The Border of India
A personal reflection on a country of long borders — 15,106.7 kilometres of land and 7,516.6 kilometres of coastline — and what those edges have taught me about history, people and resilience.
Introduction — Why Borders Matter
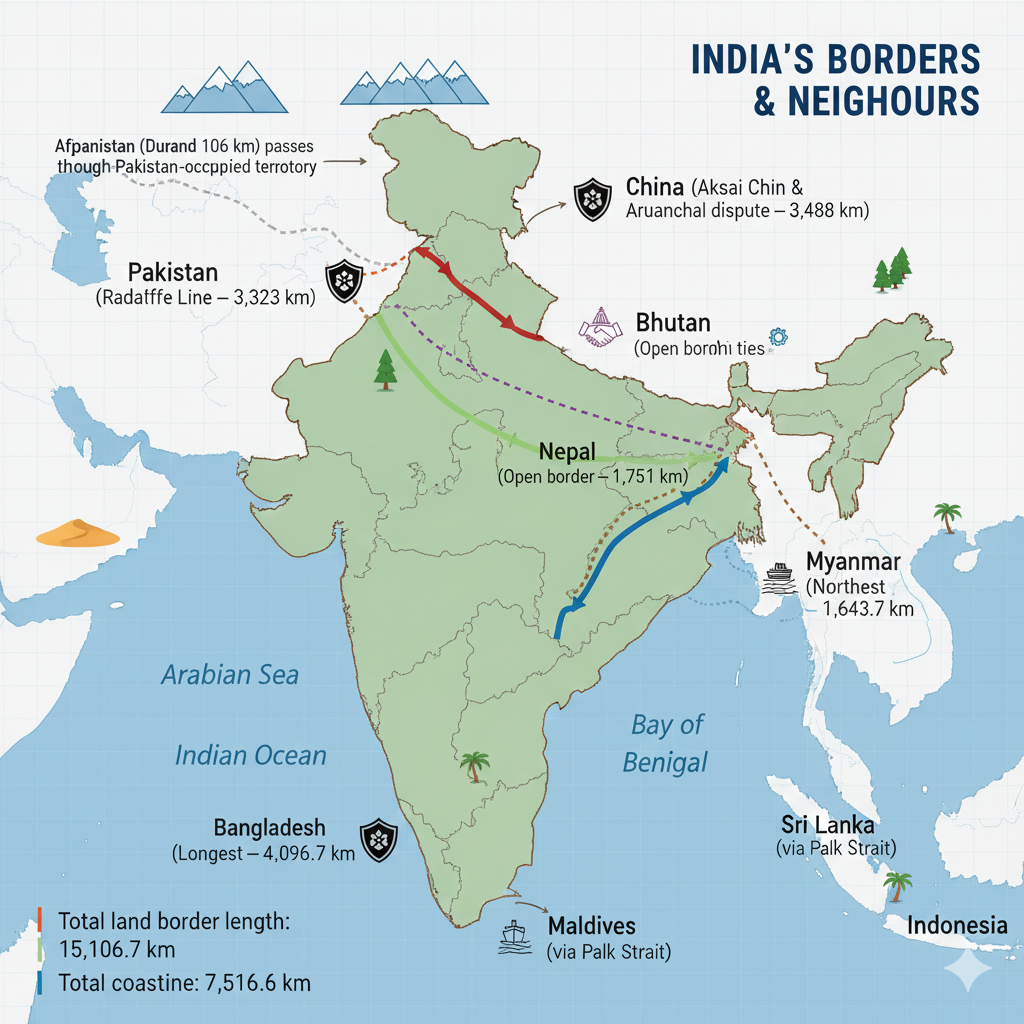
I grew up hearing stories of distant mountains and rivers that marked where one country ended and another began. For me, India’s borders are not just lines on a map; they are living places where culture, trade, memory and security meet. India’s land boundary stretches 15,106.7 kilometres and its coastline is 7,516.6 kilometres long — figures that remind me how many lives and landscapes are joined at the margins.
Who Neighbours India? — A Quick Guide
India shares its land border with seven countries. Below I list them in a simple, story-friendly way so you can picture where each neighbour meets India.
Pakistan
Region: North-west — Border length: 3,323 km
The boundary here is commonly referred to as the Radcliffe Line. For many communities along this border, history and memory remain deeply entwined with daily life.
China
Region: North & North-east — Border length: 3,488 km
The China border includes sensitive and disputed areas such as Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh. Mountains and high plateaus make this frontier one of the most challenging to administer and patrol.
Nepal
Region: North — Border length: 1,751 km
The open-border system with Nepal means easy movement for people and goods — a reminder that not all borders are barriers.
Bhutan
Region: North-east — Border length: 699 km
Bhutan and India share deep cultural and economic ties reflected in shared festivals, trade and cooperative infrastructure projects.
Bangladesh
Region: East — Border length: 4,096.7 km
This is India’s longest international border. Rivers, fences and checkpoints mark a complex boundary shaped by history and dense population centres.
