Industrial Revolution
A Detailed Introduction to the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a historic transformation that completely changed the production system, society, and the global economy. It began mainly in Europe, especially England, between the 18th and 19th centuries and later spread across the world.
Introduction to the Industrial Revolution
It was the period when machines replaced handicrafts and cottage industries. New machines and production techniques rapidly increased manufacturing, turning agricultural societies into industrial societies.
✔ Easy & comfortable to use
✔ Excellent value for money
✔ Highly rated by customers
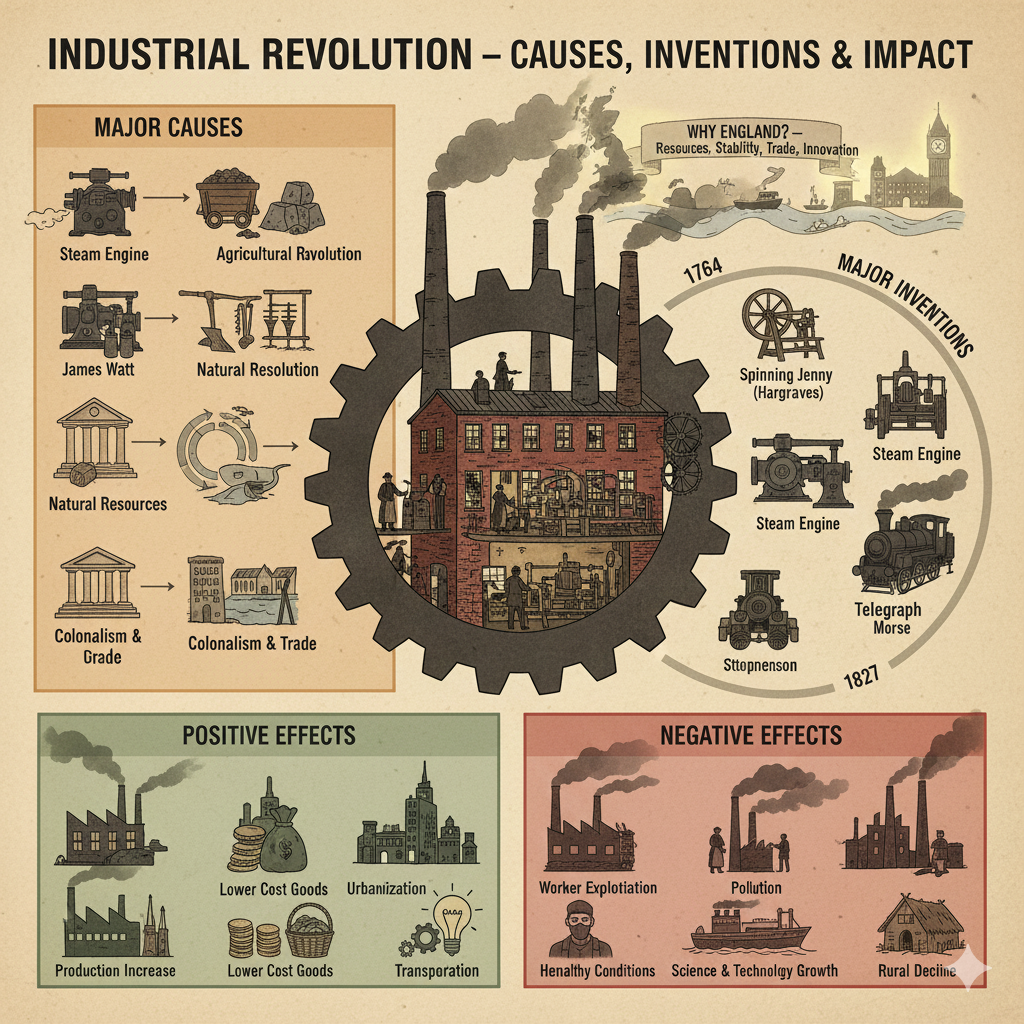
Main Causes of the Industrial Revolution
1. Scientific and Technological Progress
Scientific thinking led to new inventions and advanced techniques that made production faster and more efficient.
Key Points:
- Invention of new machinery boosted industries.
- Use of coal and iron improved factory operations.
- Colonial trade provided raw materials for industries.
- Growth in population increased the working class.
- Banking systems enabled easy capital investment.
