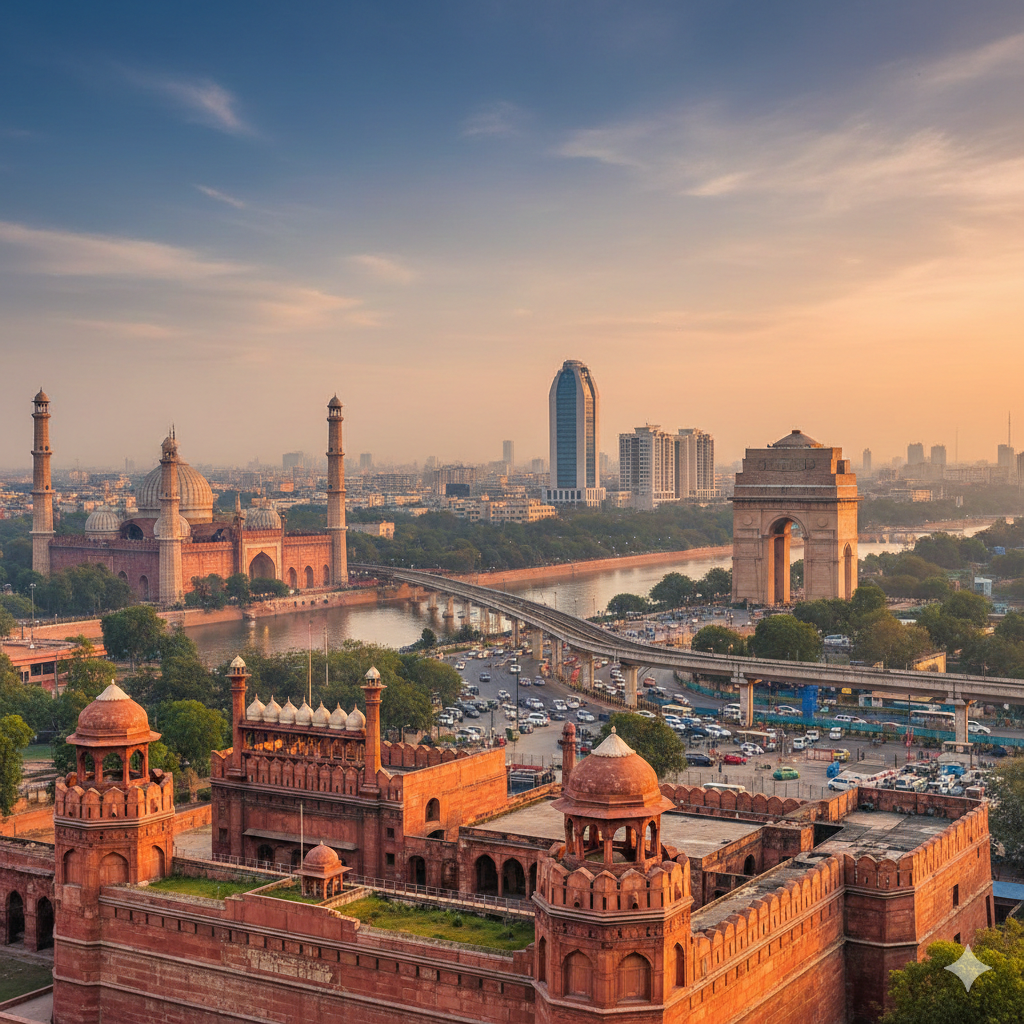
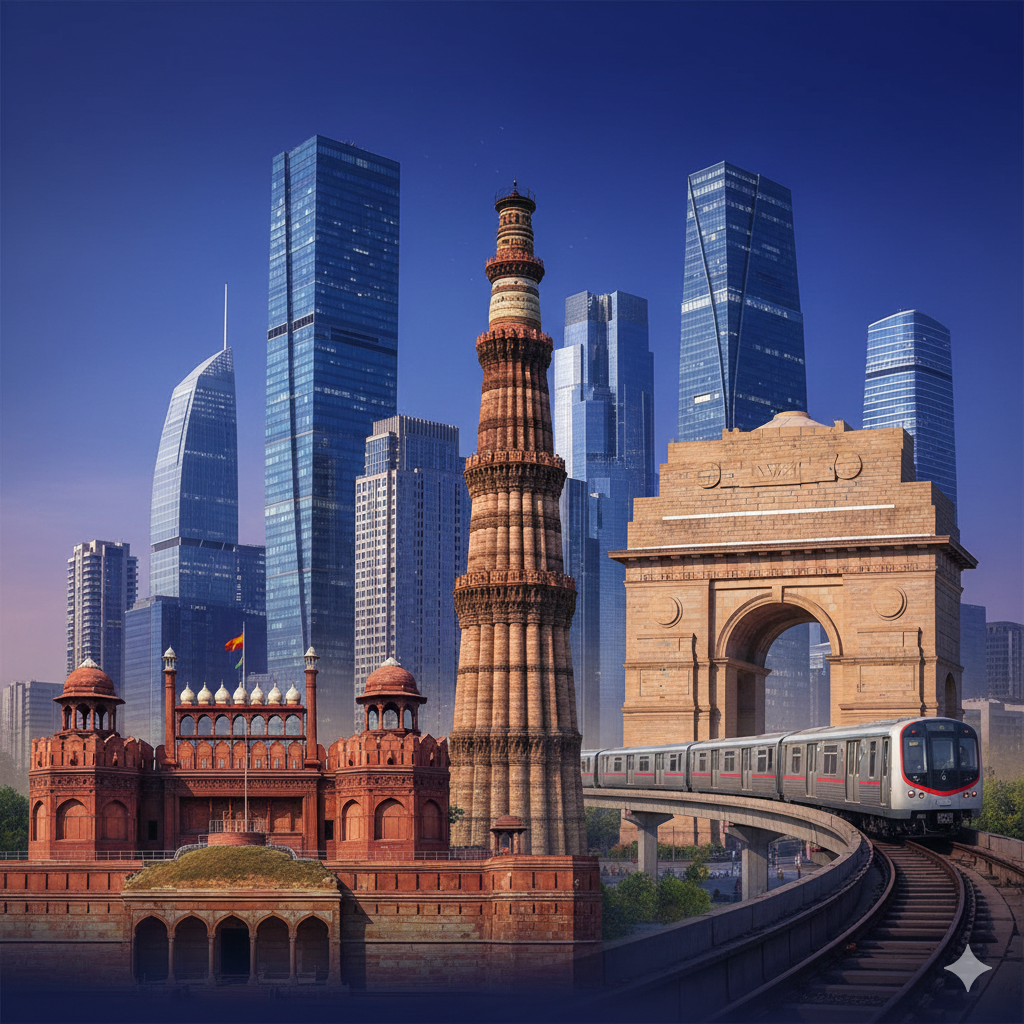
Delhi — India's Capital: A Personal Story, Learnings & Guide
An inspiring, informative account of Delhi — its history, geography, administration and key features. Updated with a 2024 population estimate.