Myanmar
Region: East — Border length: 1,643 km
India’s connection to the north-eastern states runs through this border, which links diverse ethnic and cultural regions.
Afghanistan
Region: North-west (smaller portion) — Border length: 106 km
Often called the Durand Line, this shorter frontier carries its own unique historical significance.
Maritime Neighbours
India’s maritime neighbours include Sri Lanka, Maldives and Indonesia. The sea-borne connection with Sri Lanka via the Palak Strait is a reminder that borders may be saltwater as well as soil. Maritime boundaries influence fishing rights, trade routes and cultural exchange across the Indian Ocean.
Geographical and Strategic Importance
India’s borders sweep across deserts, mountains, plains and coastlines. Each frontier carries its own climate, culture and strategic concerns. For me, two lessons stand out:
- Diversity as strength: Borders bring together many cultures and ecosystems; they are places of exchange and learning.
- Security and stewardship: Soldiers and paramilitary forces protect these edges, but local communities, trade and diplomacy are equally important in ensuring peaceful, prosperous borders.
Personal Reflections — What the Borders Taught Me
Visiting towns near the frontiers, I saw markets where goods from different countries sat side by side, and heard stories of families whose lives were shaped by decisions taken long ago. Borders can be sources of tension, yes, but they are also places of resilience — where people adapt, trade, teach, and celebrate. That human spirit is what I remember most.
FAQ — Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: Which country shares the longest border with India?
- A: Bangladesh shares the longest land border with India at 4,096.7 km.
- Q: What is the Radcliffe Line?
- A: The Radcliffe Line is the boundary demarcation line drawn in 1947 that separated India and Pakistan in the north-west region.
- Q: Are India’s borders all land borders?
- A: No. India has both land borders with seven countries and maritime neighbours such as Sri Lanka, Maldives and Indonesia. Its coastline is 7,516.6 km long.
- Q: What is the Durand Line?
- A: The Durand Line refers to the historical boundary between British India and Afghanistan; today it is recognised as the narrow frontier with Afghanistan (~106 km in India’s context).
Further Reading & Internal Link
If you found this piece useful, read more about India’s geography and border history on our India Geography & Borders page. Linking related articles helps readers and search engines discover more of your content.
India’s International Borders: Radcliffe Line, China Border, and Nepal Border
This article provides a structured, inspiring, and informative explanation of three major borders of India — the Radcliffe Line (India–Pakistan), the India–China border (LAC), and the India–Nepal border — along with historical context, disputes, and cultural ties.
Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line is a boundary drawn between India and Pakistan, created during the partition of India on 15 August 1947. It is named after its architect, British lawyer Sir Cyril Radcliffe. This line divided Punjab in the west and Bengal in the east between India and Pakistan.
Construction of the Radcliffe Line
Decision and Procedure
- The decision to partition India was taken in June 1947.
- The British government planned to create two new nations — India and Pakistan.
- Sir Cyril Radcliffe was tasked with determining the border based on geographical, religious, cultural, and economic factors.
Radcliffe Commission
- The commission consisted of representatives from India and the Muslim League.
- Its purpose was to divide the provinces of Punjab and Bengal, both religiously diverse regions.
Radcliffe’s Difficulties
- Radcliffe had never visited India and had limited understanding of local geography and culture.
- He was given only five weeks to complete the border demarcation.
- Communal riots and political disagreements complicated the process further.
Features of the Radcliffe Line
- Partition of Western Punjab: Pakistan received Lahore, Multan; India retained Amritsar, Jalandhar.
- Partition of Bengal: Muslim-majority areas went to East Pakistan (now Bangladesh); Hindu-majority regions became part of India.
Effects of the Radcliffe Line
- Communal Violence: Millions lost their lives; about 14 million people migrated across borders.
- Land Disputes: Conflicts such as Kashmir and Sir Creek emerged.
- Cultural Separation: Families and communities were divided, leaving lasting scars.
Criticism
- The line was drawn hastily, ignoring many critical ground realities.
- Several regions were assigned based on convenience rather than demographic correctness.
- The decision deepened communal tensions between the two nations.
Current Context
Today, the Radcliffe Line forms the official India–Pakistan border in Punjab and Rajasthan. In the Kashmir region, however, the boundary is known as the Line of Control (LOC), a disputed zone between the two countries.