Major Inventions and Discoveries
| Invention | Scientists / Inventors | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Spinning Jenny | James Hargreaves (1764) | Boosted the textile industry |
| Water Frame | Richard Arkwright (1769) | Improved textile production |
| Steam Engine | James Watt (1769) | Revolutionized transportation and industries |
| Railway | George Stephenson (1825) | Faster movement of goods and people |
| Telegraph | Samuel Morse (1837) | Improved communication |
Effects of the Industrial Revolution
Positive Effects
- Production increased and goods became cheaper.
- Transport and communication improved.
- Urbanization increased and new cities developed.
- Scientific and technological progress accelerated.
Negative Effects
- Exploitation of workers increased.
- Child labor and long working hours became common.
- Environmental pollution increased.
- Rural areas declined.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution ushered the world into the modern age and influenced every sector of society. Despite its negative consequences, it laid the foundation for today’s industrial and technological advancements.
Main Causes of Industrial Revolution (Detailed Explanation)
1. Scientific and Technological Progress
Scientific thinking in Europe led to major inventions that enhanced the production system.
- Steam Engine: Invented by James Watt (1769), revolutionized industries and transportation.
- Spinning Jenny: By James Hargreaves, boosted textile manufacturing.
- Power Loom: Increased cloth production rapidly.
- Iron and Steel Development: Enabled machine-building and industrial expansion.
2. Agricultural Revolution and Population Growth
The agricultural revolution improved food production, which led to population growth and availability of labor.
- New agricultural tools improved farming.
- Crop rotation maintained soil fertility.
- Population growth increased the workforce.
3. Availability of Natural Resources
- Coal: Main source of industrial energy.
- Iron Ore: Used in machines, railways and bridges.
- Rivers and Ports: Supported trade and transport.
4. Development of Capital and Banking System
- Banks provided loans to industrialists.
- Trade routes expanded through colonies.
- Stock exchange helped raise industrial capital.
5. Trade and Colonialism
- European powers imported raw materials from colonies like India, Africa, and America.
- Manufactured goods were sold in these colonies, increasing profits.
6. Development of Transport and Communication
- Railways made transportation faster and cheaper.
- Canals and waterways eased heavy-goods movement.
- Telegraph and postal services improved communication.
7. Social and Political Stability
- England enjoyed political stability and peace.
- Entrepreneurs invested in industries.
- Rural people migrated to cities, forming the working class.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution occurred due to a combination of scientific progress, agricultural changes, natural resources, capital investment, colonial trade, improved transport systems, and political stability. This revolution transformed not only the production system but also the global social and economic structure.
Scientific and Technological Progress and the Industrial Revolution
The biggest reason for the Industrial Revolution was scientific and technological progress. In the 18th and 19th centuries, various inventions in science and engineering transformed the production system, transportation, communication, and industries. These developments enabled the use of machines on a large scale, significantly improving the speed and quality of production.
1. Invention of Machines and Industrialization
Before the Industrial Revolution, production was done mainly by hand. The invention of new machines made production faster, easier, and more efficient.
(A) Technological Progress in the Textile Industry
- Spinning Jenny – 1764
Inventor: James Hargreaves
Importance: Spun multiple threads at once, increasing production efficiency. - Water Frame – 1769
Inventor: Richard Arkwright
Importance: Water-powered machine that produced stronger and more uniform thread. - Power Loom – 1787
Inventor: Edmund Cartwright
Importance: Automated loom that made cloth production quicker and easier.
(B) Improvement in the Iron and Steel Industry
- Coke-Based Iron Production – 1709
Inventor: Abraham Darby
Importance: Used coke instead of charcoal, making iron cheaper and stronger. - Bessemer Process – 1856
Inventor: Henry Bessemer
Importance: Made steel production faster and more economical; boosted railways, bridges, and machine-making.
2. Development of New Sources of Energy
(A) Invention of the Steam Engine – 1769
Inventor: James Watt
- Provided power to factories, machines, and transportation.
- Increased production dramatically.
- Used in trains and ships, accelerating long-distance trade.
(B) Use of Electrical Energy
- Michael Faraday (1831): Discovered electromagnetic induction, enabling electricity generation.
- Thomas Edison (1879): Invented the light bulb, allowing industries to work at night.
3. Revolutionary Changes in Transportation and Communication
(A) Railway and Water Transport Improvements
- Steam Locomotive – 1814
Inventor: George Stephenson
Importance: First train ran in 1825; boosted trade, travel, and urbanization. - Steamboat – 1807
Inventor: Robert Fulton
Importance: Enabled cheaper and faster water transport.