Short Introduction to Delhi
Name: Delhi
Location: Northern India
Official Status: National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi
Capital: New Delhi (seat of the Government of India)
Population: Around 3 crore (by 2024 estimate)
Official Languages: Hindi, English (widely used), Punjabi, Urdu
Major Religions: Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity and others
My Story — Why Delhi Matters To Me
I have always been drawn to cities that carry history in their stones and possibilities in their streets. Delhi is one of those rare places that blends millennia of history with a constant present — a capital city that still feels like a living museum and a bustling, modern metropolis at the same time. In this piece I share what I learned from Delhi: small moments, big impressions, and practical facts that helped me understand the city better.
Walking through lanes of Old Delhi, standing beneath the tall minarets of Jama Masjid, or passing the green lawns in Lutyens’ Delhi, I found a city that refuses to be simplified. For anyone who wants to know Delhi — whether as a visitor, a new resident, or simply a curious reader — these notes combine emotion with useful information.
Classification of Delhi
1. Administrative Classification
Delhi is a Union Territory with a special status: the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi. It has its own Legislative Assembly, a Chief Minister, and a Lieutenant Governor. Administratively, Delhi is divided into multiple districts; the most commonly referred districts include:
- New Delhi
- North Delhi
- South Delhi
- West Delhi
- East Delhi
- Central Delhi
- North West Delhi
- South West Delhi
- North East Delhi
- South East Delhi
- Shahdara
2. Geographic Classification
Geographically, Delhi lies on the banks of the Yamuna River and sits in a semi-arid zone. It is surrounded on three sides by the state of Haryana, and on the east by Uttar Pradesh. The city's location has shaped its climate, water resources, and expansion patterns.
3. Historical Classification
Delhi's history is layered across ages — ancient, medieval, and modern — with several distinct historic settlements:
- Ancient Delhi: Indraprastha — referenced in the Mahabharata.
- Medieval Delhi: Sites such as Tughlaqabad, Siri, and Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi).
- Modern Delhi: British-era developments, including Lutyens' Delhi and the establishment of New Delhi in 1931.
4. Urban and Rural Classification
Delhi has a mix of dense urban neighborhoods and rural outskirts. Urban zones include New Delhi, South Delhi, and Central Delhi, while rural pockets and peri-urban villages exist in areas such as Narela and Bawana.
5. Economic Classification
Economically, Delhi hosts commercial, industrial, and residential hubs:
- Commercial areas: Connaught Place, Nehru Place, and other market districts.
- Industrial areas: Okhla, Narela, Bawana, Mayapuri and similar industrial clusters.
- Residential areas: Examples include Safdarjung / Spring Kunj, Rohini, Dwarka, Lajpat Nagar and others.
Key Features of Delhi
Political Centre
Delhi is the political heart of India. Iconic institutions such as the Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan (President's residence), and the Supreme Court are all located here. This concentration of national institutions gives Delhi unique administrative significance.
Tourism and Heritage
Delhi is rich in monuments and pilgrimage sites. Major attractions include:
- Red Fort
- Qutub Minar
- India Gate
- Jama Masjid
- Akshardham Temple
Academic and Medical Institutions
Delhi is home to several premier institutions of education and healthcare, including Delhi University (DU), Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), IIT Delhi, and AIIMS. These institutions draw students and professionals from across India and abroad.
Transport and Connectivity
The Delhi Metro is one of the largest and most modern urban rail networks in India, connecting not only the city's central areas but also long-distance suburbs and neighboring towns. Good road and rail links, plus an international airport, make Delhi a major transit hub.
My Learnings from Delhi — Practical & Inspiring
Embrace Complexity
Delhi taught me that a city can be many things at once: ancient and modern, quiet and chaotic, formal and informal. Embracing that complexity is the first step to understanding and appreciating it.
History Shapes Everyday Life
Walking through Delhi made me realise how history is woven into the present. The layout of neighborhoods, the markets, and even the festivals reflect layers of time. When you notice this, the city becomes richer.
Diversity as Strength
The linguistic, religious, and cultural diversity in Delhi is visible in food, architecture, and daily life. That diversity creates opportunities for learning, business, and human connection.
Practical Tips for Visitors & Newcomers
- Plan visits to major monuments early in the day to avoid heat and crowds.
- Use the Metro for fast, reliable travel across long distances in the city.
- Try local food lanes with an open mind — they are among the best ways to experience Delhi.
- Respect local customs around places of worship and heritage sites.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the official name of Delhi?
- Delhi is officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi. New Delhi is the seat of the central government.
- How large is Delhi's population?
- Delhi's population is estimated at around 3 crore (30 million) by 2024 estimates. Population figures change over time with migration and growth.
- Which languages are commonly spoken in Delhi?
- Hindi and English are widely used. Punjabi and Urdu are also commonly spoken in many neighborhoods.
- What are the must-see monuments in Delhi?
- Popular monuments include the Red Fort, Qutub Minar, India Gate, Jama Masjid, and Akshardham Temple.
Delhi — Detailed Introduction: History, Geography, Administration & Learnings
This article provides a clear, corrected and SEO-friendly expansion of Delhi's key aspects: historical background, geography, administration, population, urban development, education, economy, transport and culture.
Introduction
Delhi — the capital region of India — is a city of immense historical, cultural, political and economic importance. With a recorded past stretching back thousands of years, Delhi has served as the capital for many empires and remains a living blend of heritage and modernity.
This detailed introduction covers Delhi's history, geography, administration, culture and other important aspects to give readers a thorough understanding of the city.