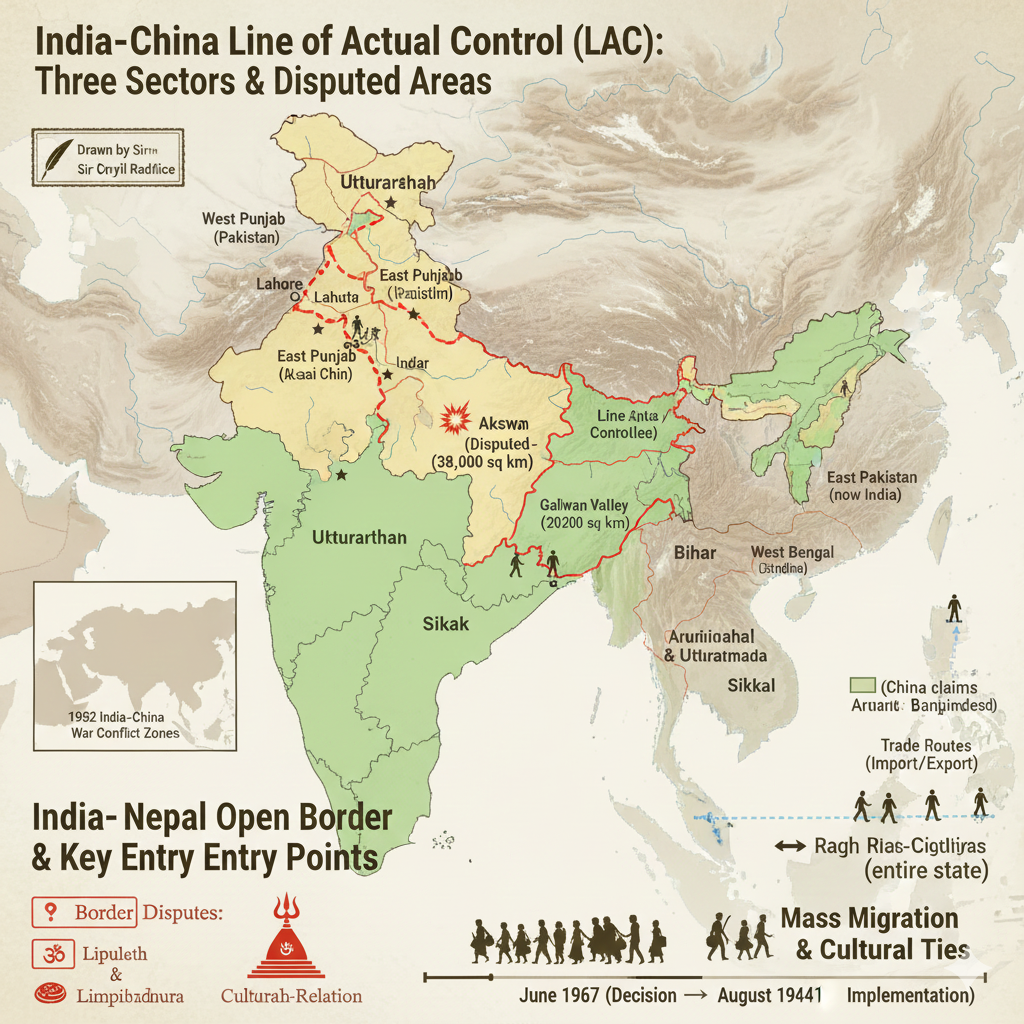
Border of China and India
The India–China border lies in the north and north-east, stretching approximately 3,488 km. It is officially called the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and is divided into three major sectors.
Border Areas
Western Region (Ladakh)
- Located near Jammu–Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Aksai Chin is the key disputed area — controlled by China but claimed by India.
- Aksai Chin was a primary cause of the 1962 India–China war.
Central Region (Uttarakhand & Himachal Pradesh)
This region sees occasional minor clashes but remains comparatively less disputed.
Eastern Region (Arunachal Pradesh)
- China claims parts of Arunachal Pradesh as “South Tibet”.
- China occupied several areas during the 1962 war but later withdrew.
Main Disputed Areas
- Aksai Chin: About 38,000 sq km; China built a major strategic route here.
- Arunachal Pradesh: India’s important state containing sites like Tawang.
Border Disputes and Efforts
- 1962 War: A major turning point worsening bilateral relations.
- 1993 & 1996 agreements: Steps taken to reduce troop presence and maintain border peace.
- 2020 Galwan Valley clash: One of the most serious confrontations in decades.
Geographical & Strategic Importance
The border passes through the Himalayas, making it extremely challenging. China’s rapid border infrastructure development and India’s corresponding strategies add to the region’s sensitivity.
Border of Nepal and India
Nepal is a landlocked nation north of India, sharing a 1,751 km open border extending from Uttarakhand to West Bengal.
Features of the Border
Open Border System
- Under the 1950 Treaty of Peace and Friendship, India and Nepal share an open border.
- Citizens can travel freely without visas or passports.
- Trade, cultural ties, and social exchanges thrive through this border.
Indian States Bordering Nepal
- Uttarakhand
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- West Bengal
- Sikkim
Main Border Points
- Raxaul–Birgunj (major trade route)
- Sunauli–Belhiya (tourist gateway)
Border Disputes
- Kalapani Dispute: Nepal claims the area; India considers it part of Uttarakhand.
- Lipulekh & Limpiyadhura: Nepal included these regions in its new map; India disputes this.
- Water-sharing disputes: occur in lowland border regions.