(B) Improvements in Communication
- Telegraph – 1837
Inventor: Samuel Morse
Importance: Allowed long-distance messaging within seconds; improved trade and administration. - Telephone – 1876
Inventor: Alexander Graham Bell
Importance: Made instant communication possible.
4. Improvement in Medical Science and Living Standards
✔ Comfortable & easy to use
✔ Great performance & value
✔ Popular choice on Amazon
- Edward Jenner (1796): Developed smallpox vaccine.
- Louis Pasteur (1860s): Discovered Germ Theory.
- Joseph Lister (1867): Introduced antiseptic surgery.
5. Scientific Progress in Agriculture
- Seed Drill – 1701
Inventor: Jethro Tull
Importance: Increased agricultural productivity. - Crop Rotation: Maintained soil fertility and increased food production.
- Chemical Fertilizers: Enabled higher yields.
Conclusion
Scientific and technological progress laid the foundation of the Industrial Revolution. New inventions brought major changes in production, transportation, communication, medicine, and agriculture. Machines accelerated production and reshaped global society, economy, and industry.
Greater Use of Coal and Iron and the Industrial Revolution
Coal and iron played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution. Coal became the primary energy source, while iron was essential for constructing machines, railways, bridges, and factories. Their widespread use revolutionized industrialization and transformed global production systems.
1. Use and Importance of Coal
(A) Coal – The Main Source of Energy
Before the Industrial Revolution, energy sources were limited to water, wood, and animal power. The rise of machines increased the demand for a stronger and more efficient energy source — coal.
(B) Steam Engine and Coal
- Steam was produced by heating water with coal, powering steam engines.
- Revolutionized industries and transportation.
(C) Role of Coal in Industrial Production
- Powered machines in factories, increasing production.
- Essential for smelting iron and producing steel.
- Became an important source of electricity generation.
(D) Coal and Transportation
- Steam-powered trains depended on coal.
- Steamboats used coal for faster water transport.
- Demand for coal led to expanded mining activities.
2. Use and Importance of Iron
(A) Iron – The Backbone of Industrialisation
Iron became the core material used in machines, transport, buildings, and weapons.
(B) Techniques to Increase Iron Production
- Coke-Based Iron Production – 1709
Inventor: Abraham Darby
Importance: Made iron production cheaper and more efficient. - Bessemer Process – 1856
Inventor: Henry Bessemer
Importance: Enabled mass production of cheap and high-quality steel.
(C) Major Uses of Iron and Steel
- Manufacture of industrial machines and tools.
- Railway tracks, engines, and bridges.
- Buildings, factories, and infrastructure.
- Weapons and war equipment.
3. Changes Brought by the Use of Coal and Iron
| Area | Change |
|---|---|
| Industry | Use of large factories and machines increased. |
| Transportation | Railways and steamboats enhanced mobility of goods and people. |
| Urbanization | Worker settlements grew around industrial areas. |
| Jobs and Labor | Employment increased in mines and factories. |
| Business | Large-scale production and export became possible. |
4. Environmental and Social Impacts
(A) Positive Impacts
- Production increased; goods became cheaper.
- Transport and trade expanded rapidly.
- New employment opportunities emerged.
- Development of new cities and settlements.
(B) Negative Impacts
- Workers faced poor conditions in coal mines.
- Environmental pollution increased due to smoke and waste.
- Rural decline due to rapid industrialization.
- Child labour and long working hours became common.
Conclusion
Coal and iron were the foundations of the Industrial Revolution. Coal powered machines and transportation, while iron enabled the construction of railways, bridges, buildings, and factories. Though they brought industrial growth and new opportunities, they also caused pollution and social challenges. Overall, both resources played a central role in shaping modern industrial development.
New Trade Routes and Colonialism
The Industrial Revolution and scientific progress greatly influenced trade routes and colonialism. European countries discovered new trade routes and established colonies in Asia, Africa, America, and Australia. This expansion transformed the global economy and created new systems of trade, transportation, and political control.
1. Development of New Trade Routes
Before the Industrial Revolution, trade depended on land routes (Silk Route, Spice Route) and limited sea routes. Later, new modes of transportation developed, making trade faster and more efficient.
(A) Expansion of Maritime Trade Routes
- In the 15th and 16th centuries, European powers such as Portugal, Spain, Britain, France, and the Dutch explored sea routes.