1. Historical Background
Delhi's history dates back over 3,000 years. The city is associated with several dynasties and rulers — including the Tomars, Chauhans, the Delhi Sultanate, the Mughals and the British. Its mention as Indraprastha in the Mahabharata links Delhi to ancient Indian traditions.
Major Periods
- Ancient period: Indraprastha (Mahabharata-era reference).
- Medieval period: Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire made Delhi a major capital for centuries.
- Modern period: In 1911 the British announced the transfer of the capital from Calcutta to Delhi; New Delhi was planned and inaugurated in the early 20th century.
- Independent India: In 1950, Delhi became the seat of the Republic and evolved as the National Capital Territory.
2. Geographic Situation
Location: Northern India, largely along the western banks of the Yamuna River.
Area: Approximately 1,484 sq km.
Boundaries: Bordered on the north, west and south by Haryana; to the east by Uttar Pradesh.
Climate & Seasons
- Climate: Semi-arid with large seasonal variation.
- Summer: April–June (often very hot).
- Monsoon: July–September (main rainy season).
- Winter: November–February (can be quite cold, especially at night).
3. Administrative Framework
Delhi has a unique administrative structure as the National Capital Territory (NCT). Governance involves both the Central Government and the Delhi Government, each with specific powers.
State-like Status
Delhi is a Union Territory with a Legislative Assembly and a Chief Minister. The Lieutenant Governor is appointed by the Central Government and represents the Union.
Key Branches of Power
- Legislature: Delhi Legislative Assembly — handles many local laws (note: some subjects such as land and police fall under Central control).
- Executive: Chief Minister and Council of Ministers handle executive functions within delegated subjects.
- Judiciary: Delhi High Court adjudicates legal matters for the territory.
Districts
Delhi is administratively divided into 11 districts. Typical district-level officials include the District Magistrate (DM), Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM), Tehsildar and other officers.
| # | District | Typical Headquarters (example) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Delhi | Kanhaiya Nagar (example) |
| 2 | Central Delhi | Daryaganj |
| 3 | North Delhi | Civil Lines |
| 4 | South Delhi | Saket |
| 5 | East Delhi | Shakarpur |
| 6 | West Delhi | Rajouri Garden |
| 7 | North West Delhi | Keshav Puram |
| 8 | South West Delhi | Dwarka |
| 9 | North East Delhi | Seelampur |
| 10 | South East Delhi | Defence Colony |
| 11 | Shahdara | Shahdara (Nand Nagri area) |
Police Administration
Delhi Police functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs (Central Government). The Commissioner of Police leads the force, which is organized into multiple police districts and stations.
Local Bodies
- Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD): Handles civic services such as sanitation, street lighting, parks and building permissions. In recent years, the three municipal corporations were reorganized and merged depending on administrative decisions.
- New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC): Maintains the central areas including Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament Street and parts of Connaught Place.
- Delhi Cantonment Board: Administers cantonment areas and related civic services.
National Capital Region (NCR)
Delhi is the core of the National Capital Region (NCR), a planning region that includes neighbouring cities and districts across states to coordinate urbanisation, transport and resources.
Major NCR participants: Gurugram, Faridabad, Sonipat, Panipat (Haryana); Noida, Greater Noida, Ghaziabad, Meerut (Uttar Pradesh); Alwar, Bharatpur (Rajasthan).
4. Population & Social Structure
Population: Approximately 3 crore (30 million) as of 2024 estimates. Delhi is among the most densely populated regions in India.
Languages & Communities
Official languages: Hindi and English. Other commonly spoken languages include Punjabi, Urdu and Haryanvi.
Religion & Diversity
Delhi is religiously and ethnically diverse. Major religious communities include Hindus (majority), Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Jains and Buddhists. People from almost every state of India live and work in Delhi, making it a multicultural metropolis.
5. Urban Development & Regional Classification
Delhi's urban landscape can be broadly seen in three parts:
Old Delhi
The historic core — Mughal-era monuments such as the Red Fort and Jama Masjid, narrow streets and traditional markets like Chandni Chowk.
New Delhi
The British-planned capital area with Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House, Rajpath and India Gate. Architecturally and administratively distinct from older neighborhoods.
Expansion & Residential Areas
New residential and commercial developments include Dwarka, Rohini, Saket and Mayur Vihar. The NCR (Noida, Gurugram, Ghaziabad, Faridabad etc.) forms the extended metropolitan region.
6. Education & Institutions
Delhi is a national education hub with premier universities and research institutions.
- Universities: Delhi University (DU), Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Jamia Millia Islamia, Indraprastha University.
- Technical & Medical Institutes: IIT Delhi, AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences), IIIT Delhi, NSIT and others.
7. Economy & Industry
Delhi's economy is largely service-driven, with strong contributions from banking, information technology, education, tourism and retail.
Key Economic Zones
- Commercial hubs: Connaught Place, Nehru Place, Karol Bagh and other markets.
- Industrial clusters: Narela, Okhla and Bawana.
- Tourism: Historical and religious sites, museums and modern cultural facilities attract domestic and international visitors.
8. Transportation & Infrastructure
Metro & Public Transport
The Delhi Metro is one of India's largest and most modern rapid transit systems, connecting the city with suburbs and neighbouring towns.
Roads, Rail & Air
- Major roads: Ring Road, Outer Ring Road, expressways and flyovers.
- Major railway stations: New Delhi, Old Delhi (Delhi Junction), Hazrat Nizamuddin, Anand Vihar.
- Airport: Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGI) — the primary international gateway.
9. Cultural Diversity
Delhi is a multicultural city where people from across India live and celebrate their traditions.
Festivals
Major festivals such as Diwali, Eid, Guruparv, Christmas, Holi and Lohri are celebrated widely across the city.
Food & Cuisine
Delhi's street food is world-famous — from chaat and parathas to chole-bhature and biryani. Food lanes and local markets are essential to Delhi's cultural experience.
10. Prominent Places & Attractions
Historic Monuments
- Red Fort
- Qutub Minar
- Humayun's Tomb
- Jama Masjid
Modern & Cultural Sites
- Akshardham Temple
- Lotus Temple
- India Gate
- Rashtrapati Bhavan
Museums & Markets
- National Museum, Rail Museum
- Markets: Sarojini Nagar, Chandni Chowk, Lajpat Nagar
Conclusion
Delhi is more than India's political capital. It is a city where history, culture, modernity and diversity meet. Its heritage, institutions, economic vitality and strategic importance make Delhi one of the world's significant metropolises.

