Sweden – A Developed, Peace-Loving and Inspiring Nation
Sweden is a developed, prosperous and peaceful country situated in Northern Europe. It is one of the well-known Scandinavian nations, admired globally for its natural beauty, modern society, high living standards and world-class innovation.
Short Introduction of Sweden
1. Geographic Situation
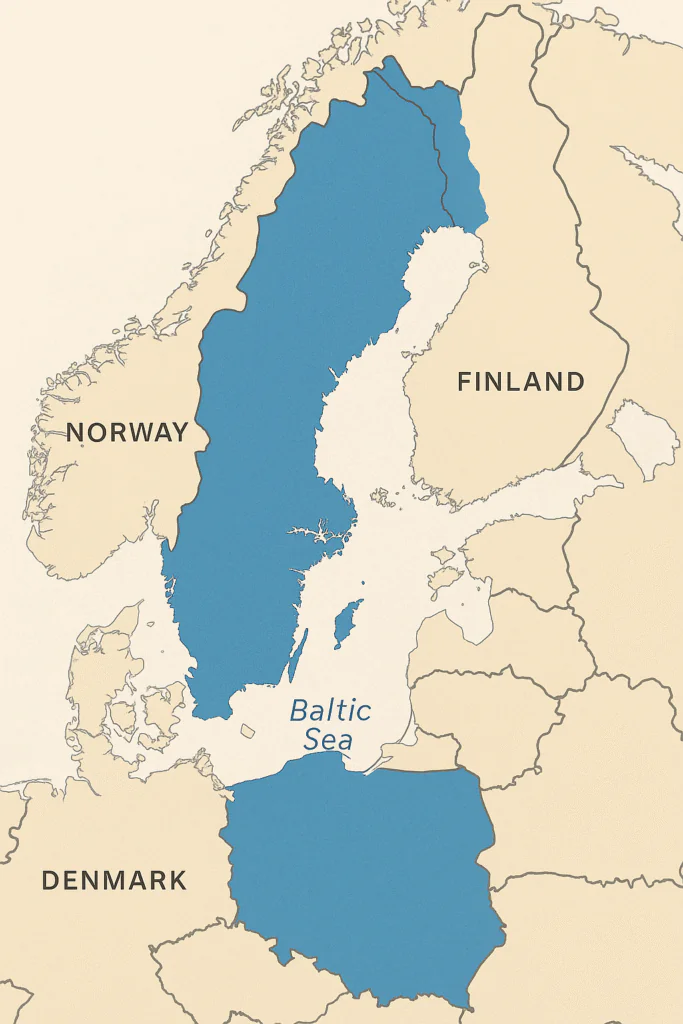
Sweden is located in Northern Europe and is famous for its beautiful landscapes, lakes and dense forests.
Geographical Overview
- Location: Northern Europe, on the Scandinavian Peninsula
- Borders:
- East: Baltic Sea
- West: Norway
- North-East: Finland
- Capital: Stockholm
- Main Cities: Gothenburg, Malmö, Uppsala
2. Political Arrangement
Sweden has a stable, transparent and democratic political system based on a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.
- Government System: Parliamentary Democracy + Constitutional Monarchy
- King: Carl XVI Gustaf (Ceremonial Head of State)
- Prime Minister: The real executive head (2025 – verify for latest update)
- Parliament: Riksdag – Unicameral legislature
3. Population and Society
Sweden’s society is known for equality, high living standards, openness and freedom.
- Population: Around 10 million
- Languages: Swedish (official), English, Finnish, Sami, Arabic, Somali
- Religion: Mainly Christian (Lutheran), but highly secular society
- Literacy Rate: 99%
- HDI: Very high, among the top countries worldwide
4. Economic Situation
Sweden has one of the world’s most balanced, strong and innovation-driven economies. It successfully blends welfare-state policies with private-sector dynamism.