- Improved ships and navigation techniques made long-distance travel easier.
Major Sea Trade Routes:
- Atlantic Route: Europe ↔ Africa ↔ America
- Indian Ocean Route: India ↔ Arabia ↔ Africa ↔ Europe
- Pacific Ocean Route: Asia ↔ America
(B) Effect on Land Routes
- Overland trade increased due to the expansion of railways.
- Older routes like the Silk Route began losing importance.
- Construction of canals such as the Suez Canal and Panama Canal shortened trade distances.
2. Expansion of Colonialism
European nations occupied new regions to gain commercial benefits. Colonies provided cheap raw materials and new markets for industrial goods.
(A) Major Colonial Countries and Their Territories
| Colonial Country | Major Colonies |
|---|---|
| Britain | India, Australia, Canada, South Africa |
| France | Algeria, Vietnam, West Africa |
| Spain | Latin America, Philippines |
| Portugal | Brazil, Mozambique, Goa |
| Dutch (Netherlands) | Indonesia, Sri Lanka |
(B) Reasons for the Establishment of Colonies
- Need for raw materials: cotton, sugar, spices, rubber, minerals.
- Search for new markets: to sell manufactured goods.
- Military and naval expansion: control over sea routes.
- Religious motives: spread of Christianity.
- Competition: European powers tried to dominate globally.
(C) British Colonialism and India
- The British East India Company established dominance from 1600 onward.
- India became a major economic centre for Britain.
- Cotton, tea, spices, and opium were exported from India.
- Indian industries and artisans suffered due to British policies.
3. Effects of New Trade Routes and Colonialism
(A) Economic Impact
- Global trade increased rapidly.
- European industries flourished with cheap raw materials.
- Colonial economies were exploited and weakened.
(B) Social Impact
- Cultural exchange took place.
- Europeans settled in many new regions.
- Local people faced oppression, slavery, and forced labour.
(C) Political Impact
- European dominance expanded globally.
- Rise of nationalism in colonies led to freedom movements.
4. Importance of Trade Routes in the Modern Era
- Suez Canal (1869): Reduced Europe–Asia distance by 7,000 km.
- Panama Canal (1914): Linked Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- WTO: Global regulation of trade practices.
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Modern re-engineering of trade routes.
5. Conclusion
New trade routes and colonialism reshaped the global economy. European countries expanded trade, transportation, and political influence by establishing colonies. While it accelerated industrialization, it also led to exploitation, inequality, and instability in colonized regions.
Growth of the Working Class With the Industrial Revolution
With the Industrial Revolution and the rise of capitalism, the working class grew rapidly. People who earlier depended on agriculture and handicrafts began working in factories due to the increasing use of machines. This revolution changed not only production but also the social structure.
1. Rise of the Working Class
(A) Formation of the Working Class
- Traditional artisans and handicrafts declined due to machines.
- More people began working in factories.
- Workers faced long working hours, low wages, and poor conditions.
(B) Factors Behind the Growth of the Working Class
- Industrial Revolution: Increased demand for factory labor.
- Urbanization: People migrated from villages to cities.
- Agricultural Reforms: Machines reduced farm jobs.
- Population Growth: More people needed employment.
✔ Easy & comfortable to use
✔ Great value for everyday use
✔ Highly recommended by customers
2. Condition and Problems of Workers
(A) Poor Working Conditions
- 12–16 hour workdays.
- Hot, dirty, unsafe factories.
- Frequent accidents due to machines.
(B) Low Wages and Economic Exploitation
- Men, women, and children were paid extremely low wages.
- Factory owners focused only on profits.
- Women and children received even lower pay.
(C) Child Labour
- Children worked on dangerous machines.
- Serious injuries were common.
- Lack of education kept them in poverty.
(D) Health Problems
- Workers became sick due to unhygienic conditions.
- Overcrowded slums spread infectious diseases.
- Clean water and medical facilities were unavailable.
3. Working-Class Struggle and Reform Movements
(A) Rise of Trade Unions
- Trade unions fought for worker rights.
- Strikes and protests demanded better wages and conditions.
- Unions helped reduce working hours.
(B) Major Labour Movements
- Chartist Movement (1838–1857): Demanded voting rights and better conditions.
- Eight-Hour Movement: Workers demanded an 8-hour workday.
- Marxist Ideology: Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels published “The Communist Manifesto” (1848).