Top Amazon Product
Discover this great product on Amazon — click below to view the latest price, key features, and customer reviews!
👉 View on Amazon(Amazon Affiliate Link – Thank you!)
Summary (Quick Facts)
| Administrative status | National Capital Territory (NCT) with Legislative Assembly |
|---|---|
| Districts | 11 |
| Police control | Delhi Police (Central Government, Ministry of Home Affairs) |
| Local bodies | MCD, NDMC, Cantonment Board |
| NCR | Includes cities from Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan |
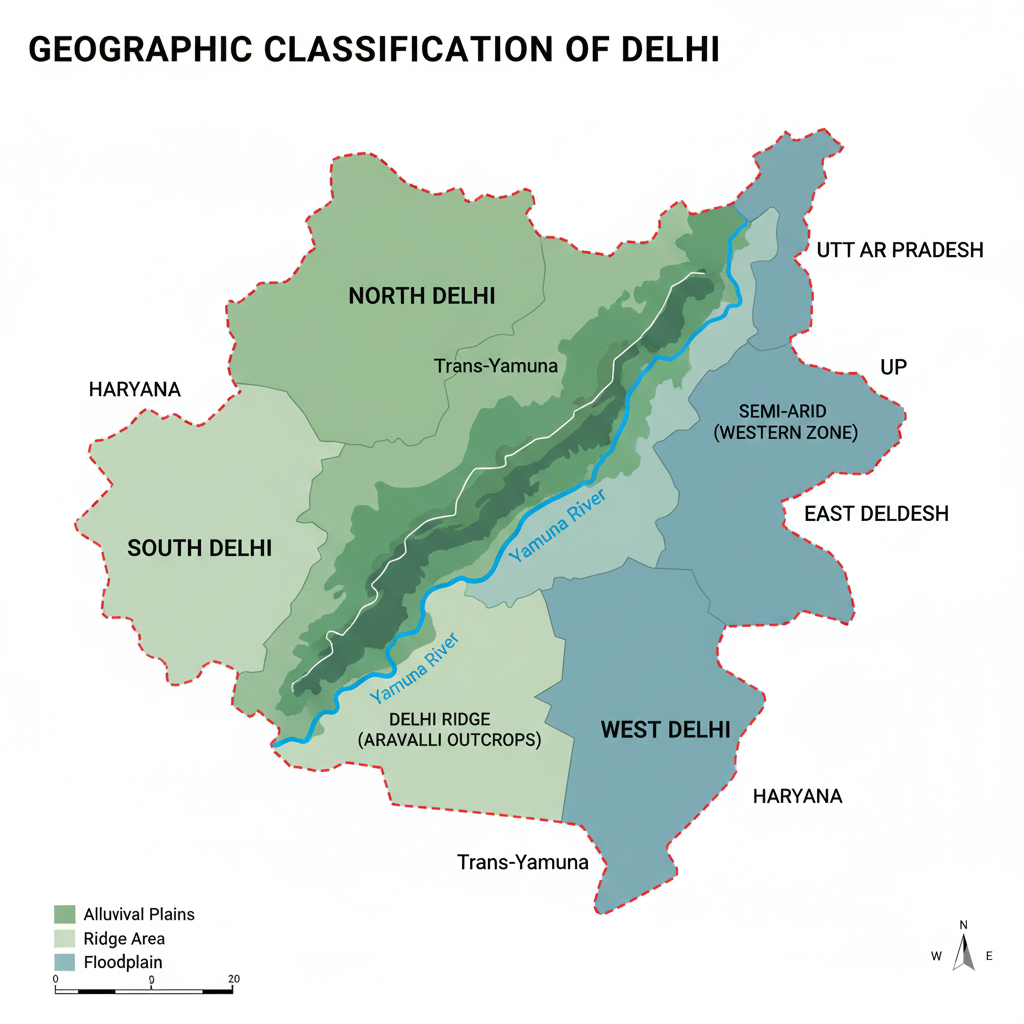
2. Geographic Classification — Geographical Classification of Delhi
Overview
Delhi's geographic composition shapes its political, environmental and economic character. Below is a clear, corrected and SEO-friendly expansion of Delhi's geographic classification, covering location, area, topography, climate, water sources, regional zones, green areas, and environmental challenges.
A. Geographic Location
Latitude: 28.40°N to 28.88°N
Longitude: 76.84°E to 77.34°E
Mean elevation: about 216 metres (≈711 feet) above sea level.
Position: Delhi is located in northern India, mainly along the western bank of the Yamuna River.
Boundaries: Bordered to the north, west and south by the state of Haryana; to the east by the state of Uttar Pradesh (Ghaziabad, Noida area).
B. Area
Total area: Approximately 1,484 sq km. Delhi is relatively small in area but has a very high population density compared to most Indian states/territories.
C. Topography & Landforms
Delhi's landscape is primarily a flat alluvial plain with local variations. Key topographic features:
- Alluvial plains: Fertile plains along the Yamuna formed by river deposits; includes floodplains (Yamuna khadar).
- Ridge & low hills (Aravalli outcrops): Small hill mounds and the Delhi Ridge — western/southern parts have rocky, elevated stretches that are part of the Aravalli range extension.
- Sandy & semi-arid zones: Western parts of Delhi tend to be drier and more sandy due to lower rainfall and soil characteristics.
- Green belts: Natural ridges and plantation belts help form Delhi's green lung areas.
D. Climate
Delhi experiences a semi-arid climate with strong seasonal contrasts. Typical seasonal pattern and features are summarized below.
| Season | Duration | Typical features |
|---|---|---|
| Summer | April – June | Hot to very hot; daytime temperatures can reach ~45°C. |
| Monsoon / Rainy | July – September | Main rainfall period; average annual rainfall ~700–800 mm (varies yearly). |
| Autumn / Post-monsoon | October – November | Clear skies, pleasant days and cooling nights. |
| Winter | December – February | Cold nights, frequent fog and lows often near 4°C in cold spells. |
E. Water Sources & Water Bodies
Primary river: The Yamuna is Delhi's main natural watercourse and has historically been central to settlement and economy. Today it is ecologically stressed and suffers from pollution, but remains important geographically and culturally.