- GDP: ~$650 billion (2025 estimate)
- GDP per capita: $60,000+
- Main Sectors: IT, Automobiles (Volvo, Scania), Telecom (Ericsson), Music (Spotify), Iron & Steel, Wood
- Currency: Swedish Krona (SEK)
1. Detailed Geographical Situation of Sweden
A Beautiful Country on the Scandinavian Peninsula
Sweden stretches around 1,600 km from north to south, covering a total area of approximately 450,000 sq. km, making it the third-largest country in Western Europe.
Major Geographic Features
- More than 100,000 lakes – including Vänern and Vättern
- About two-thirds of the land is covered with forests
- Scandinavian Mountains dominate the western region
- Mild climate in the south, cold and snowy in the north
- Unique phenomena like “Midnight Sun” and “Polar Night”
Important Cities
- Stockholm – Capital city located on the Baltic Sea coast
- Kiruna – Popular for viewing the Northern Lights
- Gothenburg & Malmö – Major industrial and commercial hubs
2. Political System of Sweden
A Strong and Stable Democratic Framework
Sweden’s governance emphasizes transparency, accountability and the protection of citizens’ rights.
Key Features
- Ceremonial monarch
- Prime Minister as the executive authority
- 349-member Riksdag (elected every 4 years)
- Independent judiciary
- Multi-party political system

Amazon Product Title Here
This product is designed to deliver reliable performance and everyday convenience. It offers durable build quality, easy usability, and practical features that make it suitable for regular use at home or work.
🛒 Check Price on Amazon* As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
3. Population and Society of Sweden
A Society Built on Equality, Freedom and High Living Standards
- Equality: Strong gender equality, social fairness and personal freedom
- Healthcare: Universal and high quality
- Education: Free and world-class
- Diversity: Large immigrant population adding cultural richness
- Life Expectancy: Men ~81 years | Women ~84 years
Sweden follows the philosophy of “Lagom” – meaning “not too little, not too much… just the right balance.” This principle reflects in daily life and contributes to a peaceful and content society.
4. Sweden’s Economic Status
One of the World’s Strongest and Most Innovative Economies
Major Economic Characteristics
- Mixed economy with welfare support and a strong private sector
- High tax rates but excellent public services
- Ranked consistently in the top 5 of the Global Innovation Index
- Home to world-famous brands like Volvo, Ericsson, IKEA, Spotify
Major Exports
- Machinery
- Vehicles
- Electronics
- Medicines
- Wood and timber products
Major Trade Partners
- Germany
- Norway
- Denmark
- United States
- China
Conclusion – What Sweden Taught Me
Sweden is not just a developed country—it is a philosophy of life. A nation built on balance, equality, peace and human dignity. Through Sweden, I learned that true progress lies not only in economic power but also in social justice, education, health, sustainability and respect for humanity.
Sweden stands as a global model where economic development and social equality walk hand in hand. It remains an inspiration for every society aiming for long-term peace, stability and balanced growth.
5. Features and Achievements of Sweden
Sweden is a country known worldwide for its commitment to peace, innovation, social equality and eco-friendly development. These features and achievements make Sweden stand apart from many other nations.
Major Features and Achievements of Sweden
1. Peace, Calmness and Neutrality
- Since 1809, Sweden has not participated in any major war.
- The country has consistently followed a long-standing policy of neutrality.
- Often ranked among the top 10 most peaceful nations in the Global Peace Index.
2. Host of the Nobel Prizes
- Due to the legacy of scientist Alfred Nobel, Sweden hosts the Nobel Prize ceremonies every year in Stockholm (except the Peace Prize).
- This highlights Sweden’s global contribution to science, literature, and humanitarian advancement.
3. High Human Development and Quality of Life
- Sweden consistently ranks among the top countries on the Human Development Index (HDI).
- Education, healthcare, cleanliness, and safety standards are among the highest in the world.
- Ranks highly on the Global Gender Equality Index.