(C) Labour Reform Laws
| Law | Year | Major Reform |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Act | 1833 | Limited working hours for children. |
| Mines Act | 1842 | Banned women and children from working in mines. |
| Trade Union Act | 1871 | Legalised workers’ unions. |
| Minimum Wage Laws | 20th Century | Guaranteed minimum wages for workers. |
4. Working Class in the Modern Era
(A) Positive Changes
- Minimum wage laws established.
- Working hours reduced.
- Child labour prohibited.
- Social security programs (insurance, pension) introduced.
(B) Present Challenges
- Unorganized sector workers lack proper rights.
- Many jobs have become temporary due to globalization.
- Worker exploitation still exists in several countries.
5. Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution created the working class but also exposed them to harsh conditions. Over time, labour movements and laws improved their situation. Today, despite progress, challenges like unorganized labour, low wages, and worker safety persist. Continuous efforts by governments and society are needed for their welfare.
Development of Banking and Financial System
The development of banking and financial systems is closely linked to the economic progress of human civilization. In early societies, the barter system was common, but as trade expanded, the need for a structured banking and financial system grew. Over time, modern banking emerged, including commercial banks, central banks, digital banking, and financial institutions.
1. Evolution of the Banking System
(A) Banking in Ancient Times
- Early banking activities were conducted by temples and merchants.
- Forms of banking existed in ancient Mesopotamia (Babylonian Civilization) and Egypt.
- Loan and borrowing systems existed in the Harappan and Vedic periods.
(B) Medieval Banking
- Italian banks such as the Medici Bank and Venetian Bank laid the foundation for organised banking.
- In India, the Hundi system developed, where merchants used written documents for transactions.
- The establishment of the Bank of England (1694) marked the beginning of the modern European banking system.
(C) Modern Banking System
- The 19th and 20th centuries saw major banking reforms.
- The central banking system emerged, with each country establishing a central bank.
- Digital banking and online transactions made banking more convenient.
2. Major Components of the Banking System
(A) Central Bank
- Controls monetary policy.
- Manages money supply, interest rates, and the banking system.
- Examples: RBI (India), Federal Reserve (USA).
(B) Commercial Banks
- Provide savings accounts, current accounts, loans, and investment services.
- Examples: SBI, HDFC, ICICI.
(C) Cooperative Banks
- Provide loans to farmers and small businesses at low interest rates.
- Support rural economic development.
(D) Development Banks
- Provide financial assistance for large industries, infrastructure, and government schemes.
- Examples: NABARD, IDBI.
(E) Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFCs)
- Include insurance companies, mutual funds, investment firms, etc.
- Provide lending and investment services.
3. Development of the Financial System
(A) Early Financial System
- Shift from barter system to currency-based trade.
- Interest-based loan systems emerged.
(B) Industrial Revolution and the Financial System
- Industries required large-scale capital.
- Banks and stock markets grew to support industrial development.
(C) Modern Financial System
- Global growth of financial institutions.
- Introduction of credit cards, debit cards, digital banking, and cryptocurrency.
4. Improvements in Modern Banking and Financial System
(A) Digital Banking
- Net Banking: Online access to banking services.
- Mobile Banking: Banking via mobile apps.
- UPI & Wallets: Instant digital payments.
(B) Financial Inclusion
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana: Banking access to the poor.
- Microfinance: Loans to small entrepreneurs.
(C) Cryptocurrency & Blockchain Technology
- Digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Blockchain enables secure and transparent transactions.
5. Importance of Banking and Financial System
✔ Comfortable & easy to use
✔ Great value for money
✔ Popular choice among buyers
| Area | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Economic Development | Provides financial support to industries and businesses. |
| Employment Generation | Creates employment for millions of people. |
| Poverty Eradication | Offers loans and services to empower the poor. |
| Investments & Savings | Enables safe savings and investment opportunities. |
| Global Trade | Facilitates international trade and currency exchange. |
6. Conclusion
The development of banking and financial systems has been a long and evolving process. Modern digital banking has accelerated financial growth. Future innovations such as blockchain, cryptocurrency, and fintech will further transform global finance.