Other water bodies & canals
- Lakes: Bhalswa Lake, Sanjay Lake, and other small wetlands in and around the city.
- Canals: Western Yamuna Canal and smaller distribution canals historically used for irrigation and water supply.
F. Major Geographic Zones (Regional Divisions)
Delhi can be generally divided into four broad geographic/regional parts:
North Delhi (Old/Historic areas)
Includes parts of Old Delhi: historic structures, narrow lanes and bazaars (e.g., areas around Red Fort and Jama Masjid).
South Delhi
Modern, well-planned and often affluent neighborhoods: Saket, Greater Kailash, areas around Qutub Minar and Hauz Khas.
East Delhi
East of Yamuna — largely residential localities such as Laxmi Nagar and Mayur Vihar; growing commercial pockets.
West Delhi
Denser residential and industrial areas — localities like Janakpuri, Vikaspuri and nearby industrial clusters.
G. Green Areas & Forested Zones
The Delhi Ridge: A protective green spine and an extension of the Aravalli, often called the 'lungs of Delhi' due to its ecological role. Ridge sections include northern, central, southern and Tughlaqabad parts.
Parks & Gardens
- Lodi Gardens
- Buddha Jayanti Park
- Nehru Park
- Numerous neighbourhood parks and plantation belts across the city
H. Environmental Challenges
Delhi faces several serious environmental issues that affect quality of life and long-term sustainability:
- Air pollution: Delhi is among India's most air-polluted major cities; PM2.5 and seasonal smog (winter) are major concerns.
- Water pollution: The Yamuna has significant pollution loads; water quality and ecological health are degraded.
- Loss of green cover: Rapid urbanization and construction have reduced natural green areas in parts of the city.
- Groundwater depletion: Over-extraction and seasonal deficits have caused declining water tables in many areas.
Summary (Quick Facts)
| Area | ≈ 1,484 sq km |
|---|---|
| Main river | Yamuna |
| Topography | Mostly flat alluvial plains with Ridge/Aravalli outcrops |
| Climate | Semi-arid — hot summers, monsoon rains, cool winters with fog |
| Green features | Delhi Ridge, major parks and urban green belts |
| Key environmental issues | Air & water pollution, groundwater depletion, urban pressure |

Awesome Amazon Product
Discover this quality product available on Amazon — click below to view the latest price, features, and customer reviews!
👉 View on Amazon(Amazon Affiliate Link – Thank you!)

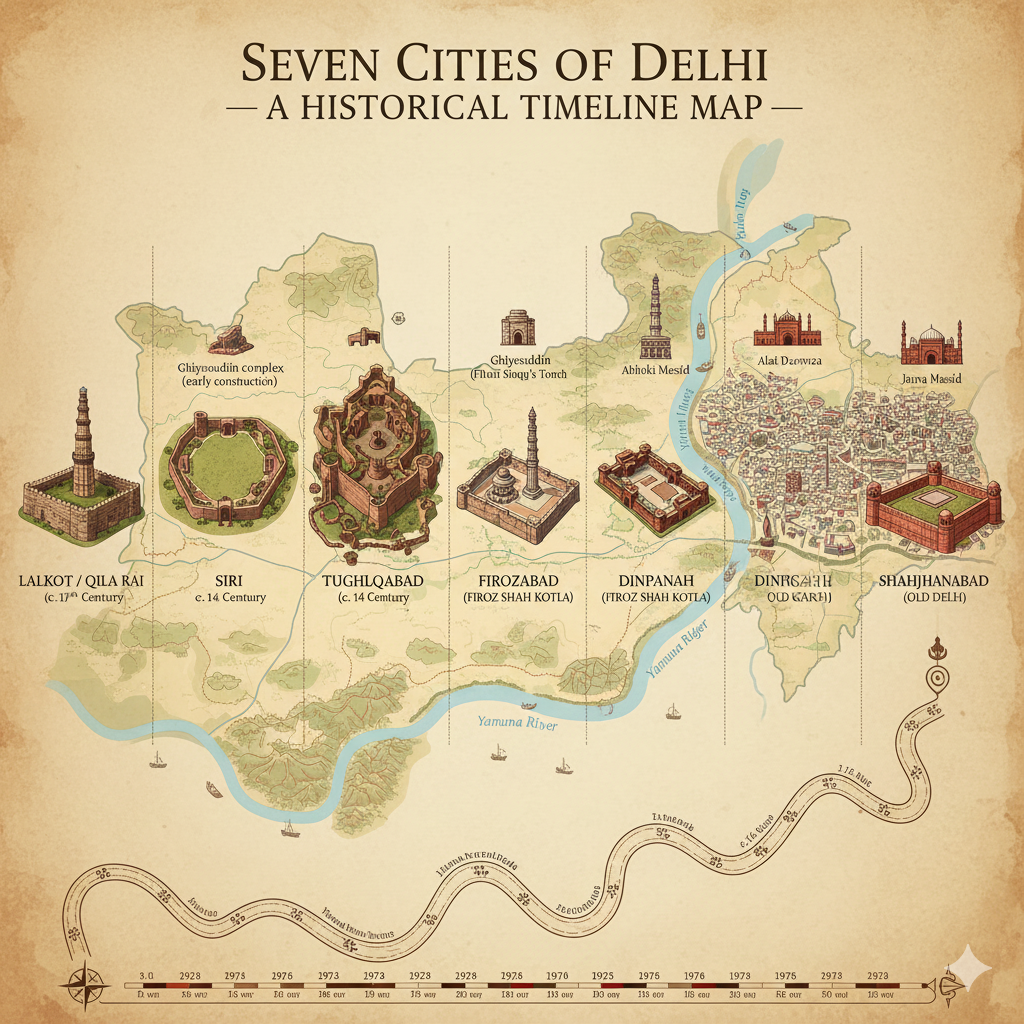
3. Historical Classification of Delhi
Delhi’s history is extremely rich, ancient and multi-layered. Since ancient times, Delhi has been considered a major centre of political power. Historically, the city is classified into the “Seven Cities of Delhi” along with the development of Modern Delhi.