4. Strong Welfare Model
- The government provides free education, free healthcare, unemployment support, and generous parental leave.
- Considered one of the strongest and most effective social security models globally.
5. Environment-Friendly and Green Energy Leader
- Over 75% of Sweden’s electricity comes from renewable sources such as hydro, wind and biofuel.
- Leads in green technology, electric vehicles and recycling policies.
- Its international image as “Green Sweden” is widely recognized.

Amazon Product Title Here
This product delivers reliable performance with a durable design and user-friendly features. It is ideal for everyday use and enhances convenience for your daily tasks, making it a practical choice for home and professional use.
🛒 Check Price on Amazon* As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
6. Global Industry and Innovation
- Home to global brands like Spotify, Skype, Klarna, IKEA, Volvo and Ericsson.
- Consistently ranks in the top 5 countries in the Global Innovation Index.
- Heavy investment in research, science and technology education.
7. Equality and Inclusive Society
- Women, minorities and the LGBTQ+ community enjoy full rights and strong legal protection.
- Sweden is known globally for women empowerment, parenting benefits and social welfare systems.
8. Education and Knowledge-Based Culture
- Free education from school to university for Swedish/EU students.
- Attracts thousands of international students every year.
- Strong performance in PISA scores and global university rankings.
9. Tourism and Cultural Heritage
- Known for the Northern Lights, picturesque lakes and vast forests.
- Famous for Midsummer Festival, Christmas traditions and Swedish design.
Conclusion
Sweden is a unique country where modernity, nature, education, equality and peace come together beautifully. Its achievements are not only in the fields of technology and economy, but also in human values and social welfare, making it a true model for the world.
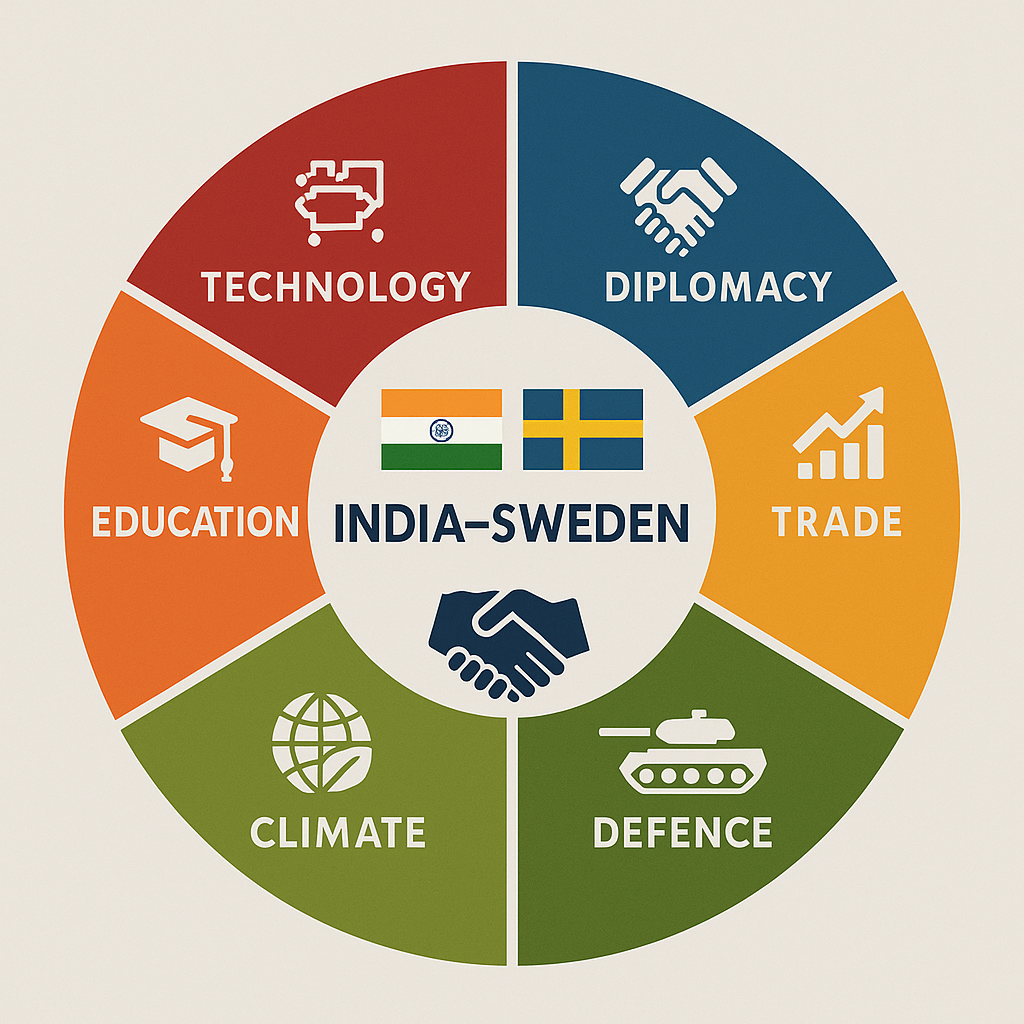
6. India–Sweden Relations
Relations between Sweden and India are strong in historical, economic, political, technological and cultural dimensions. Both countries are democratic and developing nations that share common values, innovation-driven approaches and a commitment to sustainable development.
Overview of India–Sweden Relations
1. Diplomatic Relations
- Formal diplomatic ties between India and Sweden were established in 1957.
- High-level visits have strengthened cooperation:
- Prime Minister Indira Gandhi visited Sweden in 1972.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Sweden in 2018.