Social & Cultural Relations
- Roti–Beti Relations: Deep family and marriage ties across the border.
- Strong religious connection, especially due to temples like Pashupatinath (Nepal) and Kashi Vishwanath (India).
Economic & Trade Relations
- Nepal depends heavily on India for imports and exports.
- Border towns like Raxaul and Biratnagar are economic hubs.
- India supports Nepal with road, rail, and bus connectivity.
Conclusion
India’s borders with Pakistan, China, and Nepal reflect a complex blend of history, geography, culture, and security concerns. While disputes continue, strong cultural and diplomatic links ensure ongoing dialogue and cooperation.
FAQ
- Q: What is the Radcliffe Line?
- The boundary drawn in 1947 dividing India and Pakistan during partition.
- Q: What is the Line of Actual Control (LAC)?
- The official border between India and China, divided into western, central, and eastern sectors.
- Q: Why is the India–Nepal border open?
- Due to the 1950 Treaty of Peace and Friendship, allowing free movement of people and goods.
- Q: What is the main dispute between India and China?
- Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh remain the core territorial disputes.
Read related article: India’s Geopolitical Landscape
India’s Borders with Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan
This article presents a detailed, structured, and SEO-optimized explanation of India's borders with Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan — including geography, strategic relevance, historical ties, disputes, cultural connections, and future prospects.
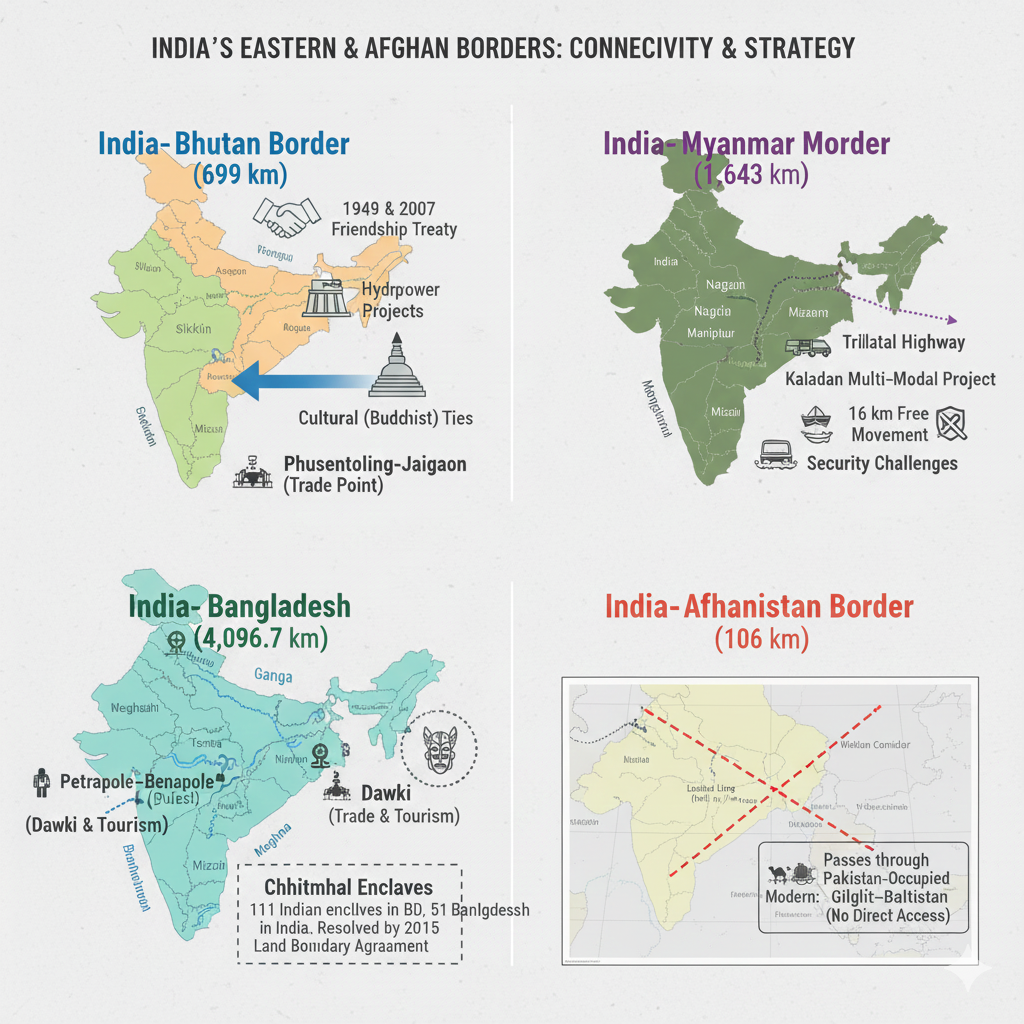
Border of Bhutan and India
Bhutan is a small but strategically important Himalayan nation located to the northeast of India. The India–Bhutan border stretches 699 km and connects India’s northeastern states with Bhutan’s mountainous terrain. This border reflects deep historical, cultural, and economic ties.