A. The Seven Historical Cities of Delhi
From the ancient period to the Mughal era, Delhi was settled in seven major phases. These are known as the “Seven Cities of Delhi”.
| Order | Historical City | Founder | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lalkot / Qila Rai Pithora | Tomar King Anangpal & Prithviraj Chauhan | 11th–12th Century |
| 2 | Siri | Alauddin Khilji | 1290s |
| 3 | Tughlaqabad | Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq | 1321 |
| 4 | Jahanpanah | Muhammad bin Tughlaq | 1327 |
| 5 | Firozabad (Firoz Shah Kotla) | Firoz Shah Tughlaq | 1354 |
| 6 | Dinpanah / Purana Qila | Humayun (Rebuilt by Sher Shah Suri) | 1530–1545 |
| 7 | Shahjahanabad | Shah Jahan | 1638–1649 |
Key Features of These Cities
- Lalkot: Delhi’s first fortified city built by the Tomars and Chauhans.
- Siri: Built by Alauddin Khilji as a defence against Mongol invasions.
- Tughlaqabad: Massive fort city with thick walls, later abandoned.
- Jahanpanah: A protective region between Siri and Tughlaqabad.
- Firozabad: Settlement near the Yamuna, built by Firoz Shah Tughlaq.
- Dinpanah: Humayun’s dream city; strengthened by Sher Shah Suri.
- Shahjahanabad: Home to Red Fort and Jama Masjid; today’s Old Delhi.
B. From Mughal to British Period
Mughal Era (1526–1857)
- Delhi served multiple times as the Mughal capital.
- Under Shah Jahan, cultural and architectural development reached its peak.
British Period (1857–1947)
- After the 1857 Revolt, Delhi came directly under British rule.
- In 1911, the British shifted the capital from Calcutta to Delhi.
- Foundation of New Delhi was laid in 1911 and inaugurated in 1931.
C. Modern Delhi
1. New Delhi
The British-planned capital designed by Edwin Lutyens & Herbert Baker, including Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House, Rajpath (now Kartavya Path) and India Gate.
2. Post-Independence Development (1947–1990)
- Rapid expansion of Delhi after 1947.
- Refugee settlements, industrial zones, DDA colonies and early infrastructure development.
3. Present-Day Delhi (1990–Present)
- Growth of NCR region—Noida, Gurgaon, Ghaziabad, Faridabad.
- Modern infrastructure: Metro, IGI Airport, expressways, flyovers.
- Urbanization, high population growth and increased pollution.
D. Chronological Phases of Delhi’s History
| Period | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Ancient | Tomar & Chauhan dynasties; Lalkot |
| Medieval | Sultanate & Tughlaq era; Siri, Tughlaqabad |
| Mughal | Shahjahanabad; cultural peak |
| British | Foundation of New Delhi; capital shift |
| Independent India | Modern capital; NCR planning |
Summary
| Historical Cities | 7 (Lalkot to Shahjahanabad) |
|---|---|
| Main Eras | Sultanate, Tughlaq, Mughal, British |
| Modern Development | New Delhi, NCR, Metro, IGI Airport |

Amazing Amazon Product
Discover this quality product now on Amazon — click below to see the latest price, key features, and customer reviews!
👉 View on Amazon(Amazon Affiliate Link – Thank you!)
4. Urban and Rural Classification of Delhi
Delhi, as India’s capital, is a vast metropolitan region. It has both urban and rural settlements that together form a unique administrative and social structure.
A. Urban Areas
Key Features:
- High population density
- Planned colonies, apartments and modern housing
- Developed infrastructure: Metro, roads, electricity, water supply
- Services: malls, hospitals, schools, offices, industries
Major Urban Zones
| Area | Notable Places |
|---|---|
| New Delhi | Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, India Gate |
| South Delhi | Saket, Vasant Kunj, Hauz Khas |
| West Delhi | Janakpuri, Dwarka, Uttam Nagar |
| East Delhi | Mayur Vihar, Laxmi Nagar |
| North Delhi | Kashmere Gate, Model Town |
Urban Statistics
About 97.5% of Delhi’s population lives in urban areas (2021 estimates).
B. Rural Areas
Features:
- Lower population density
- Agriculture-based or semi-agricultural communities
- Partially developed infrastructure
- Livelihoods based on farming, dairy, small industries
Examples of Rural Areas
| District | Major Rural Villages |
|---|---|
| South-West Delhi | Najafgarh, Kanjhawala, Chhawla |
| North-West Delhi | Narela, Bhalswa, Bawana |
| South Delhi | Villages near Mehrauli |
| East Delhi | Peripheral areas near Mayur Vihar |
There are around 300+ villages in Delhi, many of which have now become urbanized villages.
C. Urbanisation Process
- Many old villages have transformed into urban villages (e.g., Munirka, Shahpur Jat, Yusuf Sarai).
- Multi-storey buildings, PGs, flats and offices have replaced traditional structures.
D. Administrative Classification
| Category | Administrative Unit |
|---|---|
| Urban Areas | MCD, NDMC, DDA |
| Rural Areas | Revenue Department, Tehsil/SDM; (Gram Panchayats mostly inactive) |
E. Urban vs Rural Comparison
| Aspect | Urban Delhi | Rural Delhi |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Very high | Lower |
| Employment | Services & Industry | Agriculture, Dairy, Labour |
| Infrastructure | Highly developed | Partially developed |
| Administration | MCD, NDMC | Revenue-based units |
Summary
| Total Area | 1,484 sq km |
|---|---|
| Urban Area | ≈ 1,450 sq km (97.5%) |
| Rural Area | ≈ 34 sq km (2.5%) |
| Number of Villages | ~300 (many urbanised) |
| Urbanisation | Rapid conversion of villages into urban zones |
5. Economic Classification of Delhi
Delhi is one of India’s most prosperous and dynamic union territories. Its economy is largely service-driven but supported by industry, commerce and limited agriculture.
A. Main Economic Sectors
| Sector | Contribution to GSDP | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Services | ≈ 83% | IT, education, health, tourism, transport |
| Industry | ≈ 15% | Manufacturing, MSMEs, construction |
| Agriculture | ≈ 2% | Limited to rural Delhi; small-scale farming |
Delhi GSDP (2023–24): Estimated above ₹10.75 lakh crore.
B. Service Sector
- Fastest-growing and largest sector in Delhi.