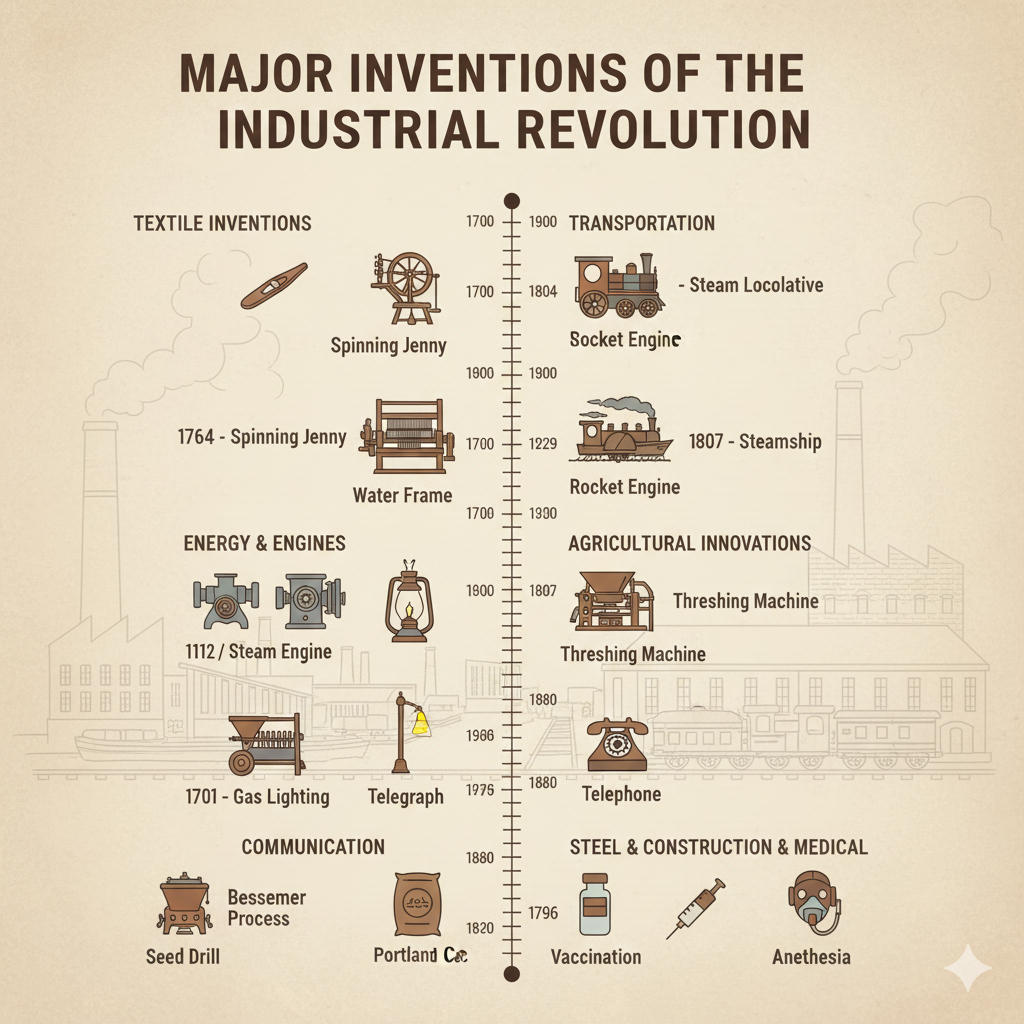
Major Inventions and Discoveries of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution completely transformed human society. During the 18th and 19th centuries, many groundbreaking inventions made production faster, cheaper, and more efficient. These innovations revolutionized industry, transport, agriculture, and communication.
1. Textile Industry Inventions
(A) Flying Shuttle – 1733
Inventor: John Kay
- Doubled weaving speed.
- Enabled wider cloth to be woven by a single worker.
- Boosted textile production.
(B) Spinning Jenny – 1764
Inventor: James Hargreaves
- Spun several threads simultaneously.
- Accelerated cotton textile production.
(C) Water Frame – 1769
Inventor: Richard Arkwright
- Used water power for faster spinning.
- Led to the rise of textile mills.
(D) Power Loom – 1785
Inventor: Edmund Cartwright
- Automated cloth-weaving process.
- Increased quality and quantity of textiles.
2. Inventions in Energy and Engines
(A) Steam Engine – 1712 & 1769
Inventors: Thomas Newcomen (1712), James Watt (1769)
- Powered factories, trains, and ships.
- Used coal as the main energy source.
- Revolutionized transportation and industry.
(B) Gas Lighting – 1792
Inventor: William Murdoch
- Factories and streets began using gas lights.
- Enabled night-time work and increased production.
3. Transportation Inventions
(A) Steam Locomotive – 1804
Inventor: Richard Trevithick
- First practical steam-powered train.