Features of the Border
Bordering Indian States
- West Bengal
- Sikkim
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
Special Border Points
- Phuentsholing–Jaigaon (West Bengal): The main trade and travel gateway between India and Bhutan.
- Movement is easy for Indians, although Bhutan regulates visas for foreign tourists.
India–Bhutan Relations
- Diplomatic Ties: Based on the 1949 Indo–Bhutan Treaty of Friendship (revised in 2007 to grant Bhutan greater autonomy).
- Economic Cooperation: India is Bhutan’s largest economic partner and development supporter.
- Hydropower Projects: Bhutan exports electricity to India, forming the backbone of its economy.
- Cultural Relations: Shared Buddhist traditions strengthen bilateral ties.
Security Cooperation
- The border is peaceful with no major disputes.
- India supports Bhutan’s security, especially near the China border.
- Doklam Standoff (2017): India intervened to prevent Chinese intrusion into Bhutanese territory.
Trade & Tourism
- Bhutan imports essentials from India, including machinery and medicines.
- Bhutan exports electricity, fruits, and handicrafts to India.
- Indian tourists enjoy visa-free access to Bhutan.
Future Prospects
- India aims to counter growing Chinese influence in the region.
- Hydropower and tourism may further strengthen economic ties.
Border of Bangladesh and India
Bangladesh lies east of India, sharing a 4,096.7 km border — India’s longest international border. It touches eastern and northeastern states and represents deep historical, cultural, and geographical ties.
Features of the Border
Bordering Indian States
- West Bengal
- Assam
- Meghalaya
- Tripura
- Mizoram
Key Border Locations
- Petrapole–Benapole: Busiest international land crossing.
- Dawki Border (Meghalaya): Major tourist and trade point.
Riverine Border
- Ganga, Brahmaputra, Teesta, Meghna rivers shape this border.
- Water-sharing agreements remain key subjects of cooperation.
Unique Feature: Chhitmahal (Enclaves)
Before 2015, tiny enclaves existed across the border. The Land Boundary Agreement (2015) resolved this by exchanging 162 enclaves — a major milestone in bilateral relations.
India–Bangladesh Relations
- Historical Ties: India supported Bangladesh’s 1971 independence struggle.
- Economic Relations: India exports textiles, machinery, and food items; imports jute and garments.
- Water Agreements: Notable treaties concern Ganga and Teesta rivers.
Border Challenges
- Illegal Migration: Long-standing issue affecting Assam and West Bengal.
- Smuggling: Human trafficking, cattle smuggling, and fake currency.
- Rohingya Crisis: Refugee flows from Myanmar into Bangladesh and India.
Peace & Cooperation
- India has fenced much of the border to reduce illegal activities.
- Cultural exchanges and easier visa processes strengthen people-to-people ties.
Border of Myanmar and India
Myanmar shares a 1,643 km border with India, connecting northeastern states and playing a key role in strategic, cultural, and economic cooperation.
Features of the Border
Bordering Indian States
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
Major Border Points
- Moreh (Manipur): Major trade gateway.
- Zorinpui (Mizoram): Vital for movement and commerce.
Open Border
Citizens of both nations may travel up to 16 km without visas, fostering cultural exchange.
India–Myanmar Relations
- Buddhist cultural ties: Strengthen spiritual connection.
- Shared tribes: Nagas, Chins and others live across both sides.
- Trade Cooperation: India imports pulses; exports medicines, machinery, etc.
Major Connectivity Projects
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Project: Links India’s northeast to Myanmar’s Sittwe port.
- India–Myanmar–Thailand Highway: Boosts regional trade and travel.
Challenges
- Insurgency: Active militant groups along the border.
- Illegal Trafficking: Drugs, weapons, and human smuggling.
- Rohingya Migration: Continues to influence regional security.
- Lack of infrastructure: Border regions remain underdeveloped.
Border of Afghanistan and India
The India–Afghanistan border stretches 106 km in the northwest, historically connecting through the region of Gilgit–Baltistan (currently under Pakistan-occupied territory). The border is known as the Durand Line.
Durand Line
- Established in 1893 between British India and Afghanistan.
- Though historically significant, India currently lacks direct access due to Pakistan’s occupation of the region.
Historical Significance
- Ancient cultural links — Afghanistan was influenced by Hindu and Buddhist traditions.
- Silk Route & Khyber Pass: Major trade corridors connecting India with Central Asia.
Current Perspective
- Pakistan’s occupation disrupts direct connectivity.
- Afghanistan remains strategically vital for India.
- Instability and terrorism affect bilateral cooperation.
India–Afghanistan Relations
- Development Projects: Salma Dam, Jaranj–Delaram Highway, Parliament building.
- Education: India offers scholarships to Afghan students.
- Cultural Ties: Bollywood and Indian traditions remain popular.
- Security Concerns: Terrorism impacts both nations.