- Home to central & state government offices, embassies, MNCs and startups.
- Key service industries: IT, telecom, real estate, finance, healthcare, education.
C. Industrial Sector
Major Industrial Centres
| Area | Key Industries |
|---|---|
| Narela | Textiles, machinery |
| Bawana | Electronics, furniture |
| Mayapuri | Auto parts, scrap industry |
| Okhla | Electronics, plastics, food processing |
| Naraina | Garments, engineering goods |
Delhi has over 1.25 lakh active MSMEs across various industrial clusters.
D. Business & Markets
- Chandni Chowk: Bulk clothing, jewellery
- Karol Bagh: Electronics, automobile markets
- Nehru Place: IT hardware and software hub
- Sadar Bazaar: India’s biggest wholesale general market
- Lajpat Nagar, Sarojini Nagar: Retail fashion & food markets
E. Agriculture Sector
Agriculture forms only 2% of Delhi’s economy, mainly in rural areas like Narela and Najafgarh.
Key crops: wheat, mustard, vegetables, flowers. Dairy and livestock farming are also common.
F. Employment Classification
| Sector | Employment Share |
|---|---|
| Services | ≈ 75% |
| Industry | ≈ 20% |
| Agriculture | ≈ 5% (declining) |
G. Foreign Investment & Startups
- Delhi-NCR is one of India’s biggest startup & IT hubs.
- Major unicorns operate from Delhi, Noida and Gurgaon.
- FDI is rising in real estate, tourism, education and technology sectors.
Summary
| Area | Contribution | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Service Sector | ≈ 83% | Banking, Education, Health, IT |
| Industry Sector | ≈ 15% | Narela, Okhla, Bawana |
| Agriculture Sector | ≈ 2% | Narela, Najafgarh (limited) |
| Main Markets | — | Chandni Chowk, Karol Bagh, Nehru Place |
| Startups | Growing | Technology, Food, Education |
3. Historical Classification of Delhi
Delhi’s history is extremely rich, ancient and multi-layered. Since ancient times, Delhi has been a major centre of power in India. Historically, Delhi is classified into the “Seven Cities of Delhi” and the later development of Modern Delhi.
A. The Seven Historical Cities of Delhi
From the ancient period to the Mughal era, Delhi was established in seven major forms. These are known as the “Seven Cities of Delhi”.
| Order | Historical City | Founder | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lalkot / Qila Rai Pithora | Tomar King Anangpal & Prithviraj Chauhan | 11th–12th Century |
| 2 | Siri | Alauddin Khilji | 1290s |
| 3 | Tughlaqabad | Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq | 1321 |
| 4 | Jahanpanah | Muhammad bin Tughlaq | 1327 |
| 5 | Firozabad (Firoz Shah Kotla) | Firoz Shah Tughlaq | 1354 |
| 6 | Dinpanah / Purana Qila | Humayun (Rebuilt by Sher Shah Suri) | 1530–1545 |
| 7 | Shahjahanabad | Shah Jahan | 1638–1649 |
Key Features of These Cities
- Lalkot: Delhi’s first major fort city, settled by the Tomars and expanded by Chauhans.
- Siri: Built for security against Mongol invasions.
- Tughlaqabad: A massive walled fort city, later abandoned.
- Jahanpanah: A protective region between Siri and Tughlaqabad.
- Firozabad: Built along the Yamuna by Firoz Shah Tughlaq.
- Dinpanah: Humayun’s city; rebuilt as Purana Qila by Sher Shah Suri.
- Shahjahanabad: Home to Red Fort and Jama Masjid; present-day Old Delhi.

Awesome Amazon Product
Discover this quality product available on Amazon — click below to view the latest price, features, and customer reviews!
👉 View on Amazon(Amazon Affiliate Link – Thank you!)
B. From Mughal Period to British Rule
Mughal Period (1526–1857)
- Delhi served multiple times as the Mughal capital.
- During Shah Jahan’s reign, political and cultural growth reached its peak.
British Period (1857–1947)
- After the Revolt of 1857, Delhi came under direct British rule.
- In 1911, the British shifted the capital from Calcutta to Delhi.
- New Delhi’s foundation was laid in 1911 and inaugurated in 1931.
C. Modern Delhi
1. New Delhi
The British-planned capital (Lutyens’ Delhi) designed by Edwin Lutyens & Herbert Baker, including Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House, Kartavya Path (formerly Rajpath) and India Gate.
2. Development Period (1947–1990)
- Rapid expansion after independence.
- Refugee colonies, industrial areas, DDA housing schemes.
- Early urban infrastructure development.
3. Present Delhi (1990–Present)
- Expansion of the NCR region.
- Modern infrastructure: Metro, IGI Airport, expressways, flyovers.
- Increased urbanization, population growth and pollution.
D. Chronological Phases of Delhi’s History
| Period | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Ancient Period | Tomar & Chauhan dynasties; Lalkot |
| Medieval Period | Sultanate & Tughlaq era; Siri & Tughlaqabad |
| Mughal Period | Establishment of Shahjahanabad; cultural peak |
| British Period | Foundation of New Delhi; capital shift |
| Independent India | Development of New Delhi & NCR |
Summary
| Historical Cities | 7 (Lalkot to Shahjahanabad) |
|---|---|
| Main Eras | Sultanate, Tughlaq, Mughal, British |
| Modern Development | New Delhi, NCR, Metro, IGI Airport |

4. Urban and Rural Classification of Delhi
Delhi, being the capital of India, is also one of the largest metropolitan regions in the country. It includes both urban and rural settlements, which together create a unique administrative and social structure.
Buy Now on AmazonA. Urban Area of Delhi
Key Features
- High population density
- Planned housing, apartments and colonies
- Modern infrastructure: Metro, roads, electricity, water supply
- Presence of services: malls, hospitals, schools, offices, industries
Major Urban Areas
| Area | Notable Places |
|---|---|
| New Delhi | Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, India Gate |
| South Delhi | Saket, Vasant Kunj, Hauz Khas |
| West Delhi | Janakpuri, Dwarka, Uttam Nagar |
| East Delhi | Mayur Vihar, Laxmi Nagar |
| North Delhi | Kashmere Gate, Model Town |
Urban Population Statistics
According to 2021 estimates, about 97.5% of Delhi's population resides in urban areas. Delhi is considered one of the most urbanized regions in the world.
