to directly confront a Russia–China axis. Instead, India emphasises balance, dialogue, and pragmatic diplomacy.
By sustaining active engagement with Russia, India seeks to ensure that its security and regional interests are not marginalised.

India’s Role in a Multipolar World Order
Taking the China factor into account, India supports the creation of a multipolar world order where no single power dominates global politics. In this context, cooperation with Russia forms an important pillar of India’s long-term strategic vision.
Key Reasons Behind India Russia Relations 2025 Shift
1. Long-Term Impact of the Russia–Ukraine War
The Russia–Ukraine war that began in 2022 has evolved beyond a regional conflict and has significantly altered the global balance of power. By 2025, its long-term consequences are reshaping the broader dynamics of India Russia Relations 2025.
2. Western Sanctions and Global Polarisation
Economic and strategic sanctions imposed on Russia by the United States and Europe have created diplomatic challenges for India. India must balance its engagement with the West while preserving its traditional strategic partnership with Russia.
3. India’s Policy of Strategic Autonomy
Strategic Autonomy remains the cornerstone of India’s foreign policy. In 2025, India prefers independent decision-making based on national interests rather than aligning with any single power bloc, directly influencing its approach towards Russia.
4. Energy Security and Economic Considerations
As a rapidly growing economy, India’s demand for energy continues to rise. Access to discounted Russian oil and sustained energy cooperation have become vital for India’s economic stability and growth.
5. The China Factor and Regional Security
Growing Russia–China proximity and ongoing tensions between India and China encourage India to maintain engagement with Russia. This balancing strategy is a key driver of the evolving strategic partnership.
6. India’s Aspiration to Emerge as a Global Power
In 2025, India increasingly views itself as an emerging global power. Its active role in the G20, the Global South, and the pursuit of a multipolar world order require a more pragmatic and flexible approach toward Russia.
Opportunities and Risks for India
Key Opportunities for India
The evolving India–Russia relationship in 2025 presents several important opportunities. Through balanced and pragmatic diplomacy, India can advance its national interests more effectively.
- Strategic Autonomy: India can strengthen its ability to pursue an independent foreign policy without excessive dependence on any single power bloc.
- Energy Security: Access to discounted Russian oil and sustained energy cooperation support India’s long-term energy requirements.
- Defence Technology and Co-production: Defence collaboration with Russia, including co-production and technology transfer, complements initiatives such as Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Role as a Global Mediator: India can position itself as a bridge power facilitating dialogue between Russia and Western countries.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Alongside these opportunities, India also faces several risks and challenges that require careful management.
- Trust Deficit with Western Countries: Closer ties with Russia may generate concerns among the United States and European partners.
- Risks from Russia–China Proximity: A deeper Russia–China alignment could complicate India’s regional security environment.
- Risk of Overdependence: Excessive reliance on a single country for defence or energy could reduce India’s strategic flexibility.
- Indirect Impact of Global Sanctions: Sanctions imposed on Russia may indirectly affect India’s financial transactions and trade networks.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
By 2025, India Russia Relations 2025 have evolved beyond a single-dimensional partnership and now reflect India’s changing foreign policy priorities, strategic autonomy, and global aspirations. These ties are gradually shifting from historical dependence toward pragmatism, balance, and national interest.
Amid challenges such as the Russia–Ukraine war, Western sanctions, the China factor, and energy security concerns, India has demonstrated that its foreign policy is guided neither by external pressure nor ideological rigidity, but by dialogue, realism, and long-term strategic thinking.
Looking ahead, the future of India Russia Relations 2025 is likely to be shaped by cautious cooperation and strategic balance. India can neither afford to distance itself from Russia nor rely excessively on any single power. It is this balance that defines India’s diplomatic maturity.
From a UPSC perspective, this evolving partnership highlights a key lesson of contemporary international relations: a successful foreign policy lies in harmonising idealism with realism while safeguarding national interests in a complex and multipolar world.
UPSC Mains Model Answer (250 Words)
India Russia Relations 2025 reflect broader shifts in global geopolitics. The Russia–Ukraine war, Western sanctions on Russia, and the growing China factor have compelled India to recalibrate its foreign policy approach.
India has consistently followed the principle of Strategic Autonomy, which emphasises independent decision-making based on national interests. Instead of aligning with any single power bloc, India has adopted a multi-alignment strategy, maintaining engagement with Russia while strengthening ties with the United States, Europe, and Indo-Pacific partners.
Energy security has emerged as a crucial factor, with India importing discounted Russian crude oil to support economic stability and control inflation. At the same time, defence cooperation with Russia continues, though India is increasingly diversifying its defence partnerships under initiatives such as Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Additionally, growing Russia–China proximity presents security concerns for India, making continued engagement with Russia strategically necessary. Overall, the evolution of India Russia Relations 2025 demonstrates India’s pragmatic diplomacy, balancing realism with strategic vision in a multipolar world order.
UPSC Prelims Practice MCQs

- Strategic Autonomy in India’s foreign policy primarily refers to:
(a) Isolation from global politics
(b) Alignment with one major power
(c) Independent decision-making based on national interest
(d) Membership of military alliancesAnswer: (c)
- Which factor significantly increased India’s import of Russian crude oil?
(a) WTO agreement
(b) Western sanctions on Russia
(c) OPEC decision
(d) Currency appreciationAnswer: (b)
- The China factor in India–Russia relations mainly relates to:
(a) Trade competition
(b) Border agreements
(c) Russia–China strategic proximity
(d) Cultural exchangesAnswer: (c)
- India–Russia defence relations are currently characterised by:
(a) Complete dependence
(b) Complete disengagement
(c) Diversification and co-production
(d) Military allianceAnswer: (c)
- India supports which type of world order?
(a) Bipolar
(b) Unipolar
(c) Multipolar
(d) IsolationistAnswer: (c)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Are India Russia Relations 2025 Changing?
Global geopolitical shifts, the Russia–Ukraine war, energy security concerns, and India’s evolving foreign policy are driving changes in India–Russia relations.
Does India support Russia in the Ukraine conflict?
India has adopted a neutral stance, emphasising dialogue and diplomacy rather than military solutions.
Why is Russia still important for India?
Russia remains crucial for India’s defence cooperation, energy security, and balancing the China factor in regional geopolitics.
What is India’s foreign policy approach called?
India follows Strategic Autonomy and Multi-Alignment, allowing it to engage with multiple global powers simultaneously.