Conclusion
The borders India shares with Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan reflect deep historical, cultural, and strategic complexities. While challenges remain, cooperation and diplomacy continue to shape peaceful and mutually beneficial relations.
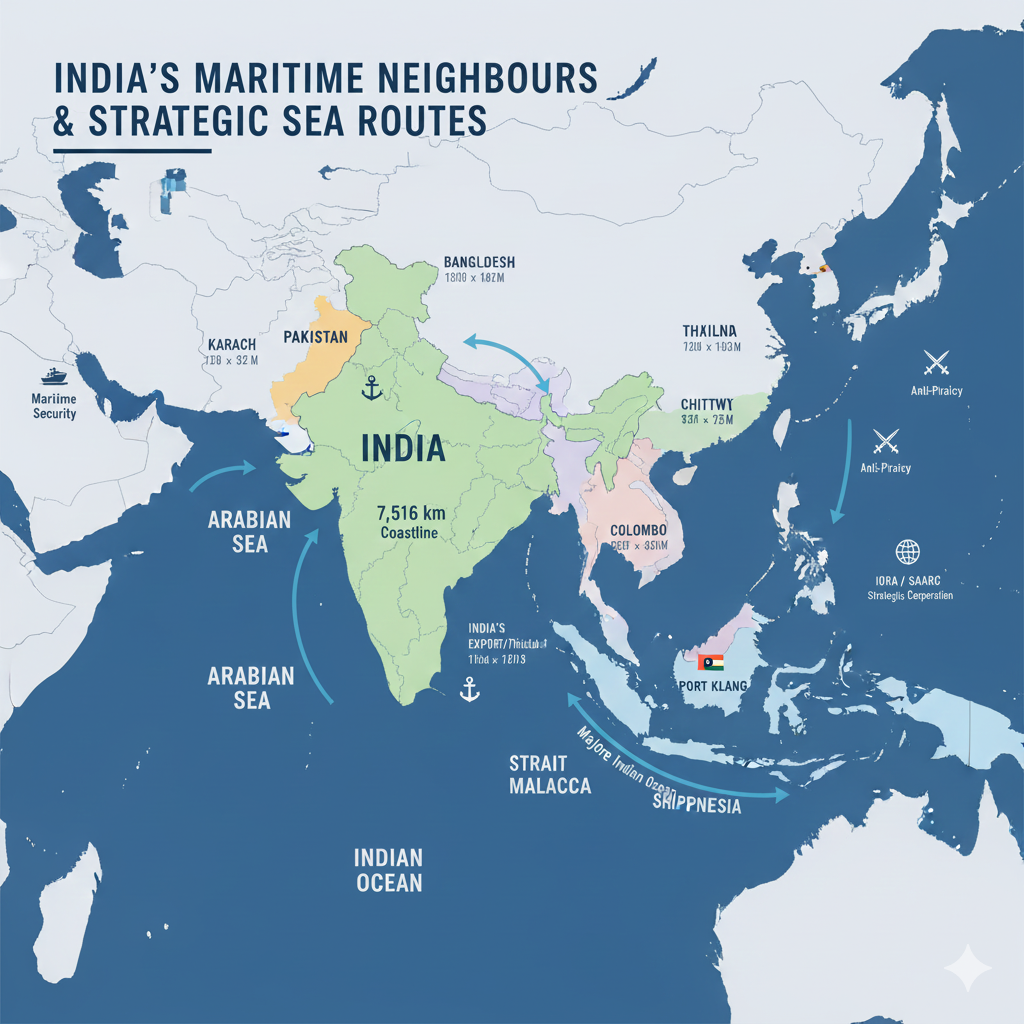
India’s Maritime Neighbours
India’s maritime neighbours are the countries located around the seas that surround the Indian subcontinent. India has a coastline of 7,516 km, stretching across the Arabian Sea in the west and the Bay of Bengal in the east. These maritime neighbours play a crucial role in India’s strategic, economic, cultural, and environmental landscape.
List of Major Maritime Neighbouring Countries of India
Pakistan (West)
Coastline
Pakistan has a coastline of 1,046 km, located along the Arabian Sea.
Importance
The Karachi port serves as an important sea route for regional trade and maritime movement.
Specific Features
Although India–Pakistan maritime relations face challenges due to the Kashmir dispute, both nations cooperate on issues like trade and climate-related concerns.
Bangladesh (East)
Coastline
Bangladesh has a coastline of approximately 580 km along the Bay of Bengal.
Importance
Ports such as Chittagong and Mongla improve India’s trade connectivity.
Specific Features
India and Bangladesh continue strengthening cooperation on maritime trade, climate change, and water-sharing issues.
Sri Lanka (South)
Coastline
Sri Lanka has a coastline of 1,340 km along the Indian Ocean.
Importance
The Colombo port is a major trading hub for India.
Specific Features
India and Sri Lanka share strong cultural, historical, and economic ties, working together on maritime trade, anti-terrorism operations, and environmental issues.