- Boosted goods and passenger transport.
(B) Rocket Steam Engine – 1829
Inventor: George Stephenson
- First commercially successful railway engine.
- Massive expansion of rail transport.
(C) Steamship – 1807
Inventor: Robert Fulton
- Ships no longer depended on wind.
- Made maritime trade faster and more reliable.
4. Agricultural Innovations
(A) Seed Drill – 1701
Inventor: Jethro Tull
- Planted seeds in neat rows.
- Increased crop output and efficiency.
(B) Threshing Machine – 1786
Inventor: Andrew Meikle
- Faster separation of grain from husk.
- Reduced need for manual labour.
5. Communication Innovations
(A) Telegraph – 1837
Inventor: Samuel Morse
- Enabled long-distance communication through Morse code.
- Revolutionized global communication.
(B) Telephone – 1876
Inventor: Alexander Graham Bell
- Allowed direct voice communication.
- Boosted business and personal communication.
6. Steel and Construction Innovations
(A) Bessemer Process – 1856
Inventor: Henry Bessemer
- Cheap and efficient method of producing steel.
- Enabled construction of bridges, railway tracks, and skyscrapers.
(B) Portland Cement – 1824
Inventor: Joseph Aspdin
- Used in constructing stronger buildings and structures.
7. Medical Innovations
(A) Vaccination – 1796
Inventor: Edward Jenner
- Prevented deadly diseases like smallpox.
(B) Anesthesia – 1846
Inventor: William Morton
- Reduced pain during surgery.
Conclusion
The inventions of the Industrial Revolution transformed industries and reshaped human civilization. They improved production, transportation, communication, agriculture, and medicine. The foundations of the modern technological world lie in these remarkable innovations.
Positive Effects of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which took place during the 18th and 19th centuries, completely transformed the world. It brought major advancements in industry, agriculture, transportation, communication and society. Although it had some negative aspects, its positive effects laid the foundation of the modern world.
1. Increase in Industrial Production
- With the use of machines, production became faster and more efficient.
- Factories enabled large-scale manufacturing compared to home-based production.
- The textile, steel and manufacturing industries expanded rapidly.
- Mass production made goods cheaper and accessible to the common people.
2. Development of New Machines and Technologies
- Inventions like the steam engine, spinning jenny, power loom, and railway engine transformed industries.
- Technological advances improved manufacturing, transport and communication.
- Innovation and scientific research accelerated significantly.
3. Creation of New Jobs and Employment Opportunities
- Millions of people found employment in factories, mines, railways and other sectors.
- People who earlier depended on agriculture received new career opportunities.
- New fields like engineering, trade, transport, and communications grew rapidly.
4. Improvements in Transportation and Communication
- The steam engine made railways and ships fast and efficient.
- Expansion of railway networks improved trade and travel.
- Road and bridge construction connected distant regions.
- Telegraph and telephone made communication quick and easy.
5. Increase in Agricultural Production
- New machines and techniques improved agricultural output.
- Use of seed drills, threshing machines and fertilizers boosted crop production.
- Higher food production reduced hunger and famine conditions.
6. Urbanization and Growth of Cities
- Industrial growth led people to migrate from villages to cities.
- Urban areas developed with new housing, markets, roads and infrastructure.
- Cities like London, Manchester, Birmingham, New York, Mumbai and Kolkata expanded rapidly.
7. Improvement in Living Standards
- People’s income increased compared to earlier times.
- Industrial goods became cheaper, increasing buying capacity.
- Electricity, gas, sanitation and other facilities improved.
8. Expansion of Global Trade and Economy
- Large-scale production boosted exports and international trade.
- The banking and financial system strengthened, providing capital to industries.
- Modern capitalism began to grow rapidly.
9. Growth of Education and Research
- Scientific discoveries increased educational demand.
- Technical institutions, schools and colleges grew in number.
- People began to study engineering, science and industry-related fields.
10. Improvement in Workers’ and Women’s Rights
- Gradually, laws were made to protect worker rights.
- Minimum wage, limited working hours and safety regulations were introduced.
- Women gained new job opportunities and educational access.
11. Scientific and Medical Advancements
- New medical discoveries and vaccinations reduced diseases.
- Anesthesia and modern surgical techniques improved healthcare.
- Hospitals expanded and medicines became more effective.
12. Utilization of New Energy Sources
- Coal and steam power became widely used in industries and transportation.
- Later electricity and petroleum-based energy systems emerged.