- Swedish Prime Minister Stefan Löfven visited India and participated in the “Make in India” conference.
- India and Sweden further expanded cooperation through the India–Nordic Summit.
2. Economic and Trade Relations
| Subject | Description |
|---|---|
| Bilateral Trade | In 2024, India–Sweden trade exceeded USD 2 billion. |
| Swedish Companies in India | Volvo, Ericsson, IKEA, H&M, AstraZeneca, Tetra Pak and others. |
| India’s Exports to Sweden | Textiles, machinery, furniture, pharmaceuticals, chemicals. |
| Sweden’s Exports to India | Vehicles, machinery, communication equipment, medicines, paper products. |

Amazon Product Title Here
Experience exceptional performance with this premium product designed for durability and everyday convenience. Its user-friendly design and reliable build provide great usability for both personal and professional needs, making it a top choice for quality-driven users.
🛒 Check Price on Amazon* As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Sweden considers India one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing markets.
3. Science and Technology Collaboration
- Under the Joint Innovation Partnership (2018), both nations collaborate in:
- Innovation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Smart Cities
- E-Health
- Research partnerships exist between IITs and top Swedish universities.
- Several Swedish companies have established R&D centers in India.
4. Education and Cultural Relations
- Swedish universities are popular among Indian students (e.g., KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Uppsala University).
- Every year, many Indian students go to Sweden for Masters/PhD under scholarships.
- A large Indian-origin community (NRIs) lives in Sweden, working in IT, healthcare, and academia.
5. Climate and Sustainable Development Partnership
- Both countries collaborate in clean energy, green technology, and recycling systems.
- Under the “India–Sweden Climate Action Partnership”, several joint environmental projects are underway.
6. Defence and Strategic Cooperation
- Sweden has proposed selling the Gripen fighter aircraft to India.
- Discussions continue on defence technology cooperation and joint development.
7. Collaboration on Global Platforms
- India and Sweden cooperate in global forums such as:
- United Nations
- World Trade Organization
- International Solar Alliance
Conclusion
India and Sweden share strong, multi-dimensional and future-oriented relations. Whether in trade, technology, education or environmental sustainability, both nations work together to address global challenges and strengthen mutual cooperation.