Myanmar (East)
Coastline
Myanmar has a coastline of 1,930 km along the Bay of Bengal.
Importance
The Sittwe port in Myanmar is key to the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Project, improving India’s sea connectivity.
Specific Features
India–Myanmar relations include strong cooperation in trade, border security, and connectivity with India’s northeastern states.
Thailand (Southeast)
Coastline
Thailand has a 1,878 km coastline along the Andaman Sea.
Importance
Thailand’s coastlines enable major trade routes between India and Southeast Asia.
Specific Features
India and Thailand work on maritime and land connectivity projects such as the India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway.
Malaysia (Southeast)
Coastline
Malaysia has a coastline of 4,675 km along the Strait of Malacca and the South China Sea.
Importance
Ports like Port Klang and Penang are essential for Indian trade.
Specific Features
India and Malaysia cooperate in trade, education, tourism, and maritime connectivity.
Indonesia (Southeast)
Coastline
Indonesia has one of the world’s longest coastlines — 54,716 km — stretching along the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea.
Importance
India imports oil, gas, and minerals from Indonesia; maritime trade routes connect India to Southeast Asia.
Specific Features
Indonesia plays a key role in regional maritime connectivity and Indo-Pacific cooperation.
India’s Cooperation with Maritime Neighbours
Maritime Security & Peace
- India cooperates with neighbouring countries to ensure maritime safety and anti-terror operations.
- The Indian Navy and Coast Guard monitor shared maritime boundaries.
Trade & Connectivity
- Major ports such as Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, and Colombo serve as critical trade hubs.
- Sea routes strengthen India’s access to global markets.
Climate Change & Environmental Cooperation
- India works with SAARC and IORA nations on climate adaptation, sea-level rise, and disaster management.
Conclusion
India’s maritime neighbours play an essential role in shaping its strategic, cultural, and economic future. Strong maritime partnerships strengthen regional peace, support trade, and help India maintain its pivotal position in the Indian Ocean region.
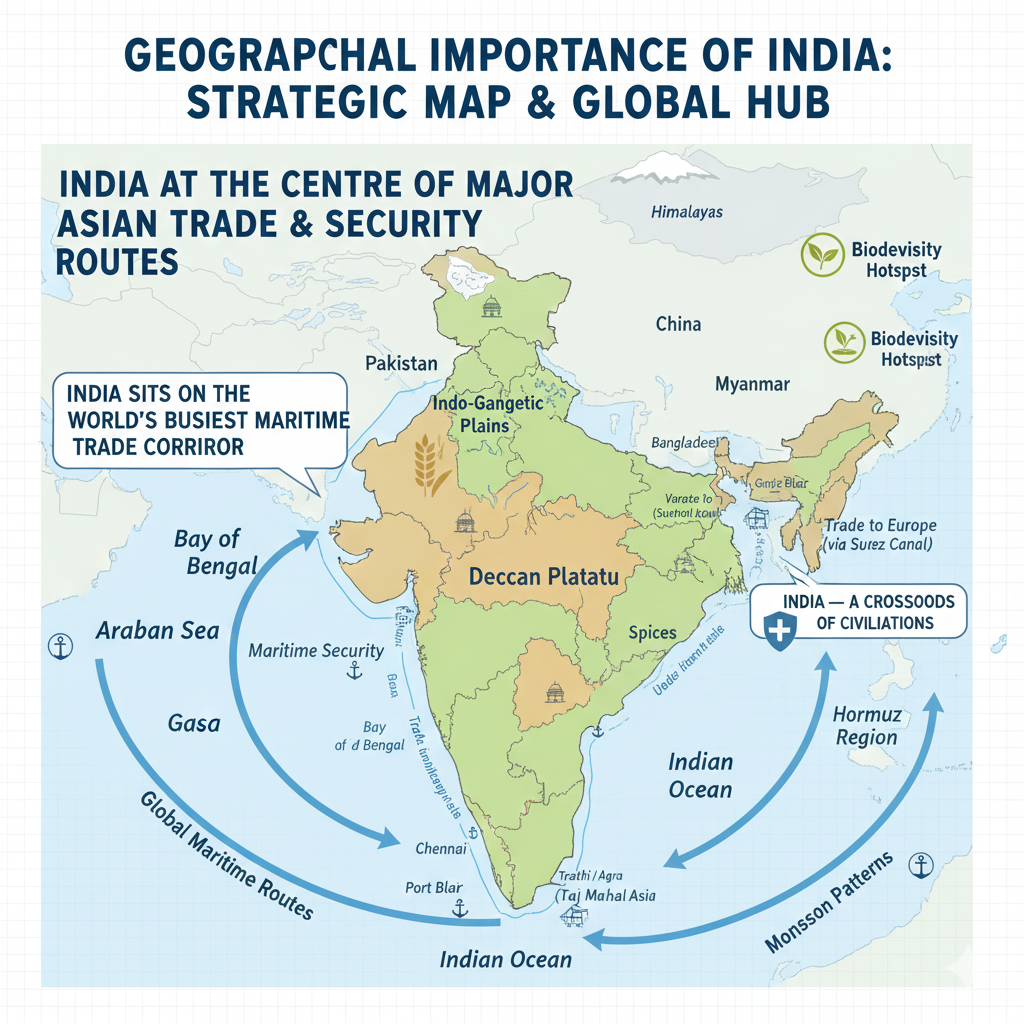
Geographical Importance of India
India’s geographical location and natural position make it extremely important in terms of global politics, trade, culture, agriculture, climate, and security. Its unique placement gives it strategic, economic, and cultural significance in South Asia and the world.