- New industries developed based on these energy sources.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution led humanity toward modernity. It increased production, expanded global trade, improved living standards, transformed transportation and communication, and accelerated scientific progress. Although it brought challenges, its positive effects became the backbone of the modern world.
✔ Comfortable & easy to use
✔ Great value for money
✔ Popular choice among buyers
Negative Effects of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution promoted economic and technological progress, but it also caused many negative effects. It adversely impacted society, the environment, workers and agriculture. While it laid the foundation of the modern world, it also created issues such as worker exploitation, social inequality, pollution and decline of traditional occupations.
1. Exploitation of Workers
- Workers were poorly paid in factories.
- They worked 12–16 hours a day with little rest.
- Factory owners focused on profit and exploited laborers.
- Women and children faced even harsher conditions.
2. Increase in Child Labour
- Children performed dangerous and difficult tasks in factories.
- They were paid extremely low wages.
- Many children became victims of diseases and accidents.
- Laws to control child labour were introduced much later.
3. Poor Working Conditions
- Factories were unsafe and unhealthy.
- Smoke, dust and toxic gases caused respiratory diseases.
- Lack of safety equipment led to frequent accidents.
- Extreme temperatures made working conditions unbearable.
4. Social Inequality
- The gap between rich and poor widened.
- Industrialists became wealthy while workers lived in poverty.
- Access to education and healthcare was limited to the rich.
- Class divisions deepened.
5. Decline of Traditional Craftsmen
- Machines replaced handicrafts and artisans.
- Traditional craft businesses collapsed.
- Artisans became unemployed and their skills declined.
6. Neglect of Agriculture
- People left agriculture to work in industries.
- Fewer farmers led to food shortages and price increases.
- Use of machines in agriculture displaced small farmers.
7. Urbanization and Slum Development
- Rapid migration to cities increased population density.
- Insufficient housing led to the growth of slums.
- Scarcity of water, sanitation and medical services caused disease outbreaks.
- Crime and poverty increased in crowded urban areas.
8. Environmental Pollution
- Coal and fossil fuels increased air pollution.
- Factories released chemicals that polluted rivers.
- Deforestation increased due to industrial expansion.
- Carbon emissions led to global warming.
9. Rise of Imperialism and Wars
- Industrial nations sought raw materials and created colonies.
- Britain, France, Germany and others occupied Asian and African regions.
- Local industries, like Indian textiles, suffered under colonial rule.
- Colonial expansion triggered conflicts and wars.
10. Impact on Family and Society
- Families separated as people migrated for factory work.
- Traditional social bonds weakened.
- Stress and mental illness increased due to harsh lifestyles.
11. Emergence of New Diseases
- Industrial towns faced respiratory and infectious diseases.
- Dirt and overcrowding spread illnesses like TB, cholera and plague.
- Lack of workplace safety led to injuries and disabilities.
12. Political Instability and Rise of Labour Movements
- Worker exploitation led to strikes and protests.
- Trade unions were formed to protect worker rights.
- Political instability increased in many industrial nations.
- Governments passed laws to improve worker welfare.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution promoted economic growth and scientific progress but also resulted in several negative impacts. Environmental damage, worker exploitation, social inequality, child labour, decline of traditional occupations and agricultural neglect were major issues. Over time, reforms and laws improved conditions, but the consequences of the Industrial Revolution are still visible today. By learning from the past, societies have worked towards creating a more balanced and fair system.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point in human history. It brought rapid growth in production, improved transportation, boosted global trade, expanded cities, and encouraged major scientific, medical, and technological advancements. These positive effects laid the foundation of the modern industrial world.
However, the revolution also created serious challenges. Workers faced exploitation, child labour increased, traditional artisans lost their livelihoods, pollution rose, and social inequality deepened. Rapid urbanization led to slums, diseases, and poor living conditions.
Overall, the Industrial Revolution was a powerful force that reshaped society. Its positive impact pushed the world toward modernization, while its negative consequences taught the importance of reforms, labour rights, environmental protection, and social balance. The lessons learned from this era continue to guide modern development and policymaking.
References
✔ Easy & convenient to use daily
✔ Excellent value for money
✔ Popular among customers
- History of the Industrial Revolution – Public Domain Sources
- Encyclopedia Britannica – Industrial Revolution Overview
- National Archives UK – Industrial Era Documents
- World History Textbooks and Academic Publications
- Public Education Resources on Industrialization