7. Tourism and Culture of Sweden
Sweden is an extremely attractive destination for tourists due to its natural beauty, historical heritage and modern cultural identity. The culture of Sweden reflects a beautiful blend of ancient traditions and contemporary thinking.
Main Aspects of Sweden’s Tourism and Culture
1. Tourist Attractions
• Nature Tourism
- Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis): Visible in the northern regions of Sweden, especially in Kiruna and Abisko.
- Lakes and Forests: Sweden has more than 100,000 lakes and vast forested areas. Vänern and Vättern are two of the largest lakes.
• Major Cities
- Stockholm: Capital and largest city. Key attractions: Gamla Stan (Old Town), Vasa Museum, ABBA Museum, Royal Palace.
- Gothenburg: Located on the west coast—famous for seafood, design shops and art galleries.
- Malmö: Connected to Denmark via the Øresund Bridge; offers a blend of modern and traditional Swedish culture.
• Other Attractions
- Icehotel (Jukkasjärvi): A world-famous hotel made entirely of ice—major attraction during winter.
- Gotland and Visby: UNESCO World Heritage site known for medieval architecture and scenic beauty.
2. Festivals and Celebrations
| Festival | Description |
|---|---|
| Midsummer Festival | Celebrated in June; marks the longest day of the year with flower crowns, dancing and traditional songs. |
| Christmas & Santa Lucia Day | Celebrated with traditional decor; Santa Lucia Day (13 December) is an iconic festival. |
| Walpurgis Night | Bonfires are lit across Sweden on 30 April to welcome spring. |
| National Day | Celebrated on June 6 with parades, cultural events and flag ceremonies. |

Amazon Product Title Here
Discover thoughtful design and reliable performance with this high-quality product built for everyday use. Its durable construction and user-friendly features ensure convenience and lasting satisfaction, making it a smart choice for practical needs.
🛒 Check Price on Amazon* As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
3. Cultural Characteristics of Sweden
• Literature and Music
- Astrid Lindgren: Renowned children's author (creator of Pippi Longstocking).
- ABBA: One of the most famous pop music groups in the world.
- Nobel Prize in Literature: Awarded annually in Stockholm.
• Film and Design
- Ingmar Bergman: Globally respected Swedish filmmaker.
- Swedish Design: Known for simplicity, functionality and beauty (IKEA is the best example).
• Food Culture
- Swedish Meatballs (Köttbullar)
- Smörgåsbord (traditional buffet-style meal)
- Salmon, Cinnamon buns, Lingonberry dishes
4. Folk Traditions and Values
| Element | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Lagom | “Not too much, not too little — just right” — the Swedish approach to a balanced life. |
| Jantelagen | Focus on humility, collectivism, equality and politeness. |
| Equality | Everyone in society is treated with equal respect and receives equal rights. |
| Love for Nature | People spend a lot of time outdoors; “Allemansrätten” gives everyone the right to access nature. |
5. Religion and Diversity
- Church of Sweden (Lutheran): Historically the main religion.
- The society today is highly secular and culturally diverse.
- Muslim, Hindu, Buddhist and Jewish communities are also present.
Conclusion
Sweden’s tourism offers a rich blend of natural beauty, historical heritage and unique cultural traditions. Its culture reflects modern thinking, equality, environmental awareness and a global outlook, making it one of the most fascinating countries in the world.
References
- CIA World Factbook – Sweden
- Encyclopaedia Britannica – Sweden
- Statistics Sweden (Official Government Site)
- Government Offices of Sweden (Official Portal)
- Sweden.se (Official Information Portal by Swedish Institute)
- World Bank – Sweden Overview
- UNDP – Sweden HDI Report
- IMF – Sweden Country Data
- Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) – Sweden
- Books:
- Daun, Å. (1996). Swedish Mentality. Penn State University Press.
- Trägårdh, L. (2009). State and Civil Society in Northern Europe: The Swedish Model Reconsidered. Berghahn Books.