1. Overview of India’s Geographical Location
India is located in South Asia and lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. Situated at the center of the Indian subcontinent, India is surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea, and the Bay of Bengal. This prime location makes India a major hub for maritime trade and regional connectivity.
India shares land borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Afghanistan. With its extensive coastline, India stands as an important center for global maritime trade and economic activity.
2. Strategic and Tactical Importance
Proximity to Neighboring Countries
India’s close geographical connections with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka allow it to influence regional politics, conflict resolution, and security discussions.
Major Power in South Asia
Due to its size, population, and economic strength, India plays a central role in maintaining the stability of the South Asian region — combating terrorism, ensuring political balance, and fostering cooperation.
Control of the Indian Ocean
India’s position on the northern edge of the Indian Ocean gives it significant strategic control over one of the world’s busiest maritime trade routes. This enhances India’s naval strength and geopolitical influence.
3. Commercial and Economic Importance
Control of Global Trade Routes
India is located along vital sea routes that connect Asia, Africa, and Europe. Its accessibility strengthens India’s participation in international trade.
Importance of Sea Routes
India lies close to critical shipping lines such as the Strait of Malacca and other passages that handle major cargo movement between Asia and Europe.
Major Commercial Ports
Ports such as Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Colombo, Hyderabad, and Visakhapatnam facilitate large‑scale maritime trade and enhance India’s economic growth.
4. Importance in Terms of Climate and Agriculture
Diverse Climate Zones
India experiences a range of climates — from tropical to moderate — making it suitable for varied agricultural production. Regions like the Gangetic Plain, Deccan Plateau, and coastal belts support rich crop diversity.
Diverse Agricultural Products
India’s geography supports cultivation of paddy, wheat, sugarcane, maize, tea, coffee, spices, fruits, and more, contributing to its identity as an agricultural powerhouse.
5. Cultural and Historical Significance
A Center of Civilizations
India’s geography has been home to major civilizations — including the Indus Valley Civilization — and the birthplace of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and many cultural traditions.
Confluence of Cultures
Its strategic position made India a meeting point of cultures, languages, religions, and trade networks, giving it unmatched cultural diversity.
Major Historical Sites
India hosts numerous historical and cultural landmarks such as the Taj Mahal, Varanasi, Kanchipuram, and many UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
6. Environmental and Ecological Importance
Wealth of Natural Resources
India’s geography provides mineral wealth, forests, rivers, fertile plains, and biodiversity hotspots. The Himalayas and the Ganga basin are crucial ecological regions.
Impact of Climate Change
India faces challenges related to climate change such as rising sea levels, floods, droughts, and extreme weather — making environmental management vital.
7. Importance in Global Politics and Security
Global Balance of Power
India’s geographical location strengthens its role in global geopolitics. Strategic cooperation with major powers like the USA, Japan, and Russia enhances regional stability.
Power in the Asia–Pacific Region
India is a major force in the Indo‑Pacific region, contributing to maritime security, diplomatic initiatives, and regional partnerships.
Conclusion
India’s geographical importance is vast — influencing global trade, culture, climate, agriculture, and geopolitics. Its strategic location in Asia and strong maritime presence along the Indian Ocean make it a key global player. Understanding India’s geography is essential for appreciating its role in shaping global politics, environmental sustainability, and economic progress.
Conclusion
India’s geographical importance is vast and multidimensional. Its unique location between the Himalayas in the north and the Indian Ocean in the south makes it a powerful centre for global trade, strategic security, cultural exchange, and environmental diversity. India’s proximity to major sea routes, neighbouring countries, and resource-rich regions strengthens its role in international politics and economic development. With its rich cultural heritage, varied climatic zones, and strategic maritime advantages, India continues to shape the future of South Asia and the global community. Understanding India’s geography is essential to appreciating its influence on world peace, prosperity, and sustainable growth.
References
- Government of India – Ministry of External Affairs: Geographical and Strategic Information
- National Atlas & Thematic Mapping Organisation (NATMO) – India: Physical and Political Features
- Survey of India – Official Maps and Geographical Data
- UN Geographical Reports – South Asian Regional Geography
- World Bank Database – India: Trade, Climate, and Agricultural Insights
- Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) – Climate and Environmental Data
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) – Maritime Cooperation Reports