B. Rural Area of Delhi
Key Features
- Low population density
- Agriculture-based or semi-agricultural communities
- Partially developed infrastructure
- Land-based livelihoods: agriculture, dairy, small-scale industries
Examples of Rural Areas
| District | Major Rural Villages |
|---|---|
| South-West Delhi | Najafgarh, Kanjhawala, Chhawla |
| North-West Delhi | Narela, Bhalswa, Bawana |
| South Delhi | Villages near Mehrauli |
| East Delhi | Peripheral areas near Mayur Vihar |
There are around 300+ villages in Delhi, many of which have now been transformed into "urban villages".
C. Urbanisation Process
- Many traditional villages have now become urbanized villages.
- Examples: Munirka, Shahpur Jat, Yusuf Sarai.
- New multi-storey buildings, PGs, flats and offices have replaced older structures.
D. Administrative Classification
| Category | Administrative Unit |
|---|---|
| Urban Areas | MCD, NDMC, DDA |
| Rural Areas | Revenue Department, Tehsil/SDM (Gram Panchayats mostly inactive) |
E. Major Differences (Urban vs Rural Delhi)
| Subject | Urban Delhi | Rural Delhi |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Very High | Relatively Lower |
| Employment | Services, Industry | Agriculture, Dairy, Labour |
| Infrastructure | Highly Developed | Partially Developed |
| Administration | MCD, NDMC | Revenue Department |
Summary
| Total Area | 1,484 sq km |
|---|---|
| Urban Area | ≈ 1,450 sq km (97.5%) |
| Rural Area | ≈ 34 sq km (2.5%) |
| Number of Villages | ~300 (many now urbanized) |
| Urbanisation | Rapid; villages converting into urban regions |
5. Economic Classification of Delhi
Delhi is one of India’s most prosperous and dynamic Union Territories. Its economy is primarily service-driven but also supported by industry, commerce and limited agriculture. Below is the detailed economic classification of Delhi.
A. Main Economic Sectors of Delhi
| Sector | Contribution to GSDP | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Services | ≈ 83% | IT, education, health, tourism, transport |
| Industry | ≈ 15% | Manufacturing, MSMEs, construction |
| Agriculture | ≈ 2% | Limited farming in rural areas |
Delhi GSDP (2023–24): Estimated above ₹10.75 lakh crore.
B. Service Sector
The service sector is the backbone of Delhi’s economy and the fastest-growing sector.
- Headquarters of Central and State Government offices
- Embassies, multinational companies and startups
- Major service industries:
- IT and Telecom
- Real Estate
- Banking and Finance
- Education (DU, JNU, IIT Delhi)
- Healthcare (AIIMS, Max, Fortis)
C. Industrial Sector
Delhi hosts several small, medium and large industrial clusters.
Major Industrial Centres
| Area | Key Industries |
|---|---|
| Narela | Textiles, machinery |
| Bawana | Furniture, electronics |
| Mayapuri | Auto parts, scrap industry |
| Okhla | Electronics, plastics, food processing |
| Naraina | Garments, engineering goods |
Delhi has more than 1.25 lakh active MSMEs across various sectors.
D. Business and Markets
Delhi is one of India’s biggest commercial centres. Its markets influence the entire NCR and northern India.
| Market | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Chandni Chowk | Bulk clothing, jewellery |
| Karol Bagh | Electronics, automobiles |
| Nehru Place | IT hardware & software |
| Sadar Bazaar | Wholesale general goods |
| Lajpat Nagar, Sarojini Nagar | Retail fashion & food markets |
E. Agriculture Sector
Agriculture contributes only about 2% to Delhi’s economy, mainly in rural areas like Narela and Najafgarh.
Major Crops: Wheat, mustard, vegetables, flowers.
Dairy and livestock farming also contribute to rural livelihoods.
F. Employment Classification
| Sector | Employment Share |
|---|---|
| Service Sector | ≈ 75% |
| Industrial Sector | ≈ 20% |
| Agriculture Sector | ≈ 5% (declining) |
Delhi’s unemployment rate is higher than the national average, but self-employment and startup activities are increasing.
G. Foreign Investment and Startups (FDI & Startups)
- Delhi-NCR is one of India’s biggest startup and IT hubs.
- Noida and Gurgaon host many unicorn companies.
- Foreign investment is rising in real estate, technology, tourism and education sectors.
Summary
| Area | Contribution | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Service Sector | ≈ 83% | Banking, Education, Health, IT |
| Industry Sector | ≈ 15% | Narela, Okhla, Bawana |
| Agriculture Sector | ≈ 2% | Narela, Najafgarh (limited) |
| Main Markets | — | Chandni Chowk, Karol Bagh, Nehru Place |
| Startups | Growing | Technology, Food, Education |
Conclusion
Delhi stands as one of India’s most influential and historically layered cities. From the ancient Tomar and Chauhan settlements to the grand Mughal capital of Shahjahanabad and the planned British-built New Delhi, the city has evolved through several eras of political, cultural and architectural transformation.
Today, Delhi represents a powerful blend of urban modernity and traditional heritage. Its vast metropolitan region includes both highly developed urban zones and pockets of rural communities, each contributing to the city’s diverse social and administrative character. With strong service, industrial and commercial sectors, Delhi continues to be a major economic engine for northern India and a growing hub for startups and foreign investment.
Despite challenges such as population pressure, pollution and rapid urbanisation, Delhi’s strategic importance, dynamic economy and cultural vibrancy make it a uniquely significant metropolis—one that connects India’s ancient roots to its modern aspirations.

Top Amazon Product
Discover this quality product available on Amazon — click below to view the latest price, features, and customer reviews!
👉 View on Amazon(Amazon Affiliate Link – Thank you!)
References
- Government of NCT of Delhi. Official Statistics & Reports.
- Census of India (2021 & 2011 Data). Population and Urban–Rural Classification.
- Delhi Development Authority (DDA). Master Plan of Delhi.
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). Delhi Monuments & Historical Records.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs. NCR Regional Plan & Urbanisation Reports.
- Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MOSPI). GSDP & Economic Indicators.
- Delhi Transport Corporation & DMRC. Transport and Metro Data.
- India Meteorological Department (IMD). Climate and Weather Records.


